What is OpenSearch?
OpenSearch empowers you to ingest, secure, search, aggregate, view, and analyze your data efficiently. Its robust features are particularly useful for log analytics and enhancing search functionality in modern applications—especially when traditional relational databases fall short.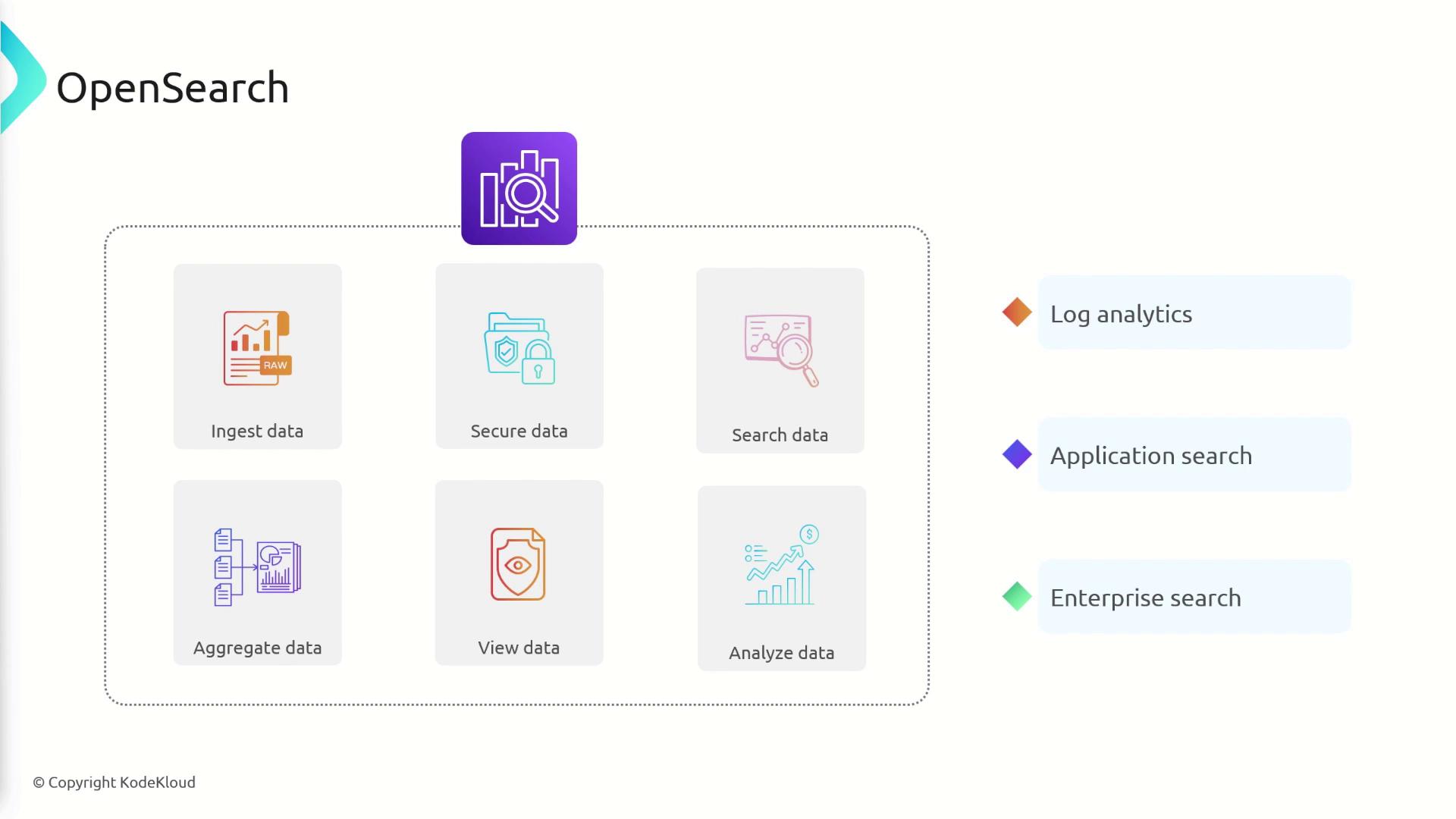
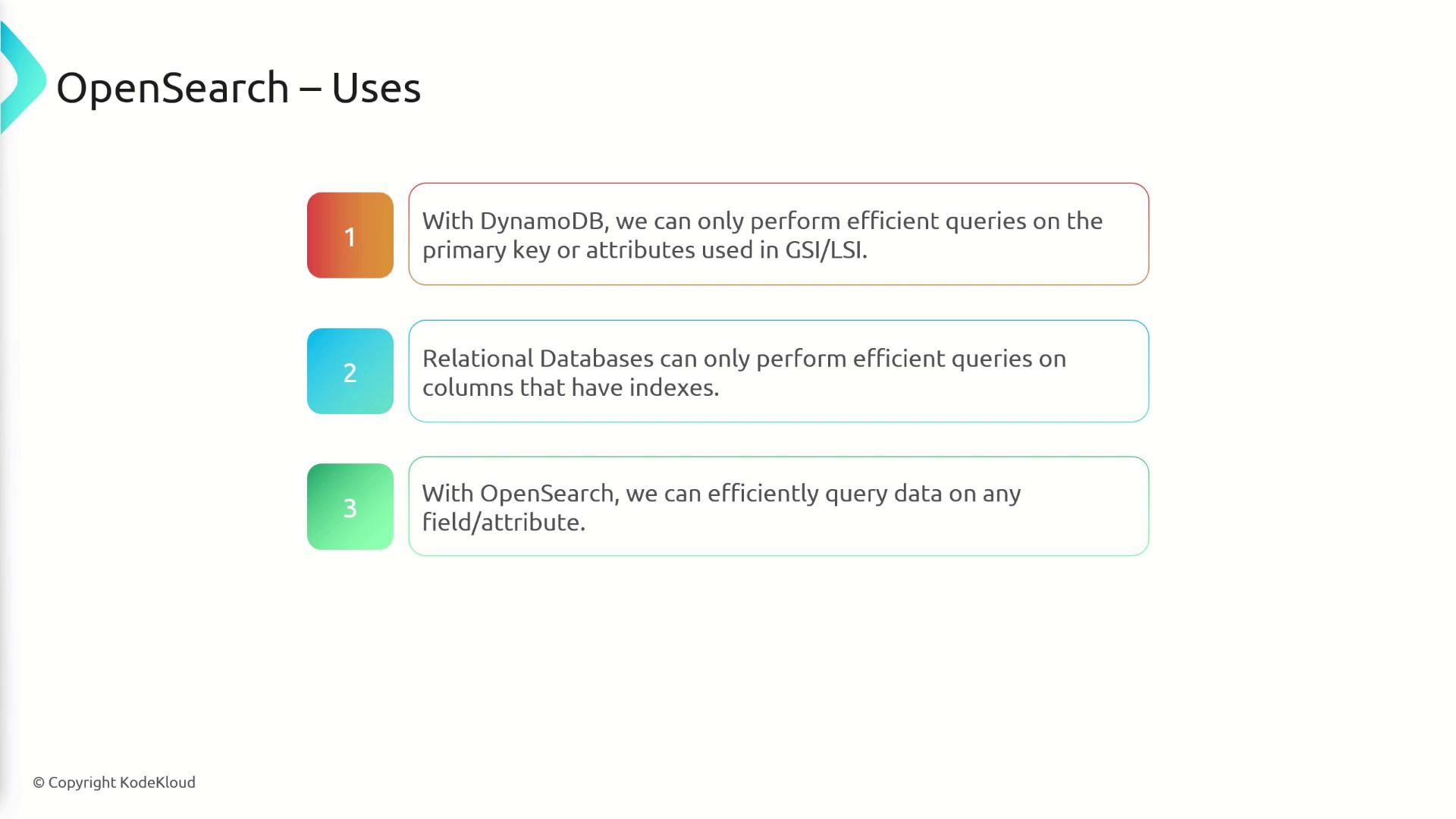
OpenSearch allows efficient queries on any field, making it ideal for versatile search functionalities.
Managed Service and Query Capabilities
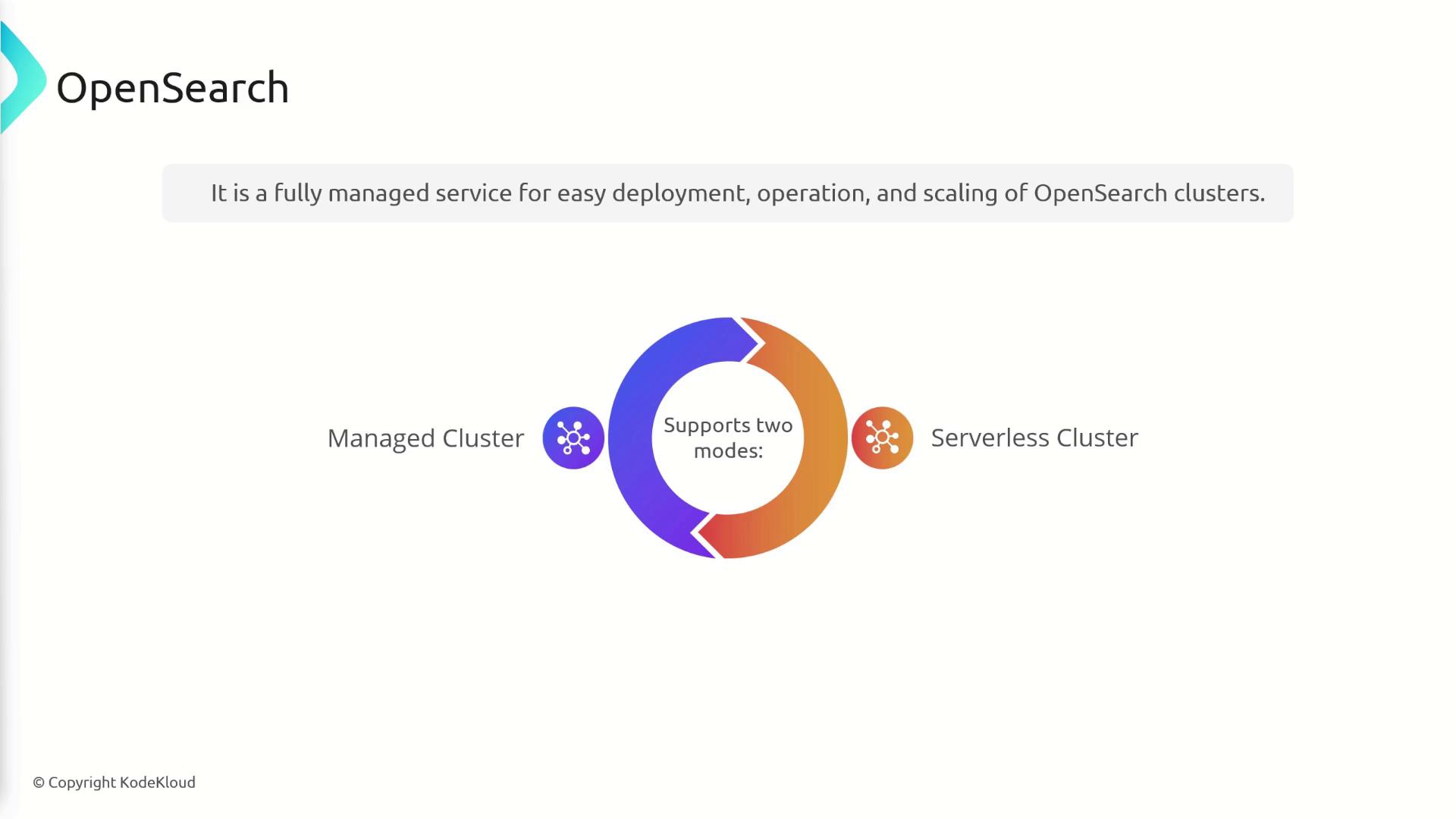
OpenSearch is provided as a fully managed service, simplifying the tasks of deploying, operating, and scaling clusters. It supports two distinct modes:- Managed Cluster Mode
- Serverless Cluster Mode
Integrating OpenSearch into Your Application
Integrating OpenSearch into your application architecture is straightforward. Imagine a setup where your primary data is stored in databases such as Amazon RDS or DynamoDB. For every database update—whether it’s creating, updating, or deleting records—the corresponding data is simultaneously synchronized to OpenSearch. This dual-database strategy ensures that while CRUD operations are managed efficiently through your primary database, powerful search queries run on the OpenSearch index. When you insert, update, or delete an entry in your primary database, OpenSearch receives a corresponding update. Therefore, when you perform searches, your application leverages the indexed copy in OpenSearch to deliver fast and comprehensive results.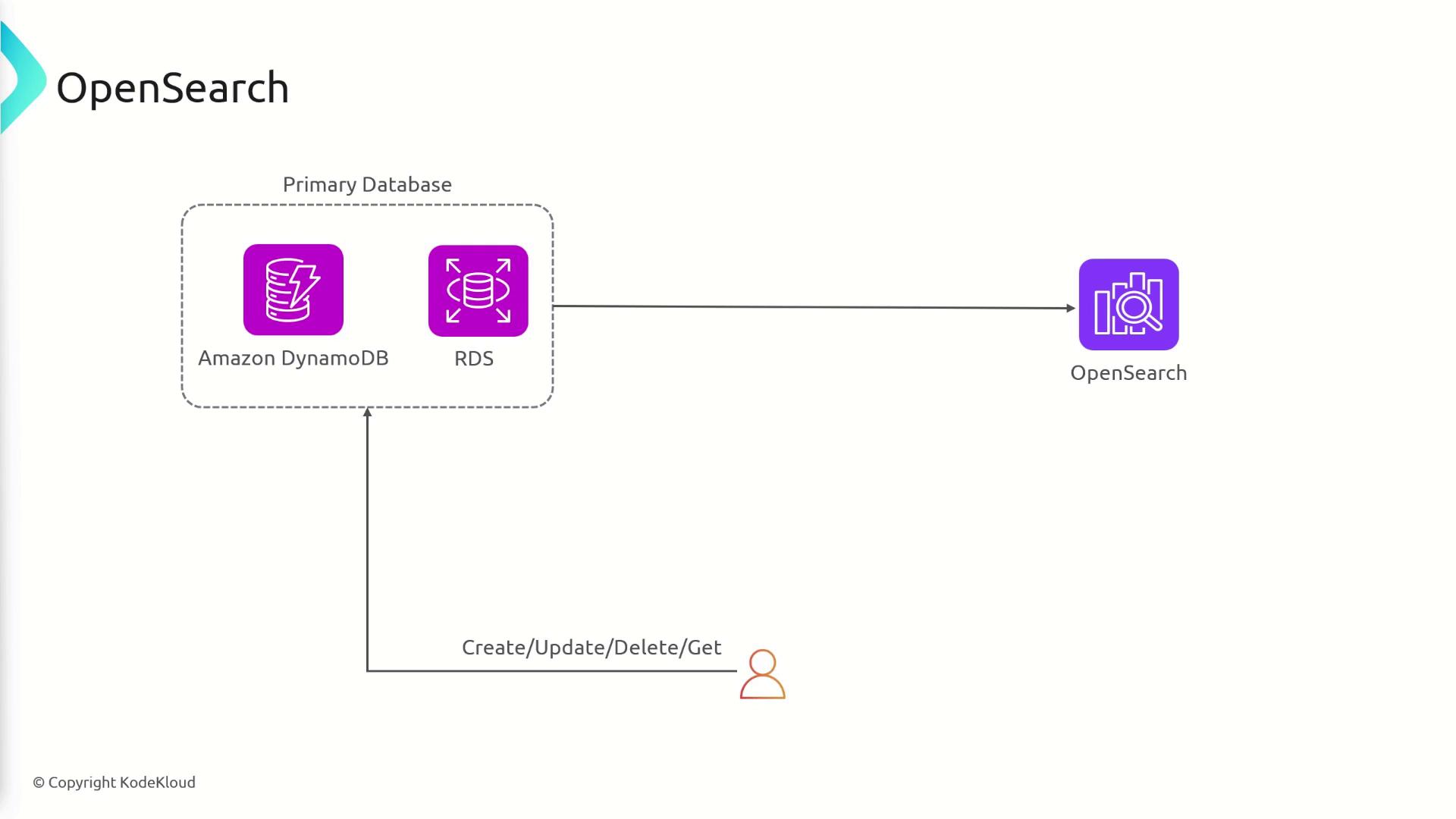
Ensure continuous synchronization between your primary database and OpenSearch to maintain data consistency across your applications.
Summary
OpenSearch, a fork of Elasticsearch managed by AWS, offers a fully managed service that streamlines the deployment, operation, and scaling of search clusters. Its unique ability to conduct efficient queries on any field makes it an excellent choice for log analytics and dynamic search functionalities.