AI-Assisted Development
Introduction to AI Assisted Development
Introduction to AI Assisted Development
Welcome to our deep dive into AI Code Completion. In this article, we explore how generative AI tools are revolutionizing coding and software development. Rather than serving as a sales pitch, this guide examines the benefits, potential risks, and practical strategies for integrating these technologies into your workflow.

We will discuss various adoption strategies along with approaches for risk mitigation. The era of generative AI in DevOps and software development isn’t coming—it’s already here. Over a million developers are leveraging tools like GitHub Copilot, which we will review in detail.
How Generative AI Tools Work
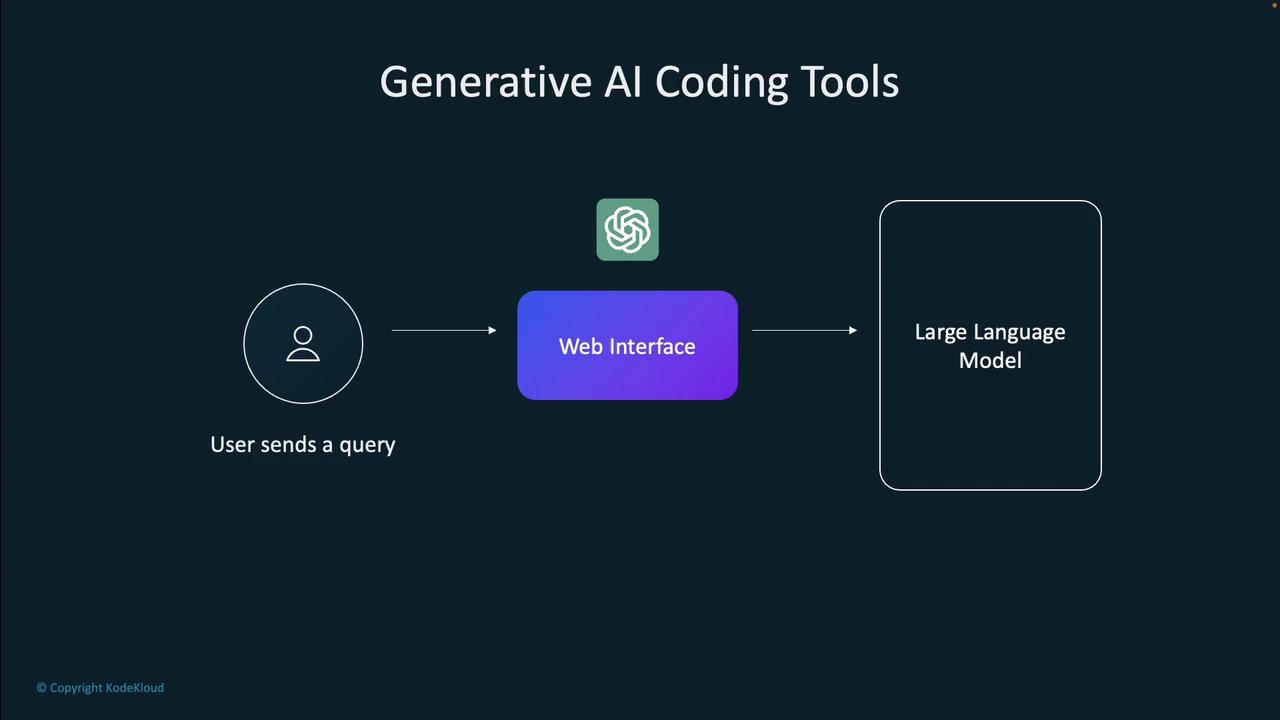
Generative AI coding tools operate in a user-friendly way. You submit a query or prompt via a web interface, and the tool processes it using a large language model. Instead of simply retrieving data from a database, the response is dynamically generated based on statistical likelihoods.
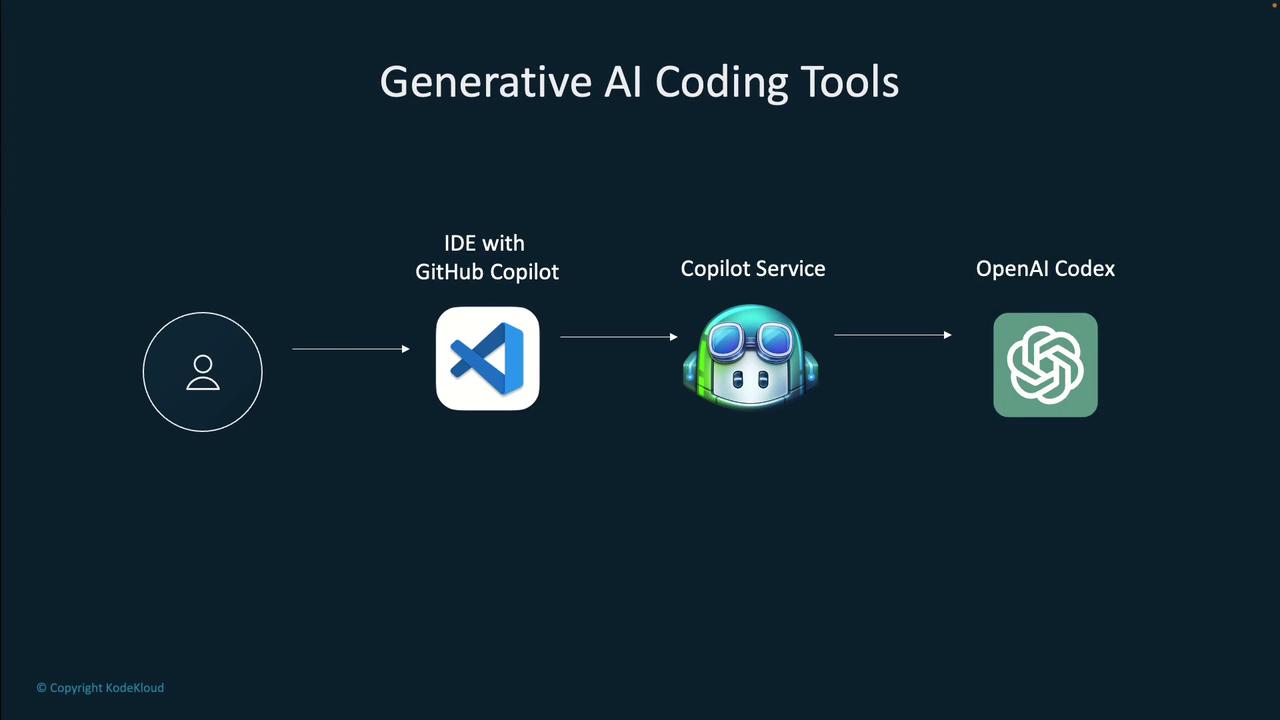
For example, when using GitHub Copilot within an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), your code context is sent to a service where an OpenAI Codex model—trained on publicly available code—evaluates it. The tool then returns a code completion suggestion that appears within your IDE. You can choose to accept, modify, or provide feedback on the suggestion, which helps improve future outputs.
Code Completion: Then vs. Now
Traditional tools like IntelliSense offer syntax highlighting, basic code completions, and debugging with predefined rules. In contrast, generative AI tools leverage deep learning from extensive codebases to deliver innovative and context-aware suggestions.
Consider the example below illustrating code completion within a Flask application:
if request.endpoint == 'delete-cookie':
response = make_response(render_template('index.html', data=None, session_id=None))
response.delete_cookie('session_id')
return response
@app.route('/quiz/<question_id>/<question_number>', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def quiz(question_id, question_number):
our_session = request.cookies.get('session_id')
thisquestion = None
# Set the path to the database
db_path = 'data/questions.db'
# Call the function and store the returned data in a variable
with DatabaseConnection(db_path) as cursor:
# Further processing...
While IntelliSense focuses on enforcing syntax and security, AI-powered tools can also generate entirely new code, write tests, fix issues, document code, and answer code-related questions.
For instance, an AI tool can automatically generate documentation in your code, as seen in the example below:
@app.route('/', methods=['GET'])
def index():
# tabnine: test | fix | explain | document | ask
db_path = 'data/questions.db'
with DatabaseConnection(db_path) as cursor:
session = Session(cursor)
questions = Questions(cursor)
our_session_id = request.cookies.get('session_id')
print("session id is " + str(our_session_id))
if our_session_id is None:
print("We have no session id; must be first time")
Code Testing with AI Assistance
Generative AI tools extend their capabilities beyond code suggestions to include testing. They can analyze your project and generate unit tests to ensure that your application works as intended. Consider the following example of a unit test for a Flask application:
import unittest
from your_app import app # Import your Flask app
class TestRoutes(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.app = app.test_client()
def test_delete_cookie(self):
response = self.app.get('/delete-cookie')
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)
self.assertEqual(
response.headers.get('Set-Cookie'),
'session_id=; Path=/; Expires=Thu, 01 Jan 1970 00:00:00 GMT'
)
def test_quiz(self):
response = self.app.get('/quiz/1/1')
# Add further assertions as required
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
This example demonstrates how AI-assisted tools can automatically inject and manage test cases to maintain high code quality.
Evolving Interaction Modes
The interaction paradigm for AI-assisted tools is shifting towards chat-style interfaces, similar to ChatGPT or Gemini. This evolution allows developers to maintain continuous dialogue with the tool, ask questions about their code, and have real-time modifications applied to their projects.
Overview of Popular Tools
Below is an overview of several popular AI-assisted coding tools:
GitHub Copilot
Developed in collaboration with OpenAI, GitHub Copilot is one of the most robust code-completion tools available today. Its training on vast amounts of public code enables it to provide highly accurate suggestions.

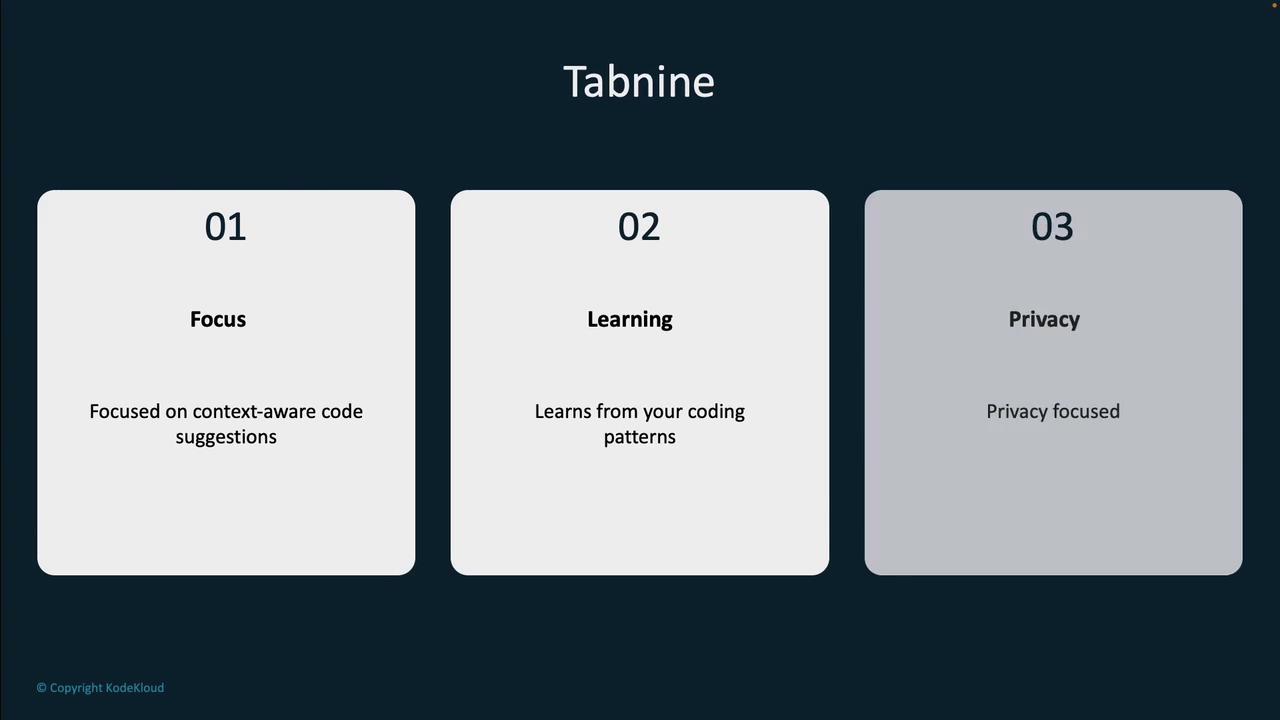
Tabnine
Tabnine emphasizes fast, context-aware code suggestions that learn from your unique coding patterns. One notable feature is its ability to run local instances, ensuring that your code remains private.
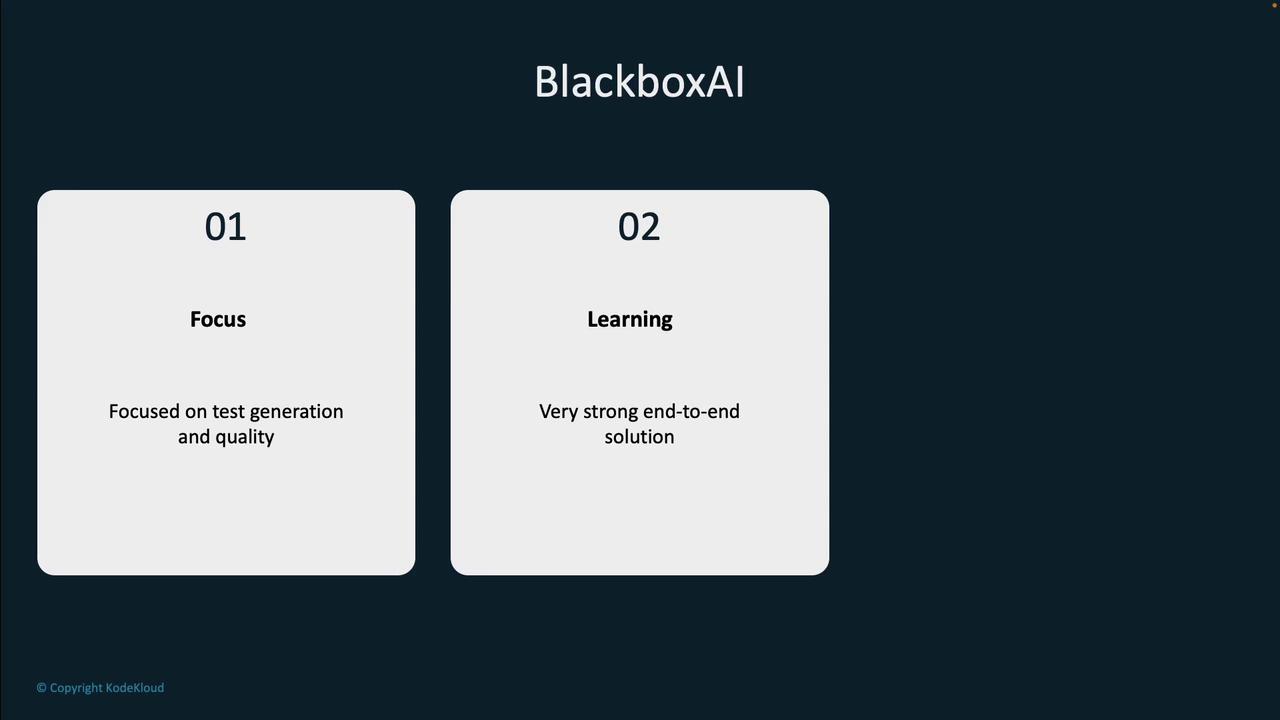
BlackboxAI
Recognized for its capabilities in code completion, test generation, and documentation, BlackboxAI provides an end-to-end solution that significantly enhances code quality and streamlines error resolution.
Developer-Focused vs. General-Purpose Tools
While multi-purpose tools like ChatGPT offer a wide range of functionalities from documentation to debugging, tools designed specifically for developers—such as Cursor—provide an immersive IDE experience and even support local model execution to enhance security.

A comparative view of these advanced coding tools reveals the distinctive strengths of each option:

Note
Keep in mind that while AI tools are incredibly powerful, they should complement a developer's expertise rather than replace it. Always review and test generated code to ensure it meets your project's standards.
Concluding Thoughts
In this article, we explored the transformative landscape of AI-assisted development tools—from code completion and automated testing to real-time project modification and documentation. Millions of developers are already benefiting from these tools to boost productivity and enhance code quality. However, it is crucial to balance these benefits with potential concerns regarding security and model accuracy.
By understanding both the capabilities and limitations of tools like GitHub Copilot, Tabnine, and BlackboxAI, developers and decision-makers can effectively integrate generative AI into their workflows and make informed choices.
Happy coding!
Watch Video
Watch video content