AI-900: Microsoft Certified Azure AI Fundamentals
Fundamental AI Concepts
What Is Artificial Intelligence
In this article, we explore the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its practical applications across various industries. At its core, AI encompasses software and systems designed to mimic human intelligence. This allows machines and programs to perform tasks that once required human insight, such as face recognition, natural language understanding, and data-driven decision-making. By learning from experience and adapting to new inputs, AI continues to transform the way we interact with technology.
With a foundational understanding of AI, let’s explore some of its key applications in detail.
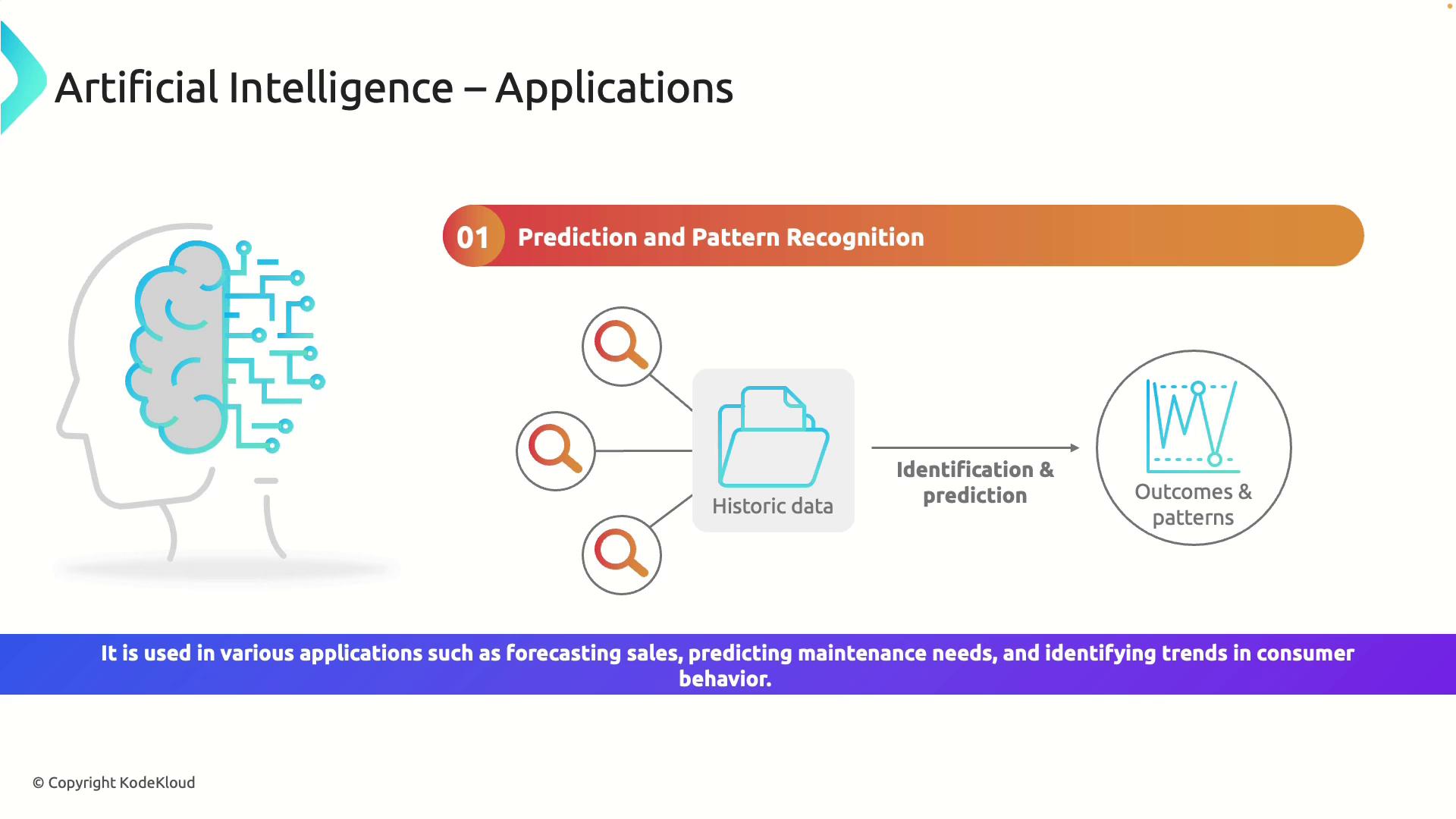
Prediction and Pattern Recognition
One of the most impactful applications of AI is its ability to analyze historical data to identify patterns and predict future trends. In business, AI systems can forecast future sales by analyzing past sales data and market trends. Similarly, in equipment maintenance, AI can analyze performance data to predict when a machine may require service.
Note
This predictive capability is essential in industries such as retail, manufacturing, and finance, where data-driven decision-making can optimize operations.
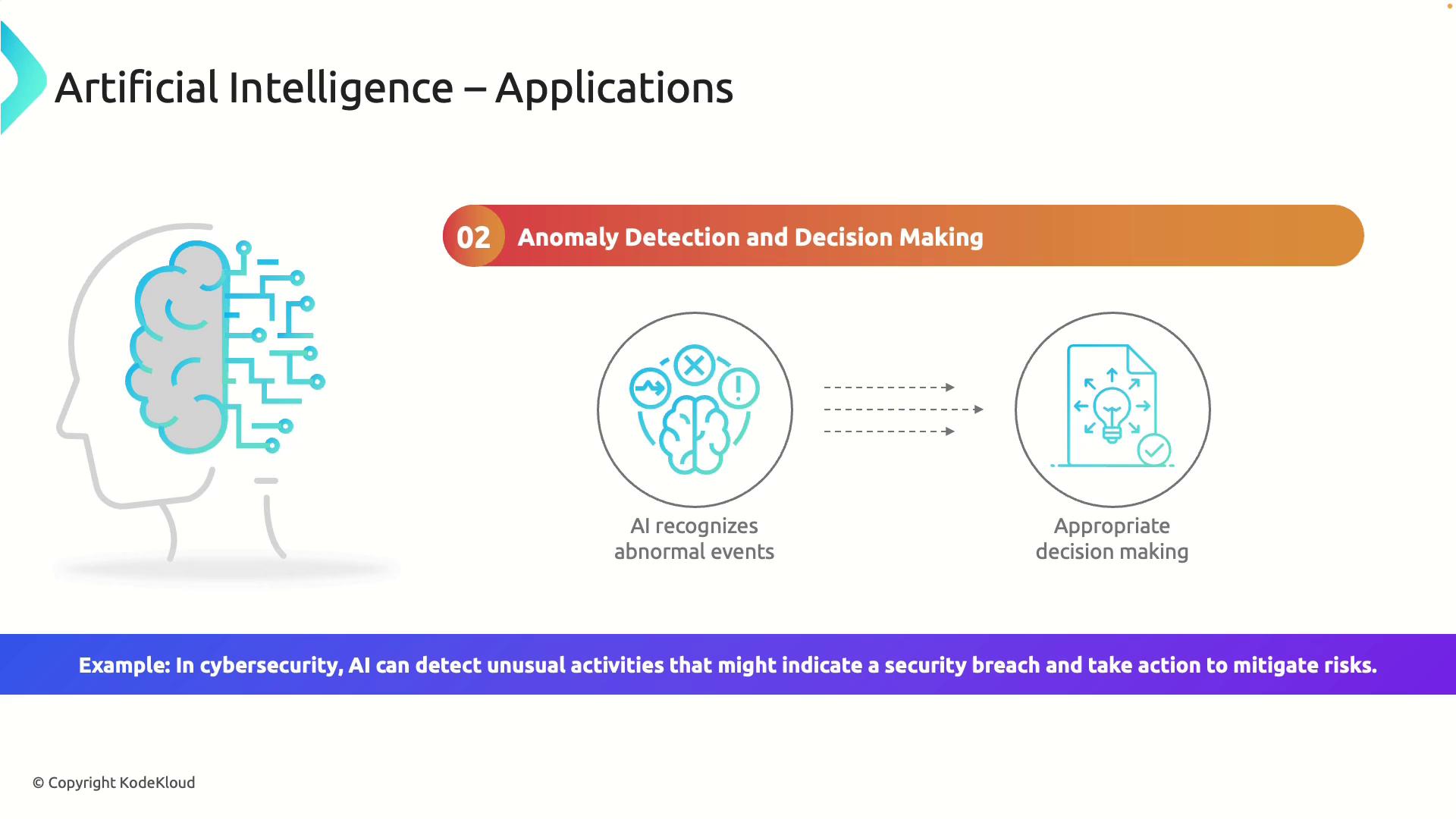
Anomaly Detection and Decision-Making
AI excels in detecting anomalies—those unusual occurrences that deviate from expected behavior—in various systems. For instance, in cybersecurity, AI monitors network activities to spot irregular behaviors that might indicate a breach. Once detected, AI systems can immediately take action, such as blocking suspicious activities or alerting security personnel.
Warning
In fields like finance and healthcare, early anomaly detection is critical. In finance, it can prevent fraud by flagging unusual transactions, while in healthcare, it can prompt early interventions for abnormal health indicators.
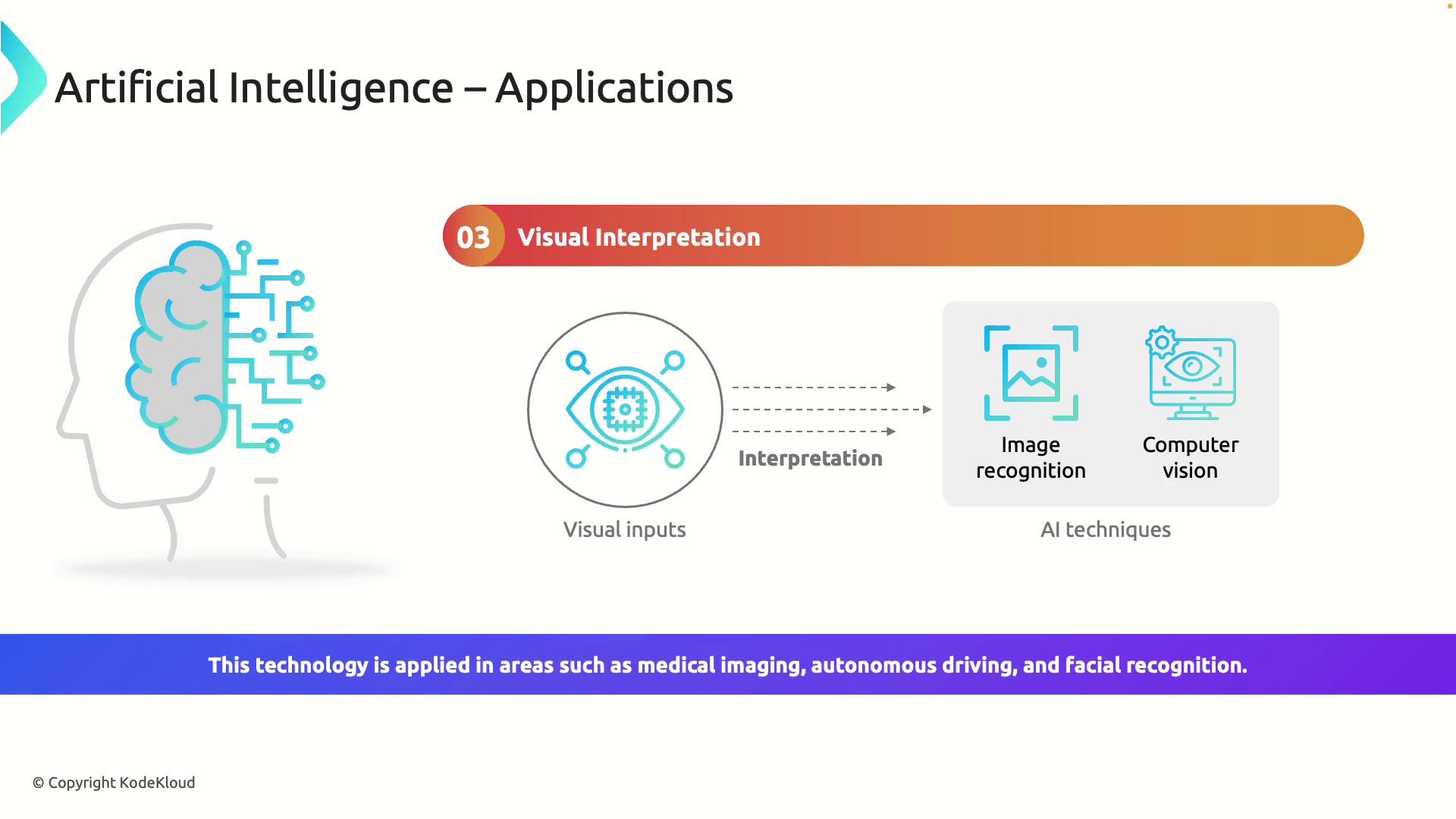
Visual Interpretation
Visual interpretation is transforming many sectors by enabling machines to process and analyze visual data. In medicine, AI systems interpret medical images like X-rays and MRIs to assist in disease diagnosis. Similarly, in the realm of autonomous driving, AI processes real-time video data to identify and respond to objects on the road, including vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic signals. Facial recognition systems powered by AI further highlight its ability to interpret complex visual data.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Another critical capability of AI is Natural Language Processing (NLP), which empowers systems to understand and interact with human language. NLP is behind virtual assistants such as Siri and Alexa, enabling them to process spoken commands to perform tasks like setting reminders, playing music, or answering queries. Through NLP, the gap between human communication and machine interaction is steadily diminishing, making technology more accessible.
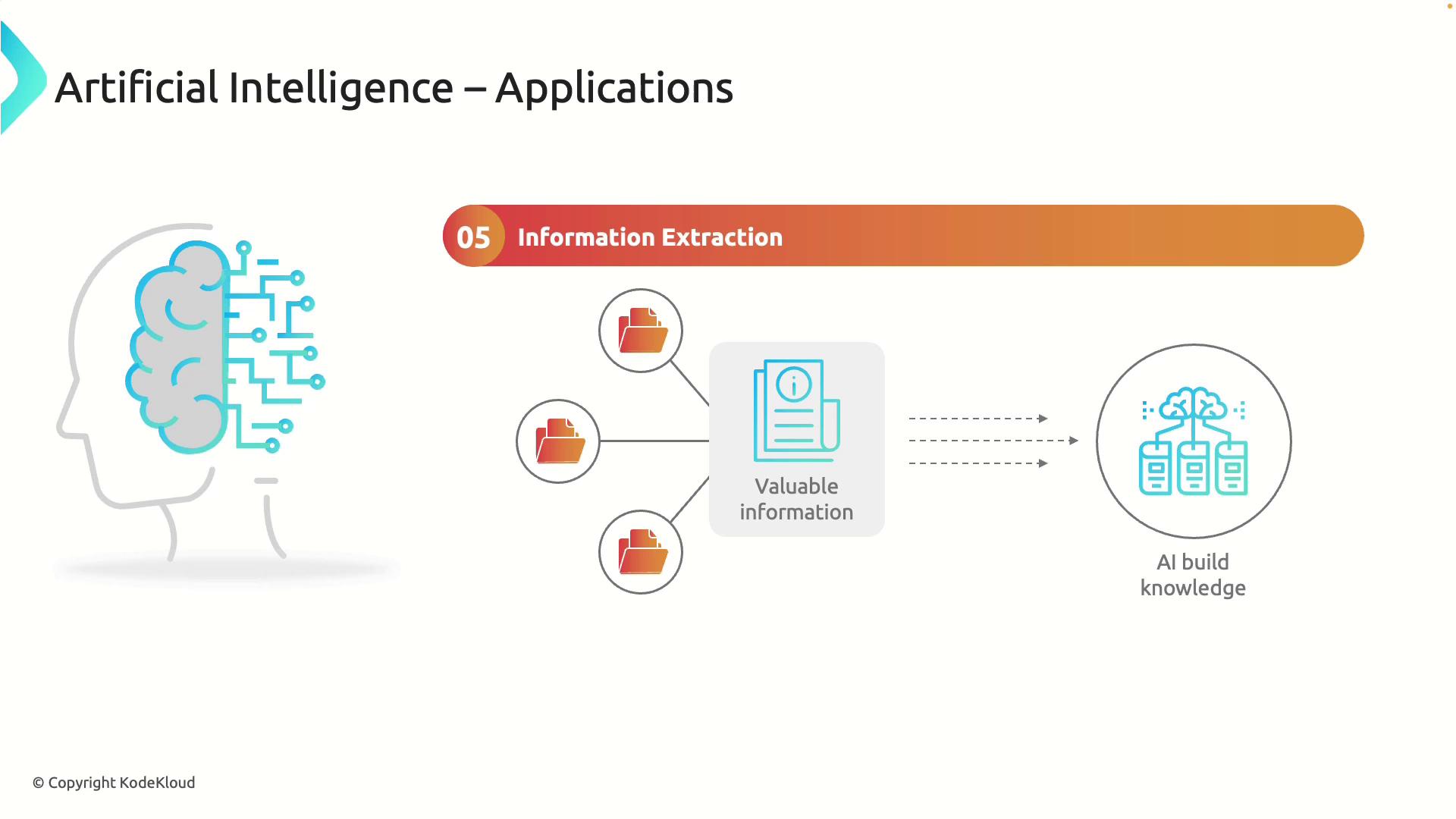
Information Extraction
AI's robust data analysis abilities extend to information extraction, where systems scan large volumes of text and data to identify and compile relevant insights. For example, an AI platform can analyze thousands of research articles or news items to extract key trends and information, proving invaluable in scientific research and market analysis.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is not just an advanced technological concept—it is a practical tool that addresses real-world challenges and drives innovation across industries. From forecasting future trends to interpreting complex visual data and processing human language, AI continues to evolve and shape the future of technology.
For additional reading on AI applications and more, check out these resources:
Now that we have a comprehensive overview of AI's core capabilities, we can proceed to explore common AI workloads and how they are implemented in modern technology.
Watch Video
Watch video content