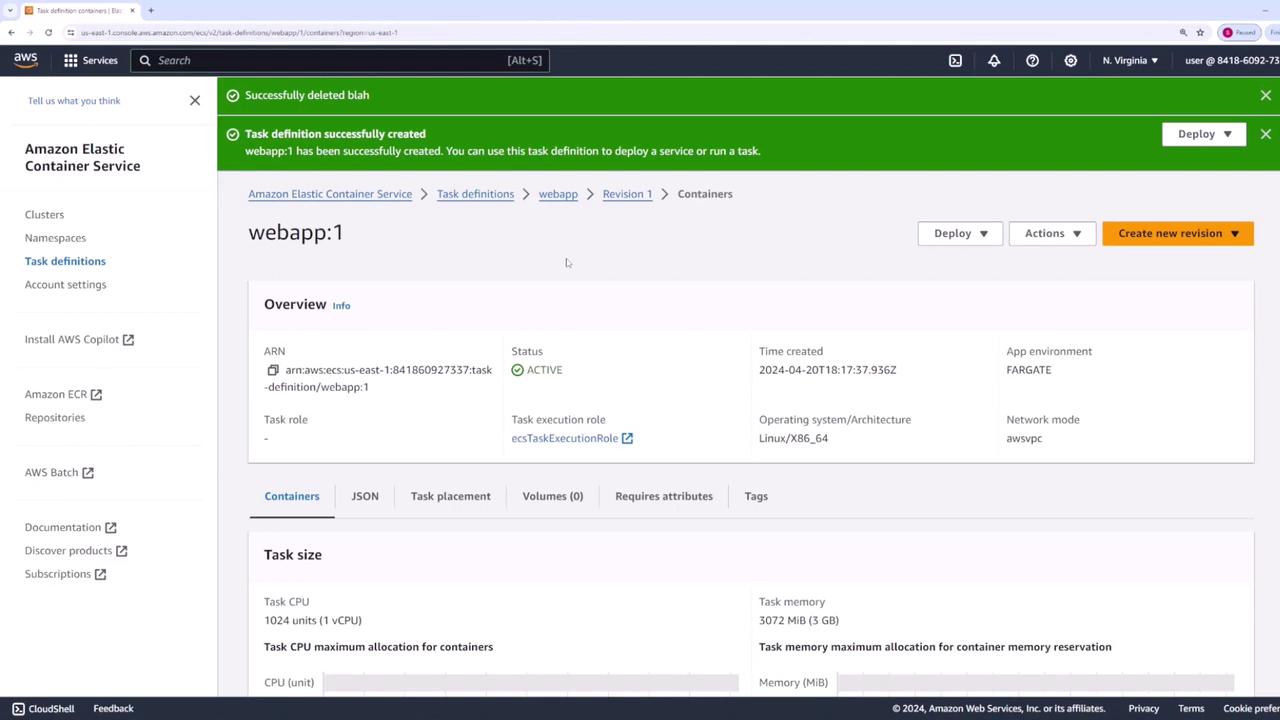
Creating the Task Definition
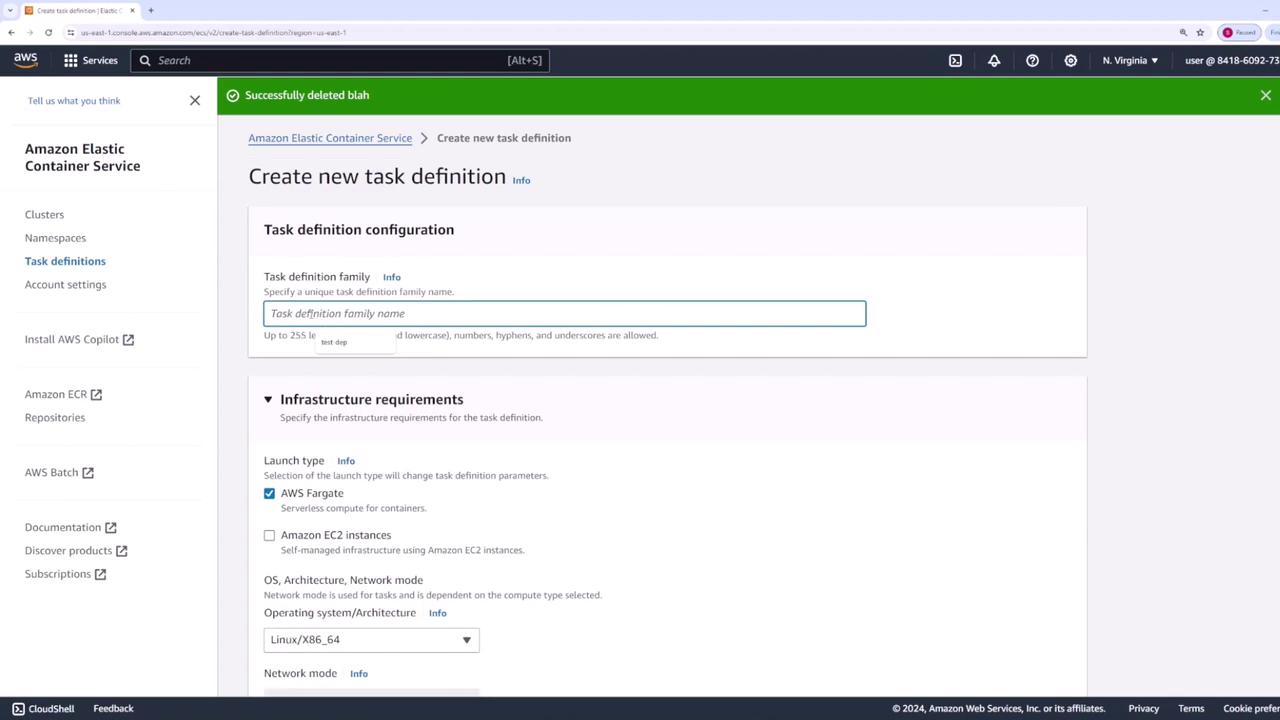
Begin by navigating to the “Task Definitions” section in the AWS ECS console and create a new task definition:- Name the task definition “web app.”
- Select the launch type “AWS Fargate.”
- Use the default task size settings, as this demo employs an Nginx container.
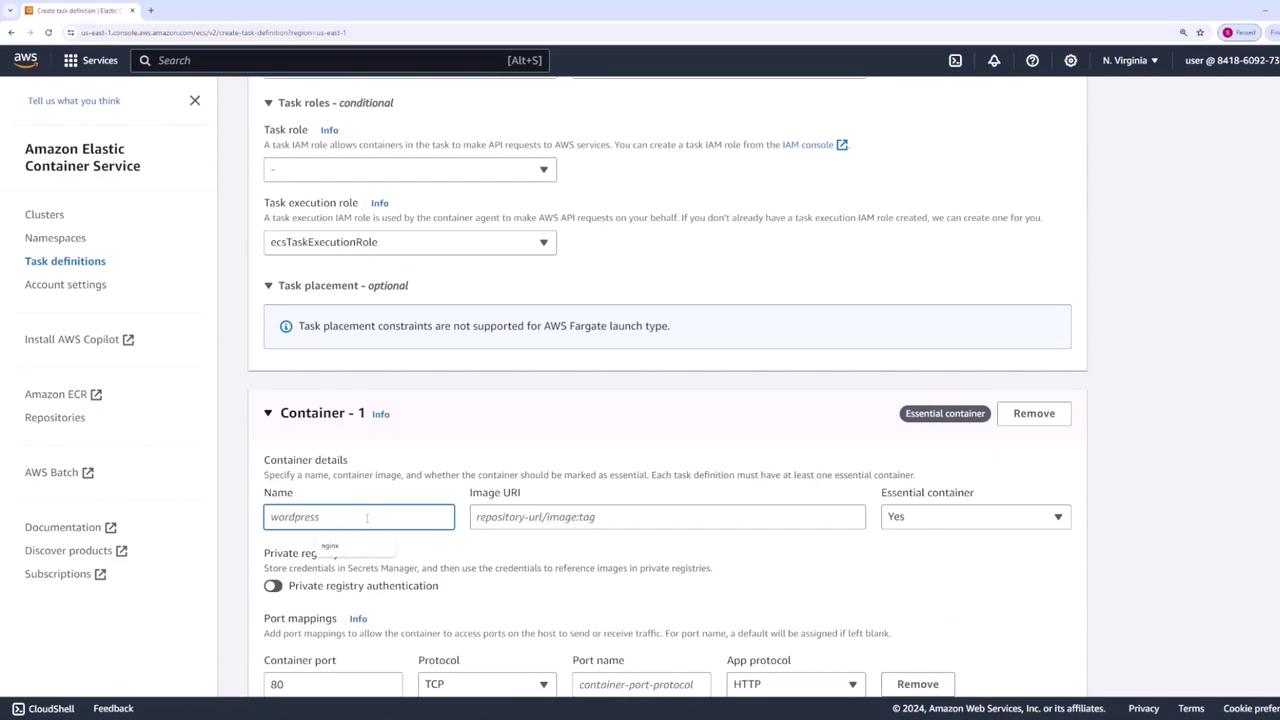
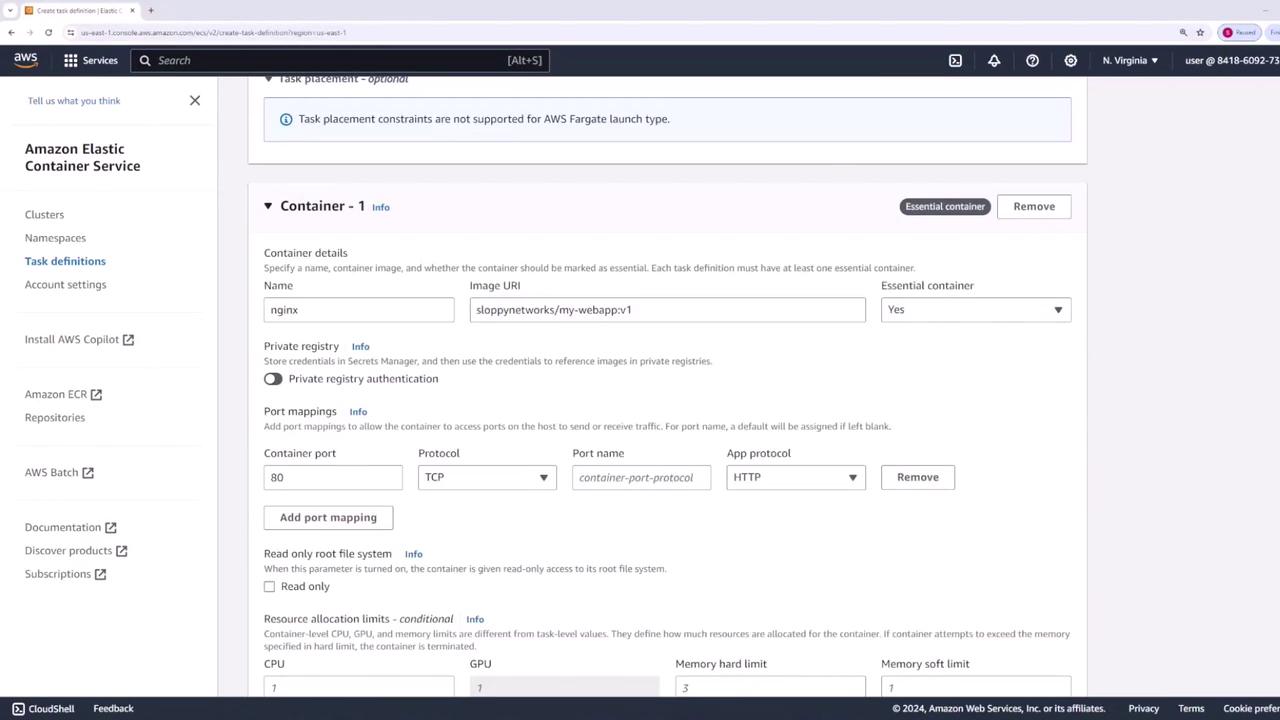
Creating the ECS Service
With the task definition ready, you can now create your first ECS service within your cluster:- Navigate to your main cluster and click “Create Service.”
- Choose the launch type “Fargate.”
- For the application type, select “Service” and use the “web app” task definition.
- Set the revision to version one (v1) and name your service “web app.”
- Define the desired task count as five (i.e., five containers will run).
- Rolling Update: Updates a few containers at a time until the new version is fully deployed.
- Blue-Green Deployment: Managed via CodeDeploy.
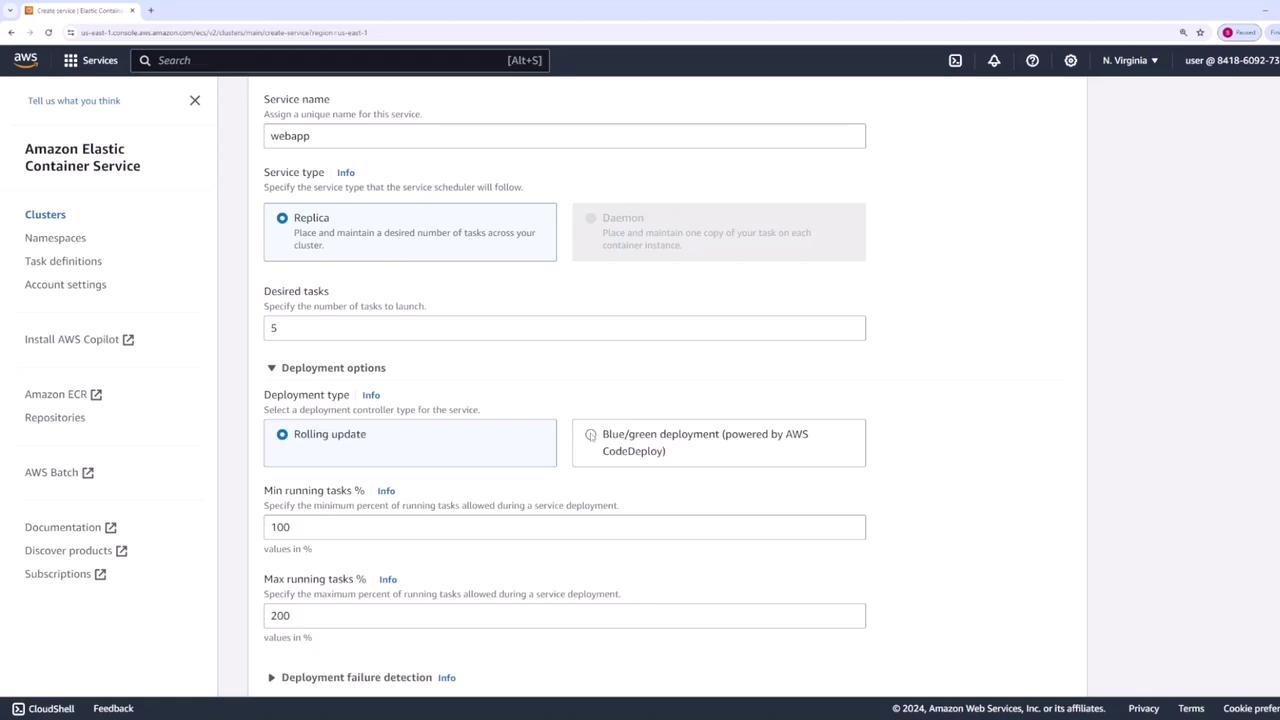
If you lower the minimum running percentage (for example, to 50%), fewer tasks might run temporarily before the new version is fully deployed. For this tutorial, we maintain it at 100%.
Networking and Load Balancer Configuration
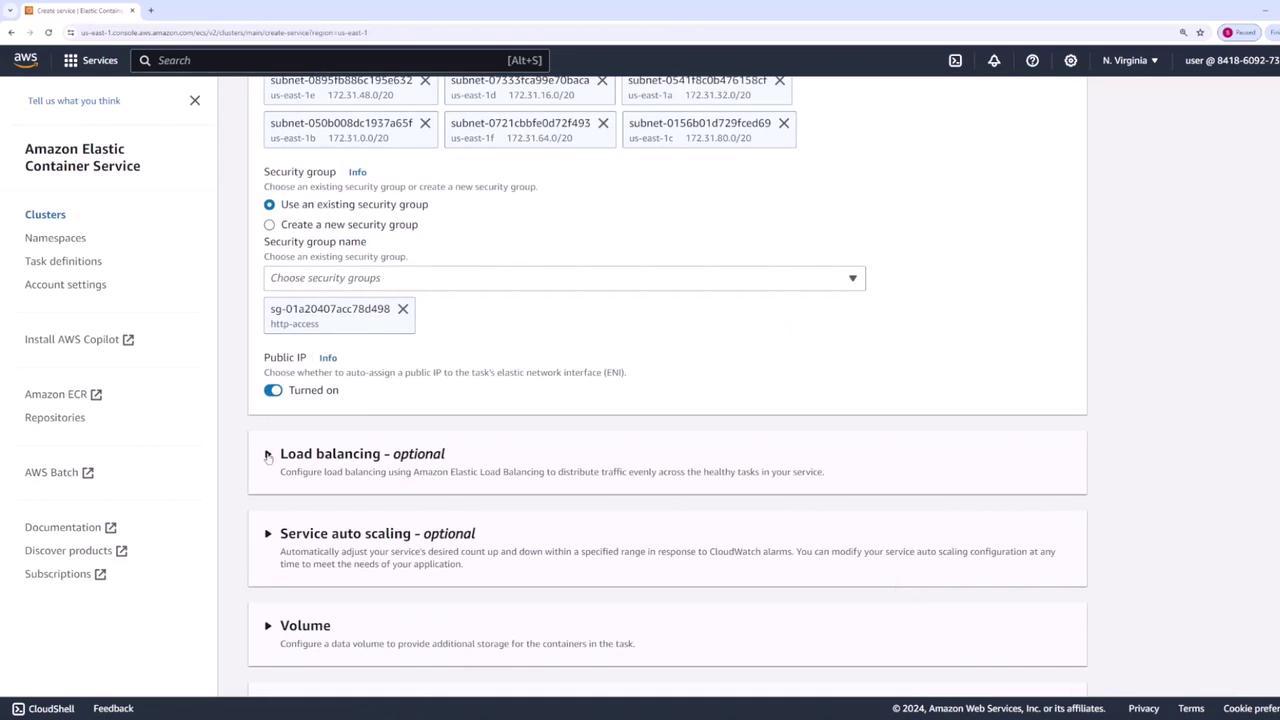
- In the networking section, retain the default subnets and VPC.
- Update the security group to allow HTTP access for the Nginx container.
- Create a load balancer to forward traffic to Nginx on port 80 and name it “web app - lb.”
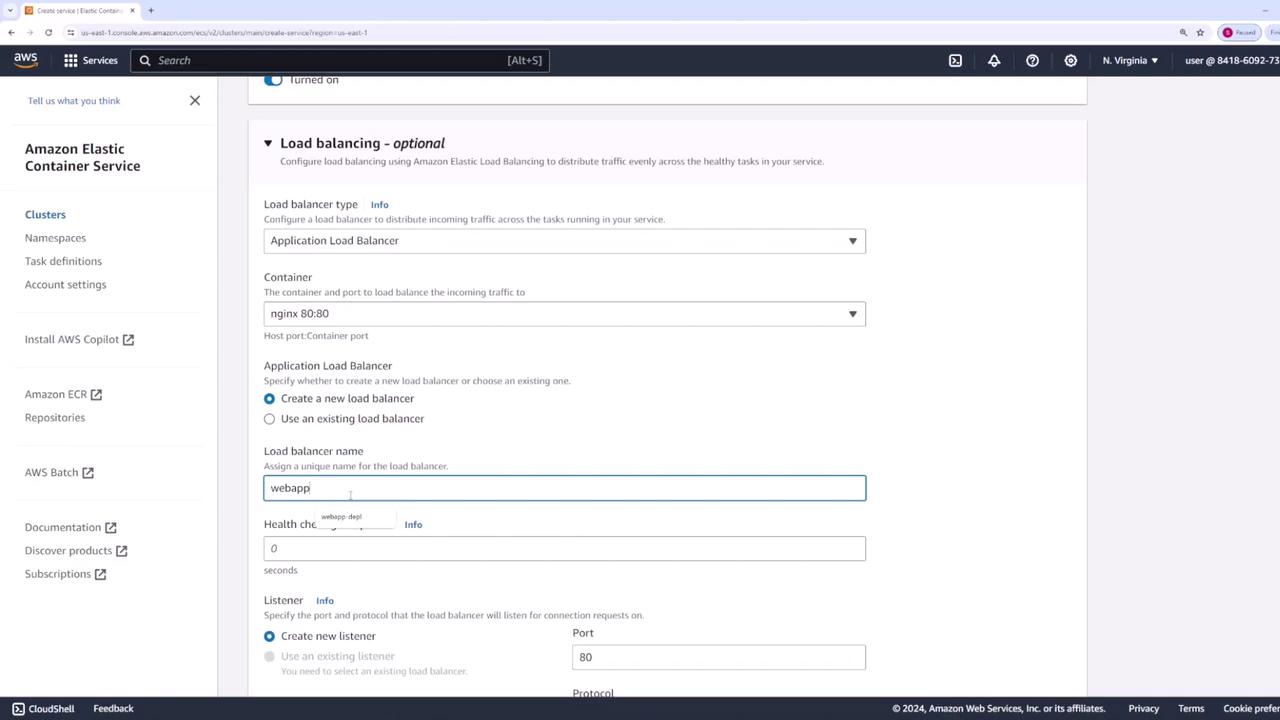
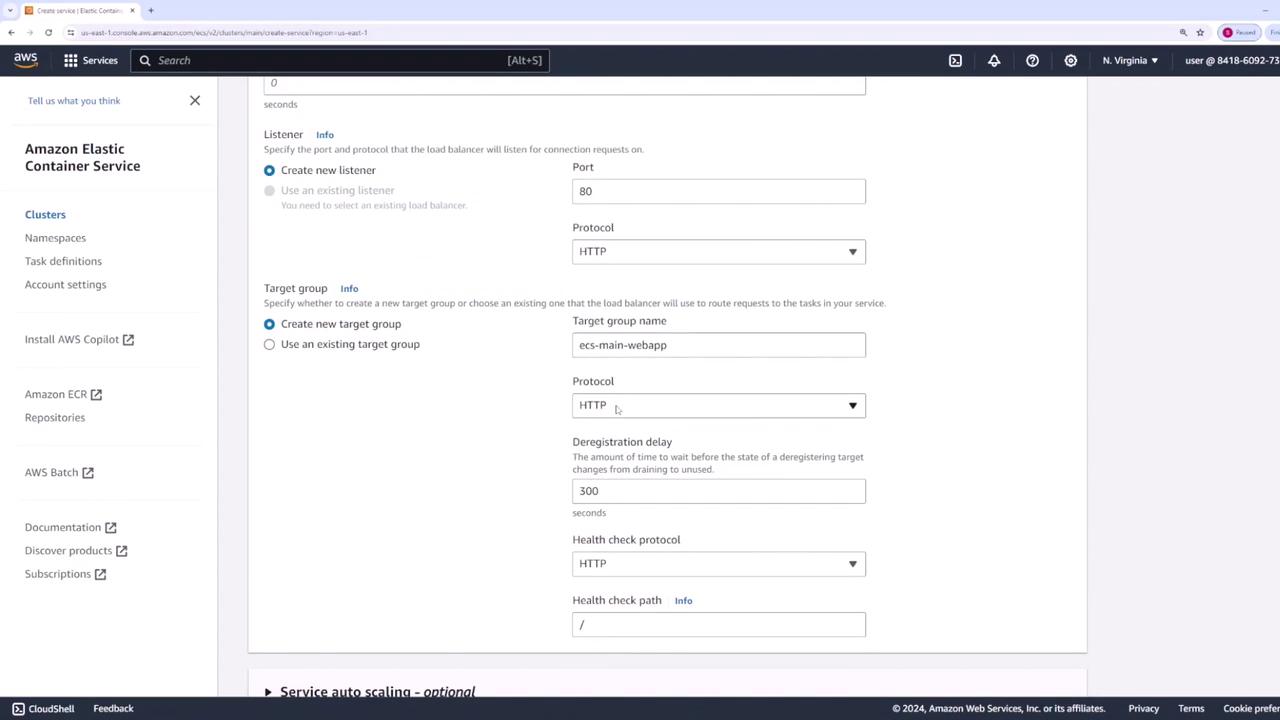
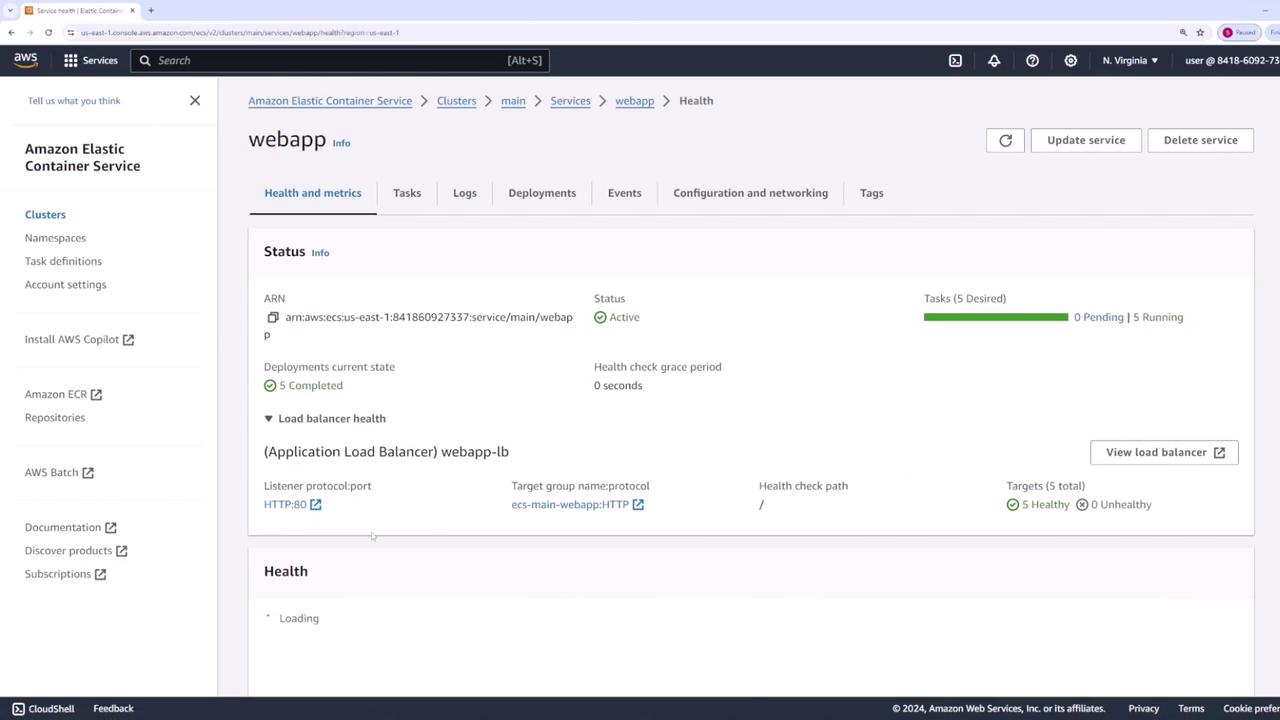
Verifying the Deployment
To confirm that your application has been successfully deployed:- Click on the load balancer associated with the service.
- Copy the load balancer’s DNS name.
- Open the DNS name in a web browser.
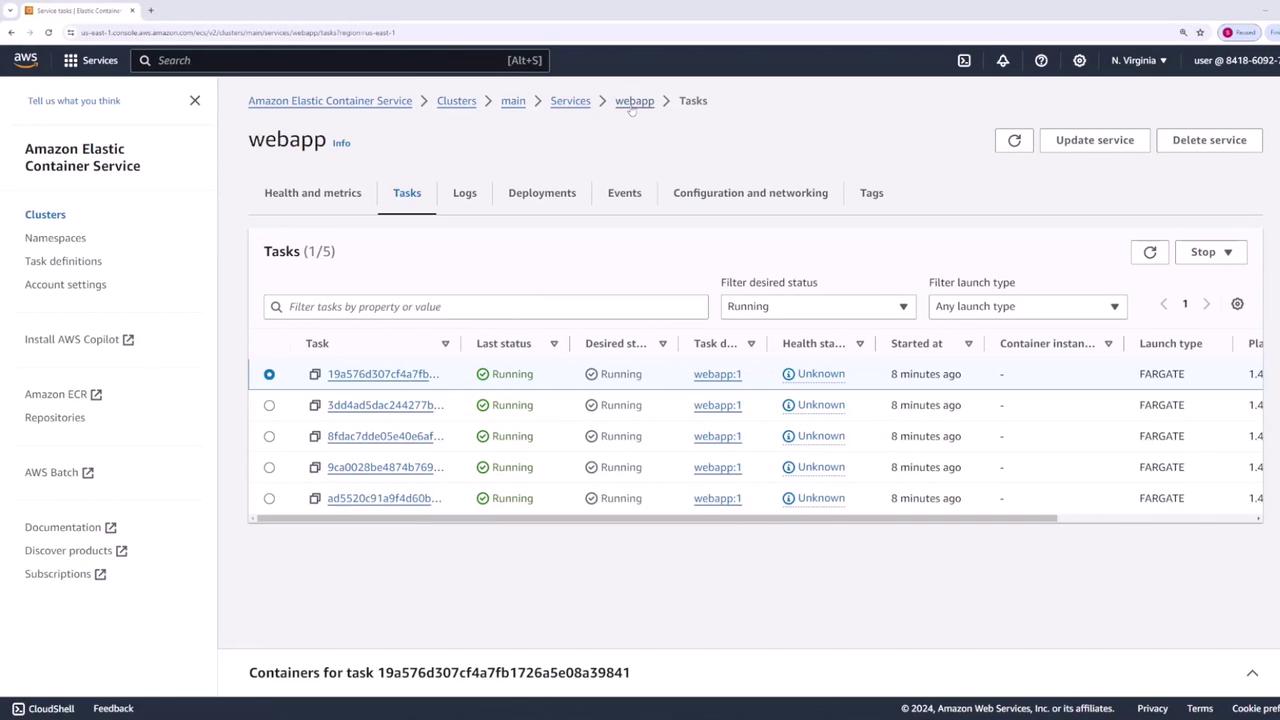
Updating the Service to Version Two
To update the application to version v2, follow these steps:- Return to the ECS console and select the “web app” task definition.
- Create a new revision by updating the container image tag from v1 to v2.
- Update the service configuration to use revision two.

- Select “Update” and then change the revision setting to two.
- Retain the same deployment settings (100% minimum and 200% maximum) to ensure that new tasks are fully deployed before the old ones are decommissioned.
- Click “Update” to trigger the deployment.
Conclusion
This lesson demonstrated the following key steps:- Creation of a task definition for an Nginx container.
- Deployment of an ECS service with load balancing on AWS Fargate.
- Use of a rolling update mechanism to perform a zero-downtime transition from version v1 to v2.
For more information on ECS deployments and best practices, explore the following resources: