AI-900: Microsoft Certified Azure AI Fundamentals
Fundamental AI Concepts
Principles of Responsible AI
As the development and deployment of AI systems continue to evolve, recognizing their profound societal impact becomes increasingly crucial. Responsible AI is dedicated to creating and employing AI technologies that benefit humanity while minimizing harm. This article details a set of guiding principles—fairness, reliability and safety, privacy and security, inclusiveness, transparency, and accountability—that address ethical challenges and mitigate associated risks in AI.
Fairness
Fairness in AI ensures that systems make unbiased decisions without favoring or discriminating against any group. For an AI system to be truly fair, it must deliver equitable outcomes for all users, irrespective of race, gender, or other characteristics. A significant challenge lies in preventing AI models from inheriting the biases present in their training data. For instance, an AI system based on historical hiring data might replicate past biases, leading to unfair recommendations.
Focusing on fairness helps ensure that AI systems serve all individuals equally and contribute to reducing inadvertent bias.
Reliability and Safety
Reliability and safety are essential attributes of responsible AI. AI systems must consistently perform their intended functions, especially in high-stakes scenarios such as healthcare or autonomous driving. Minor errors or malfunctions in these environments can lead to severe outcomes. For example, an autonomous vehicle that misinterprets a traffic signal or an AI-driven diagnostic tool that provides an incorrect diagnosis underscores the critical need for rigorous testing and robust safety measures. Similarly, consider a delivery drone that misinterprets its surroundings—this could lead to accidents, endangering both property and lives.
By prioritizing reliability and safety, AI systems are better prepared to handle complex and unpredictable situations.
Privacy and Security
Protecting user data is a fundamental aspect of responsible AI. Since AI applications frequently process sensitive information—ranging from medical records to financial details—implementing robust privacy and security measures is imperative. Insecure systems risk unauthorized data access and misuse. For example, a health monitoring application that inadvertently shares private medical data without user consent can severely compromise user trust and privacy.
Note
Implementing strong privacy and security protocols not only safeguards sensitive data but also builds lasting trust with users.
Robust privacy and security measures are essential for maintaining confidentiality and preventing potential breaches.
Inclusiveness
Inclusiveness in AI focuses on designing systems that cater to the diverse needs of all users. An inclusive AI technology is adaptable across various languages, cultures, and backgrounds. One common challenge is that many AI systems are not initially designed with such diversity in mind, which may lead to functionality gaps. For instance, a language translation service that fails to support certain dialects can inadvertently exclude a segment of its user base.
Note
Prioritizing inclusiveness in AI ensures that technology is accessible and beneficial to individuals from every demographic.
By adopting an inclusive approach, AI becomes more universally accessible and valuable.
Transparency
Transparency in AI involves making both the systems and the decision-making processes understandable to users. When AI decisions significantly impact individuals, it is crucial for users to grasp how and why those decisions were made. The complexity inherent in many AI algorithms can obscure the decision rationale, such as in the case of credit scoring systems where factors influencing scores might not be clearly communicated. This lack of clarity can foster frustration and diminish trust among users.
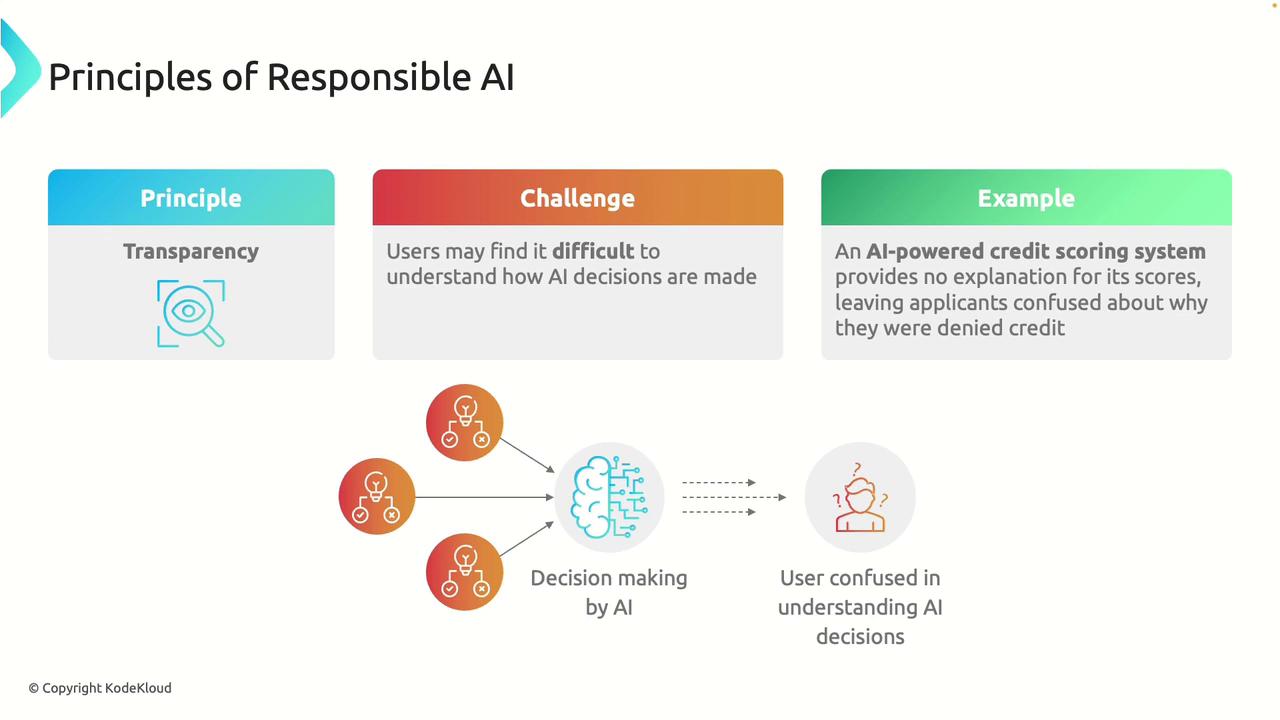
Enhancing transparency helps demystify AI decision-making, thereby strengthening user confidence and accountability.
Accountability
Accountability in AI means that every decision and action taken by an AI system has an identifiable party responsible. This is particularly challenging when multiple stakeholders—such as developers, data providers, and operators—are involved in the system's lifecycle. For instance, if an AI-based facial recognition system results in a wrongful arrest, determining accountability can be complex. Clearly defined lines of responsibility ensure that issues can be promptly addressed and corrected.
Warning
When deploying AI systems, always establish clear accountability frameworks to avoid ambiguity in responsibility and reduce the risk of harm.
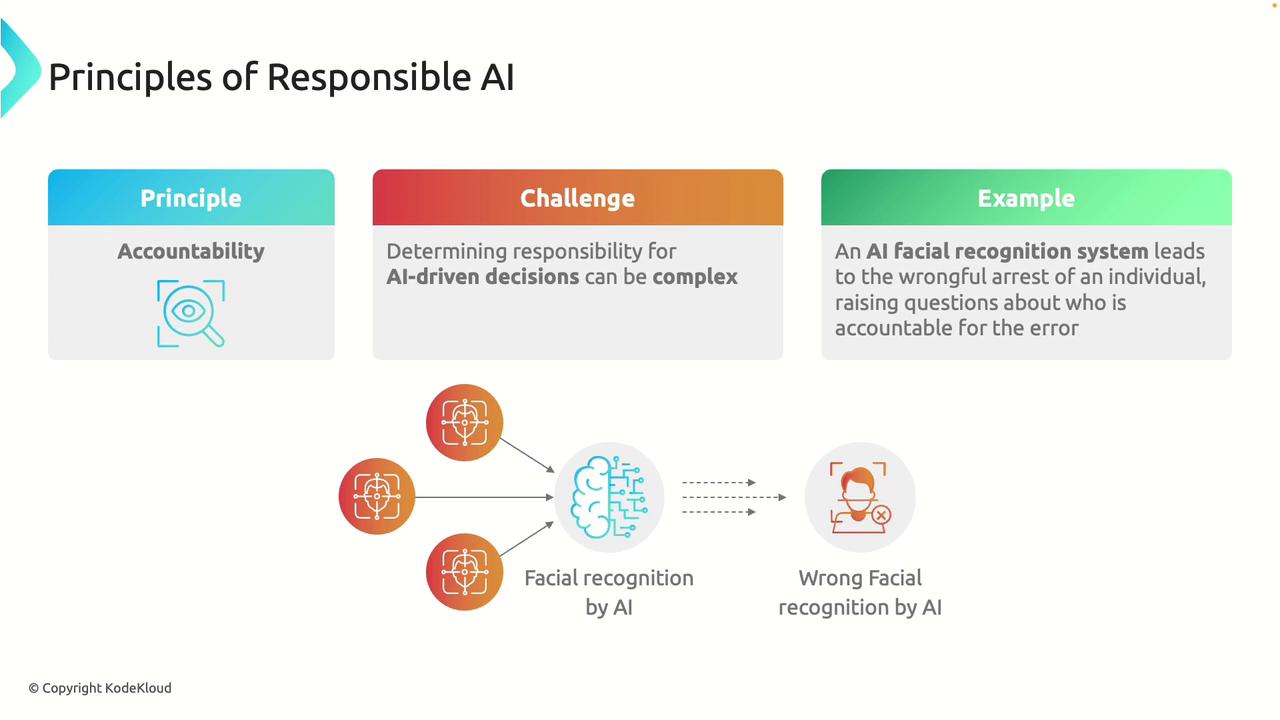
Clearly defined accountability is crucial to maintaining public trust and ensuring that any issues are efficiently resolved.
Together, these principles form a comprehensive framework for developing ethical, trustworthy, and beneficial AI systems. With a solid foundation in responsible AI practices, we are well-positioned to advance into the broader fundamentals of machine learning and explore further innovations.
Watch Video
Watch video content