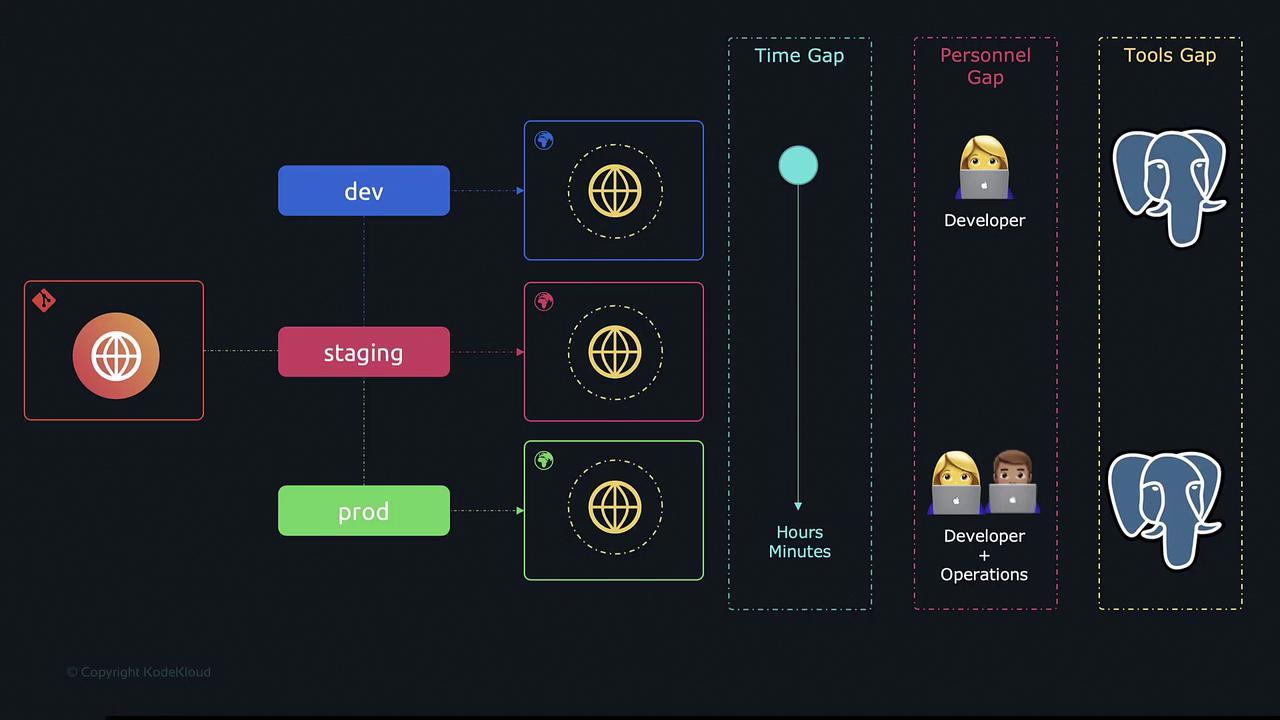
Traditional Environment Setup
Most development workflows historically involve three distinct environments:-
Development (Dev):
Developers build and test new features in this phase. Often, lightweight tools or databases (e.g., SQLite) are used to accelerate iterative development. -
Staging:
This environment closely mirrors production and is used for final testing and validation, ensuring that new changes behave as expected under realistic conditions. -
Production (Prod):
The live environment accessed by end users, which typically relies on more robust tools and services (e.g., PostgreSQL) to support real-world usage.
Challenges in Traditional Workflows
Historically, transitioning code from development to production could span weeks or even months. This separation often led to several issues:-
Time Gap:
Delays between development and production deployment can introduce discrepancies. Features may evolve after initial development, potentially affecting performance in production. -
Personnel Gap:
When separate teams handle development and deployment, operations teams might not be fully aware of the latest changes, complicating troubleshooting. -
Tools Gap:
Using different tools and environments in each stage can result in unexpected issues once changes are deployed.
The 10th principle of the 12 Factor App framework emphasizes minimizing differences between development, staging, and production. This approach streamlines continuous integration and delivery pipelines, reducing the inherent gaps in traditional setups.

Modern Practices for Dev-Prod Parity
Advances in continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery/deployment (CD) now enable teams to roll out changes in hours—or even minutes. This rapid feedback loop ensures that new changes function correctly and issues are identified early. Moreover, the adoption of modern containerization platforms like Docker has enhanced the ability to maintain similar environments across all stages. By using the same set of tools from development to production, teams can effectively minimize surprises during deployment.