Updating Requirements
To begin, update therequirements.txt file so that others can install all necessary Python dependencies in their virtual environment.
-
Activate your virtual environment:
-
Update the dependency list by running:
requirements.txt, anyone can run:
Checking .gitignore
Before pushing your code to GitHub, verify that your.gitignore file excludes unnecessary directories. Common exclusions include:
- Python virtual environments (e.g.,
venv) - Python cache directories (e.g.,
__pycache__) - IDE-specific folders (e.g.,
.vscode,.idea) - Frontend build directories (e.g.,
node_modules,dist)
Excluding these folders helps keep the repository clean and reduces clutter in version control.
Updating the README
A comprehensive README is essential. Replace any placeholder titles (such as “super image optimizer”) with a clear project title and detailed information. An effective README for this Python backend might include:- A high-level overview of the project
- Installation instructions
- Usage guidelines
Image optimizer is a simple tool designed to reduce image file sizes without compromising quality. It supports common formats like JPEG and PNG, although other formats (e.g., GIF, batch processing) are not currently supported. The tool operates as a web application.
Installation Instructions
-
Clone the Repository
-
Set Up the Virtual Environment
-
Install Dependencies
-
Set Environment Variables (Optional)
-
Run the Application
You have two options to start the app:
-
Using the Flask CLI:
-
Running the application directly:
-
Using the Flask CLI:
Using the Application
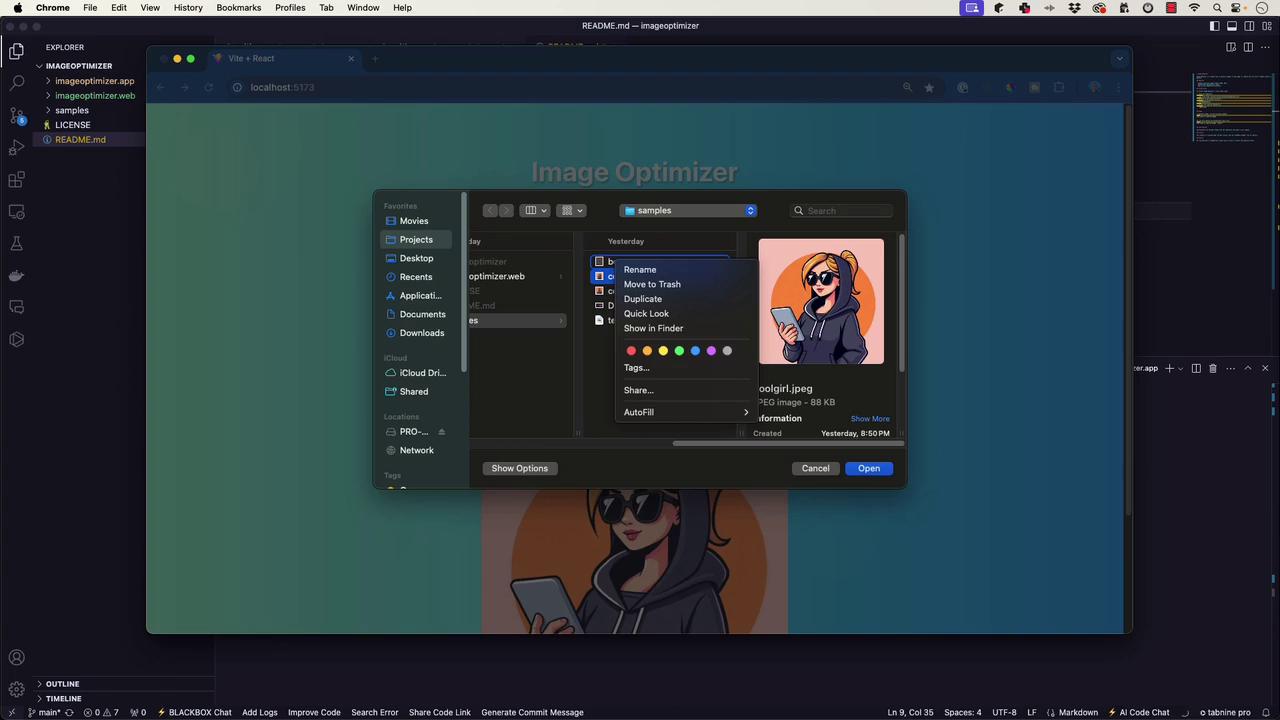
When you launch the image optimizer, the web interface should appear. For example, if you try to optimize a sample image namedcoolgirl.jpeg, you might notice that only one image is selected at a time, which confirms the current functionality.
Further Project Setup and Contributions
This article also covers additional steps for setting up both backend and frontend components. For the Flask backend, ensure that:- Your repository includes an updated README.
- The
.gitignorefile excludes unnecessary directories. - Dependency management is accurate and up to date (repeat the
pip freeze > requirements.txtcommand when needed).
-
Clone the Frontend Repository
-
Install Node.js Dependencies
Consider using AI tools like GitHub Copilot to refine portions of your README, but always manually verify the generated content to ensure it accurately reflects your project.
Summary
By updating therequirements.txt, verifying the .gitignore file, and creating a detailed README with clear installation and usage instructions, your image optimizer project is ready for public release on GitHub. This well-organized documentation and repository structure will help other developers easily clone, install, and contribute to the project.
Happy coding, and enjoy sharing your project with the community!