Container Basics
Containers bundle an application with its libraries, dependencies, and configuration files, ensuring that it runs consistently across various environments. Container orchestrators manage these containerized environments by:- Deploying containers across servers
- Load balancing incoming requests
- Ensuring container-to-container connectivity
- Monitoring container health and performance
- Restarting containers when necessary
Mastering container basics is crucial as it lays the groundwork for understanding how AWS container services operate.
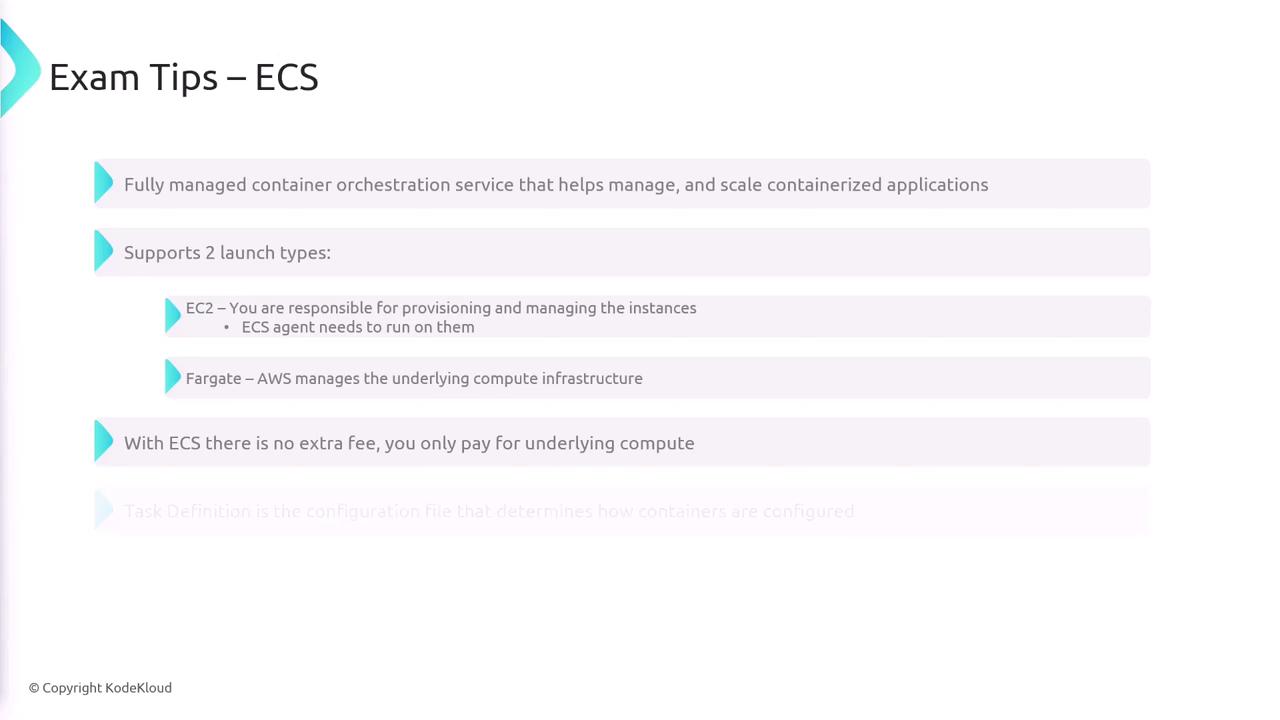
AWS ECS (Elastic Container Service)
AWS ECS is a fully managed container orchestration service designed to simplify the deployment and scaling of containerized applications. ECS supports two launch types:- EC2 Launch Type: You manage EC2 instances and install the ECS agent to handle container tasks.
- Fargate Launch Type: AWS handles the compute infrastructure, and billing is based solely on compute usage.
ECS Roles
ECS relies on two primary roles:- Container Instance Role: Assigned to your EC2 instances (or the ECS agent on these instances), this role enables pulling images, launching containers, and transmitting logs and metrics.
- ECS Task Role: Applied to tasks that require access to other AWS services.

Placement Strategies and Autoscaling
For the EC2 launch type, ECS placement strategies determine how tasks are assigned to container instances. The strategies include:| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Binpack | Places tasks on instances to minimize unused CPU and memory, thereby reducing the number of instances needed. |
| Random | Distributes tasks randomly across available container instances. |
| Spread | Evenly distributes tasks across instances based on specified attributes. |

- Tasks can autoscale based on CloudWatch metrics.
- ECS instances can be scaled using Auto Scaling Groups and Capacity Providers.
- When deploying new versions, configure both the minimum healthy percent and the maximum healthy percent to maintain service continuity.

AWS EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service)
EKS is AWS’s managed Kubernetes service, providing an easy way to deploy and manage Kubernetes clusters on AWS. With EKS:- AWS handles the Kubernetes control plane.
- You can choose between Fargate (where AWS manages compute infrastructure) or EC2 (where you manage your own instances) for worker nodes.

Familiarize yourself with both Fargate and EC2 options in EKS to choose the best fit for your application workloads.
AWS ECR (Elastic Container Registry)
AWS ECR is a fully managed container registry that supports both private and public repositories. It offers advanced features such as:- Image scanning for security vulnerabilities
- Lifecycle policies for automating image cleanup
