AI-900: Microsoft Certified Azure AI Fundamentals
Generative AI
Language Models
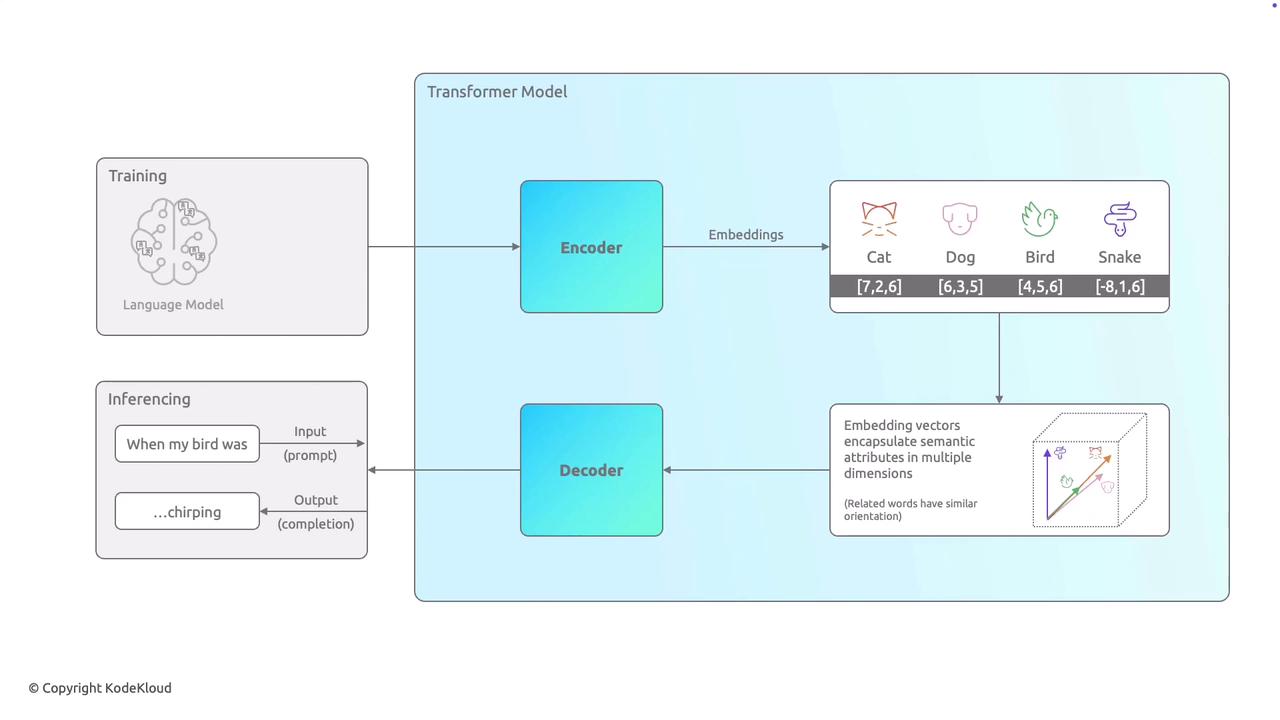
This lesson provides an overview of language models, a critical component in how AI systems understand and generate human language. At the heart of modern natural language processing (NLP) is the transformer model, which comprises two essential parts: the encoder and the decoder.
The training process begins with exposing the model to vast amounts of textual data—ranging from books and articles to websites—so it can learn language patterns, word associations, and contextual meanings. In this stage, the encoder converts each word into numerical representations called embeddings. Think of these embeddings as coordinates in multidimensional space, where words with similar meanings or contexts (for example, "cat" and "dog") are positioned close to one another.
After the training phase, the model is ready to make predictions. When given an input prompt—such as "when my bird was"—the decoder utilizes the learned embeddings and language patterns to generate a coherent continuation of the sentence. For instance, the decoder might suggest "chirping" to complete the thought naturally.
How It Works
The encoder-decoder architecture not only allows the language model to understand the context and relationships between words but also to generate coherent and contextually relevant responses.
In summary, the encoder processes and represents the meaning and relationships of words, while the decoder uses this embeddings-based information to generate human-like language. This combination enables language models to complete sentences, answer questions, and even engage in dynamic conversations by leveraging the patterns learned during training.
Next, we will explore in greater detail the training methods and strategies that make transformer models so effective in natural language understanding and generation.
Watch Video
Watch video content