Why We Need Encryption
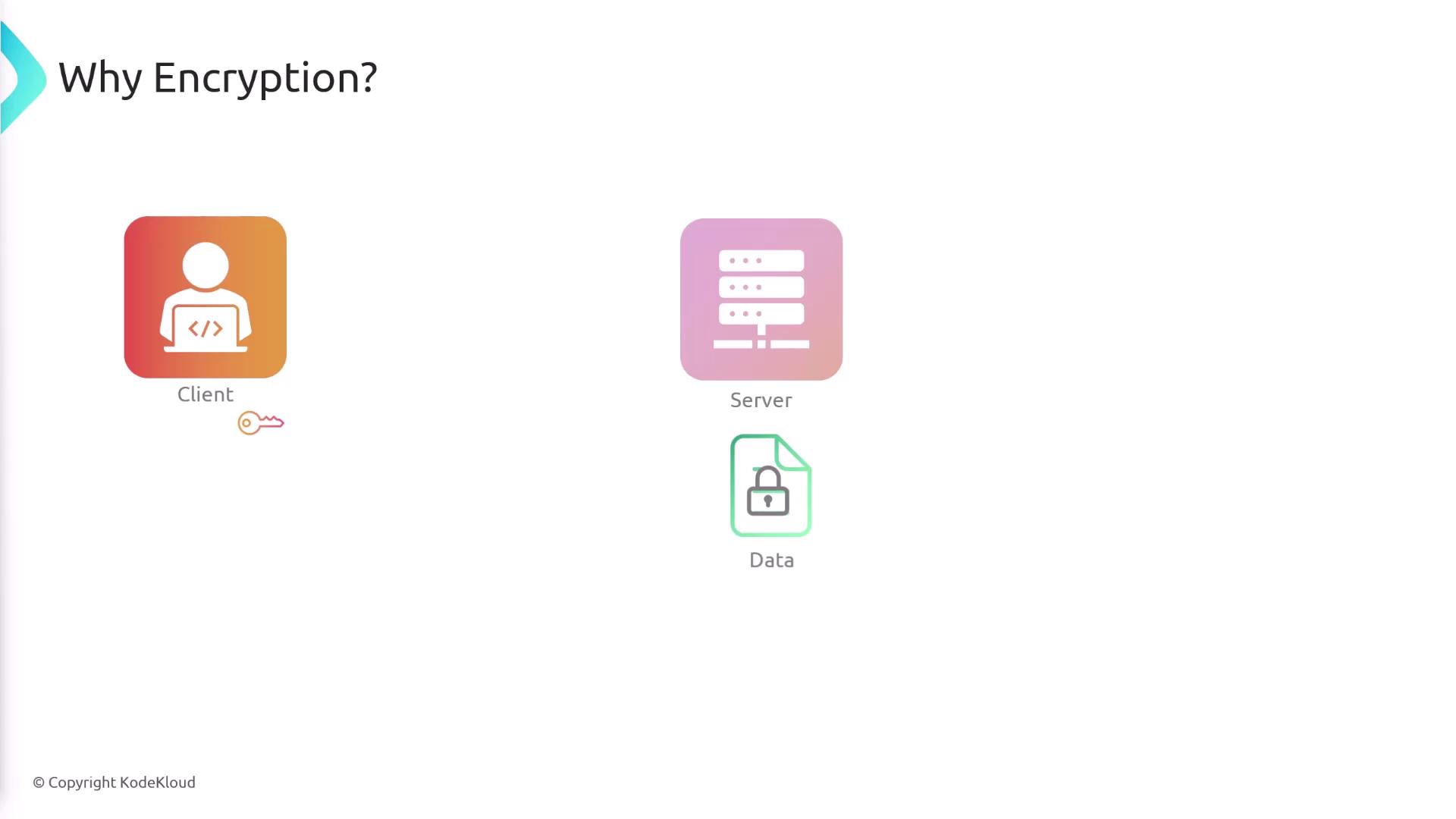
When files are uploaded to a server, they are often stored as plain text. This means that if an unauthorized party gains access, they could easily read sensitive information. Encryption addresses this vulnerability by converting data into an unreadable format—unless decrypted with the correct key. For example, encrypting your file with a cryptographic key prior to upload ensures that even if someone accesses the data, it remains secure without the corresponding key.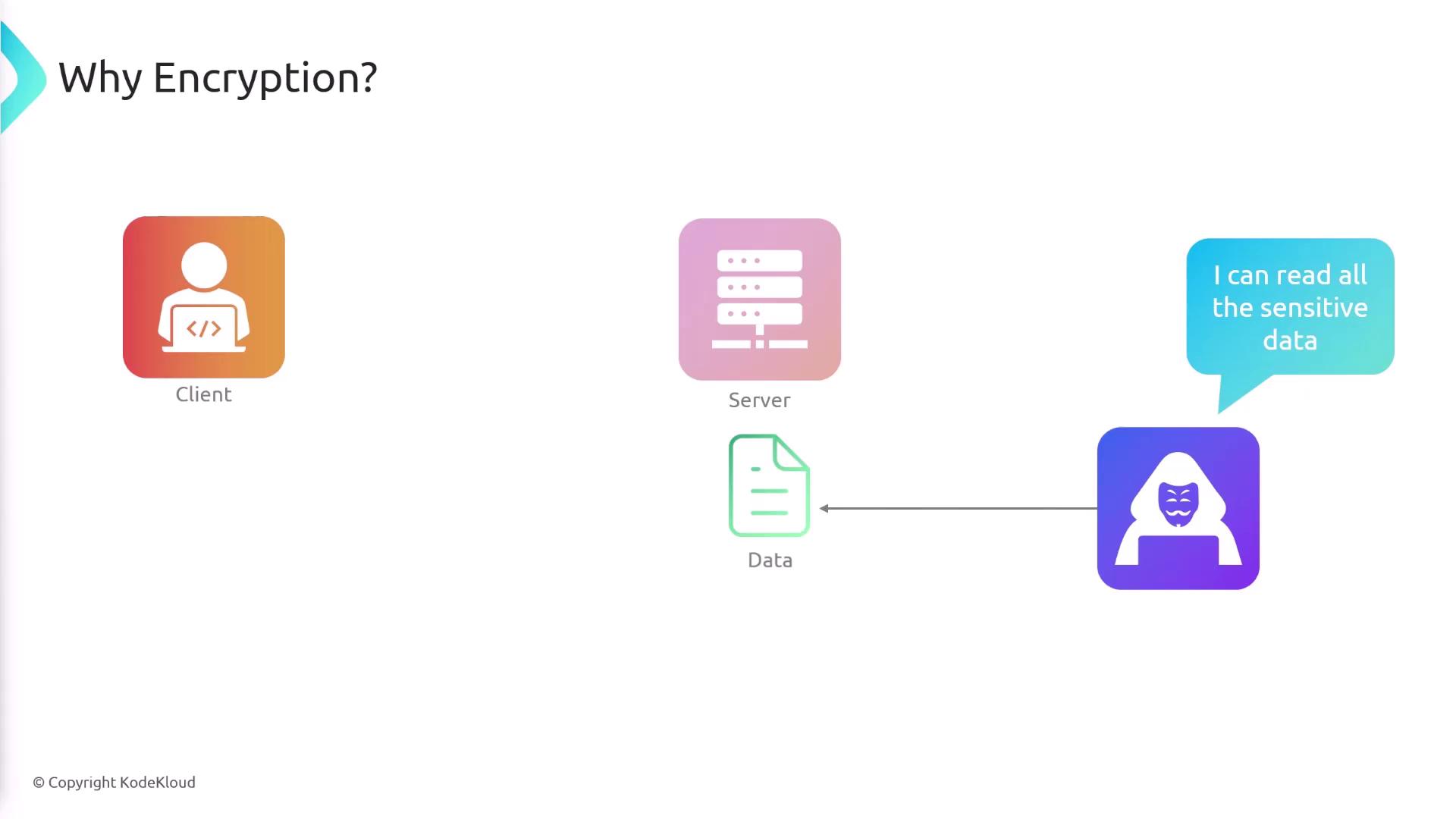
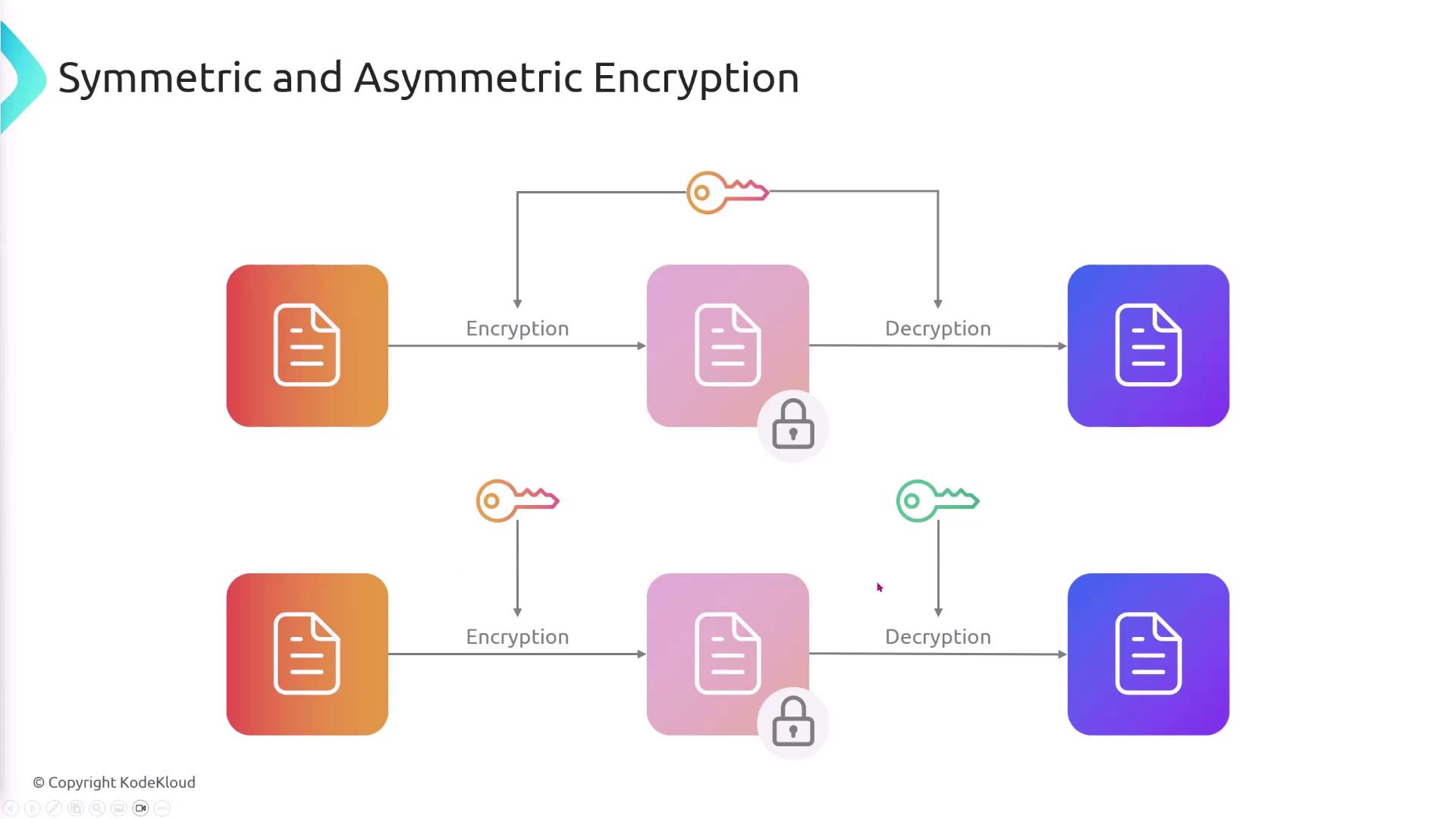
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Encryption
Encryption techniques are broadly classified into two categories:-
Symmetric Encryption:
The same key is used for both encryption and decryption. This method places significant emphasis on key management since any entity with the key can decrypt the data. -
Asymmetric Encryption:
Involves a pair of keys—a public key and a private key. Typically, data encrypted with one key can only be decrypted with the other.
Overview of AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
AWS KMS is designed to securely create, manage, and store cryptographic keys. By leveraging KMS, you offload the heavy lifting of key management to AWS, allowing for secure encryption and decryption operations via its API. AWS services such as Amazon S3, EBS, and RDS integrate with KMS to provide built-in encryption support.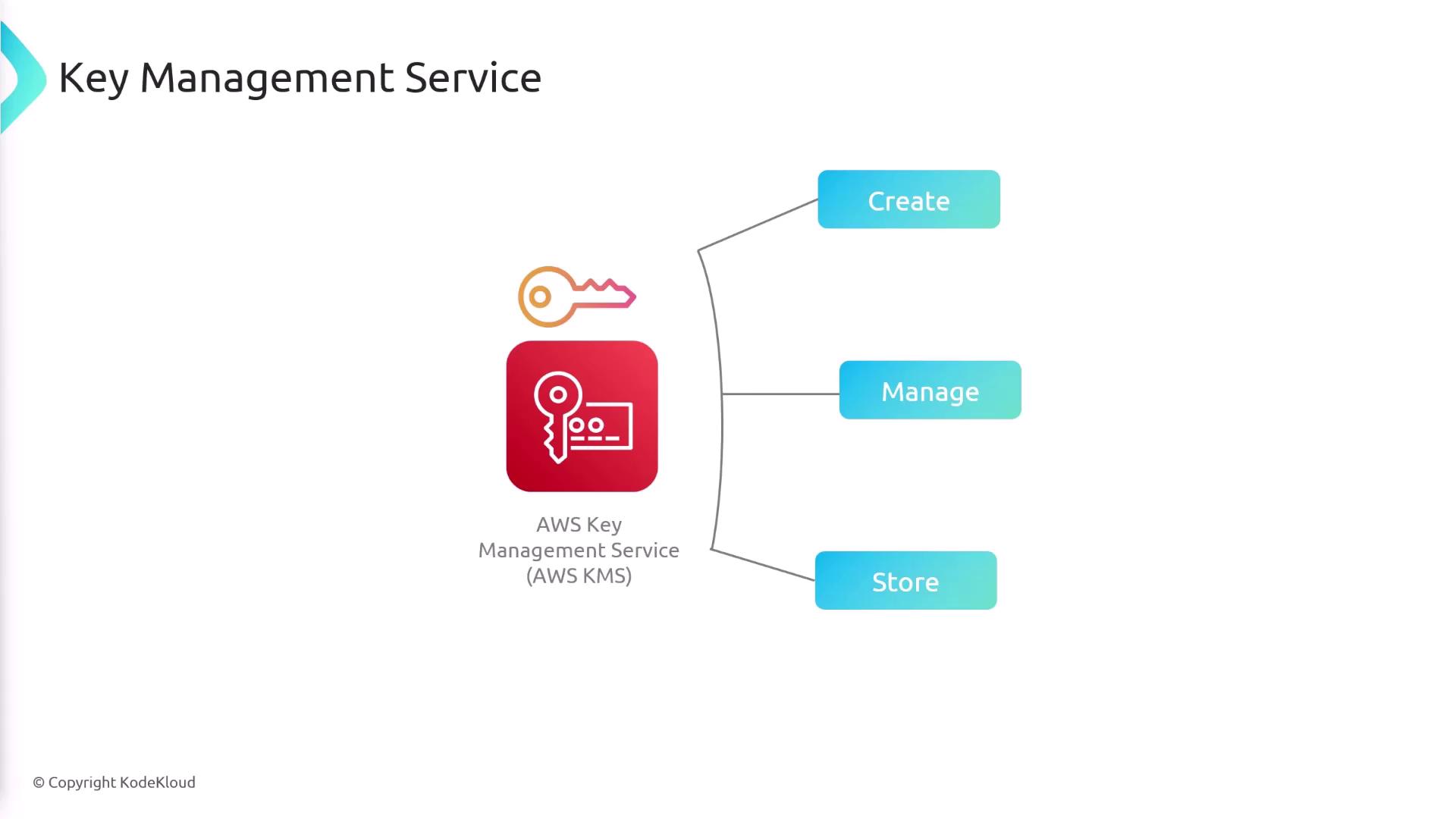
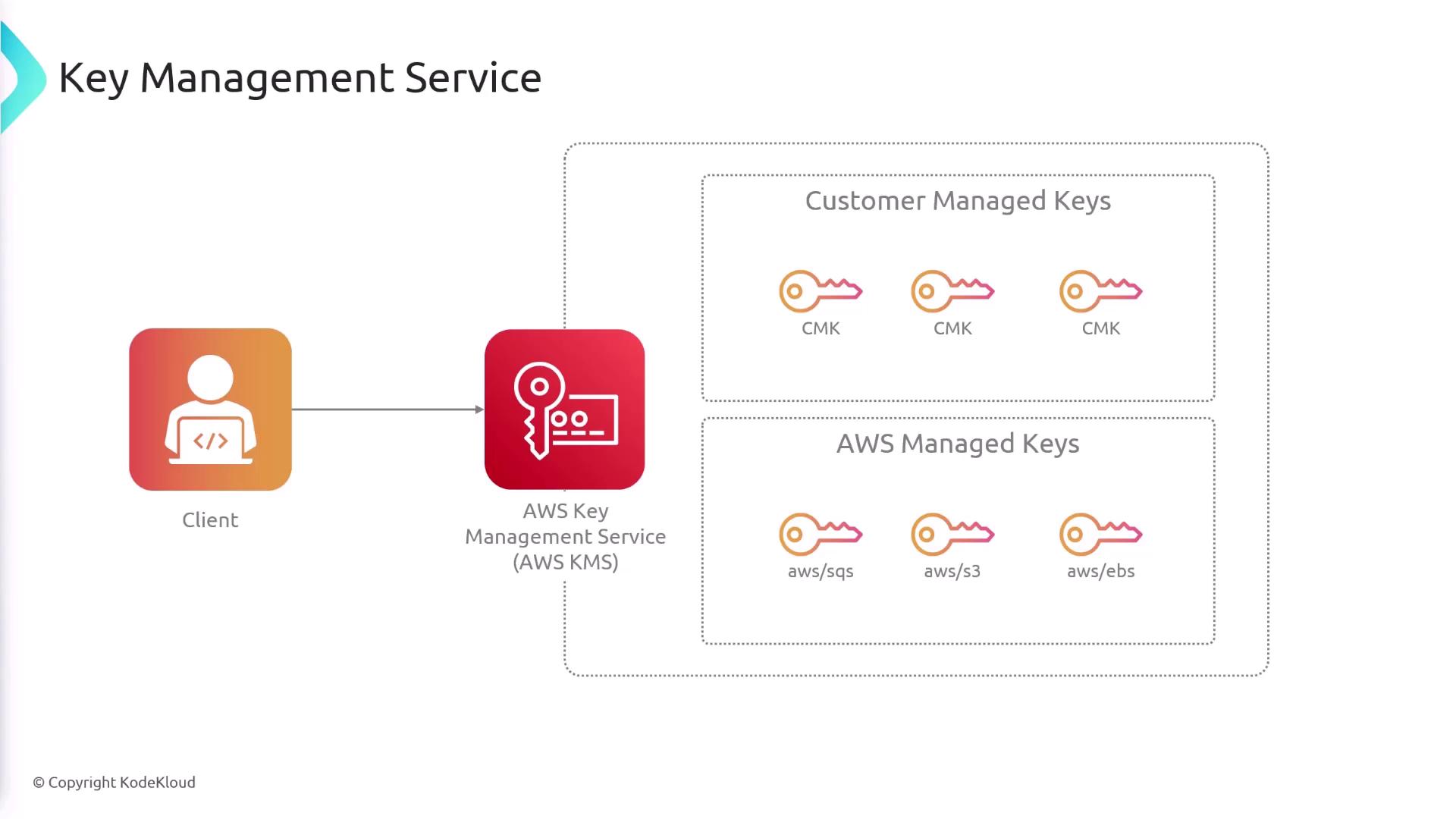
Types of Keys in KMS
KMS offers two primary categories of keys:-
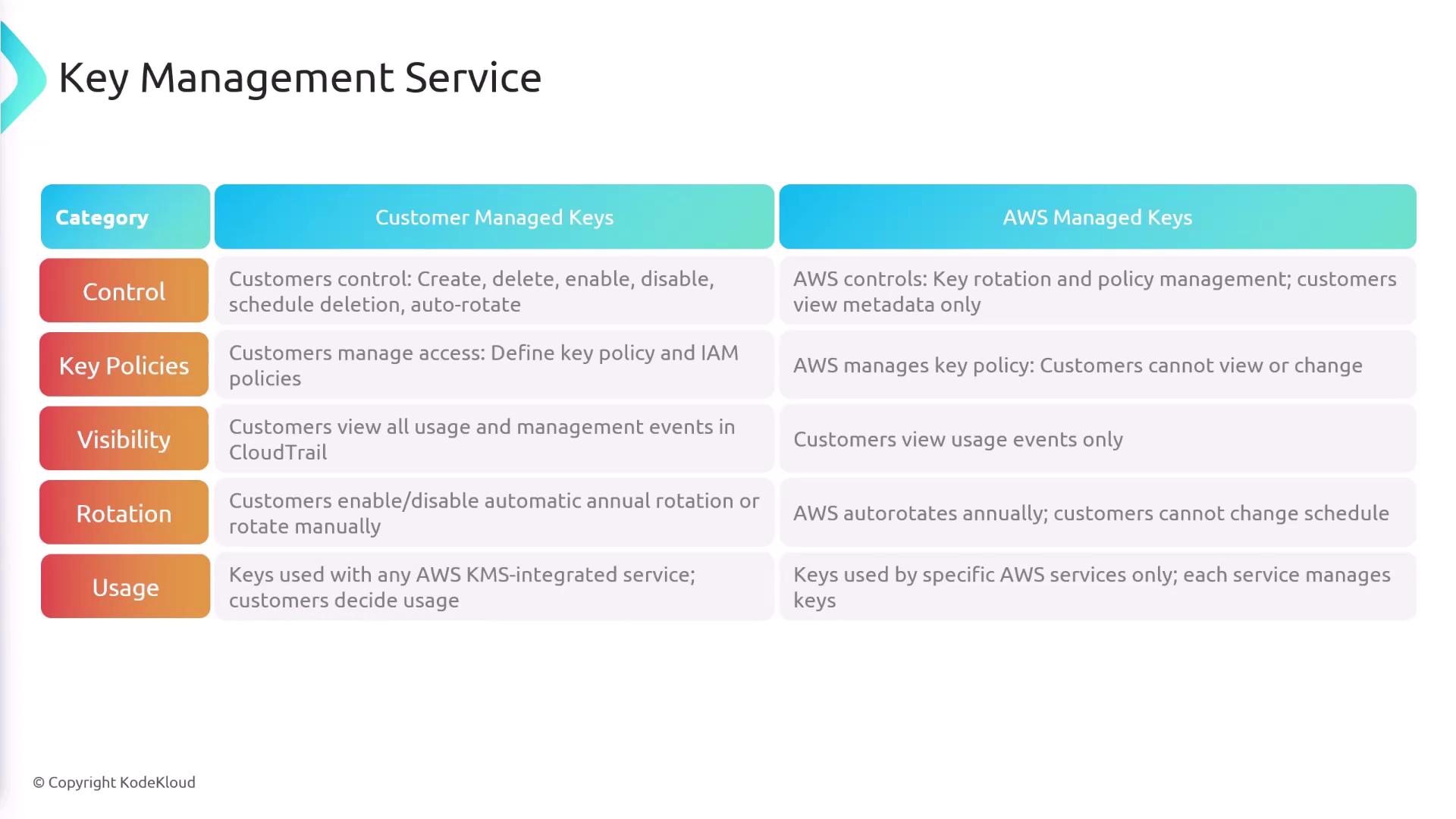
Customer Managed Keys:
These keys provide you with full control. You can manage their lifecycle (creation, deletion, enabling, disabling, and rotation), define detailed access policies, and track events via CloudTrail. -
AWS Managed Keys:
AWS automatically creates and manages these keys for services like S3 or EBS. While you can view metadata and usage events, you cannot modify the associated policies.
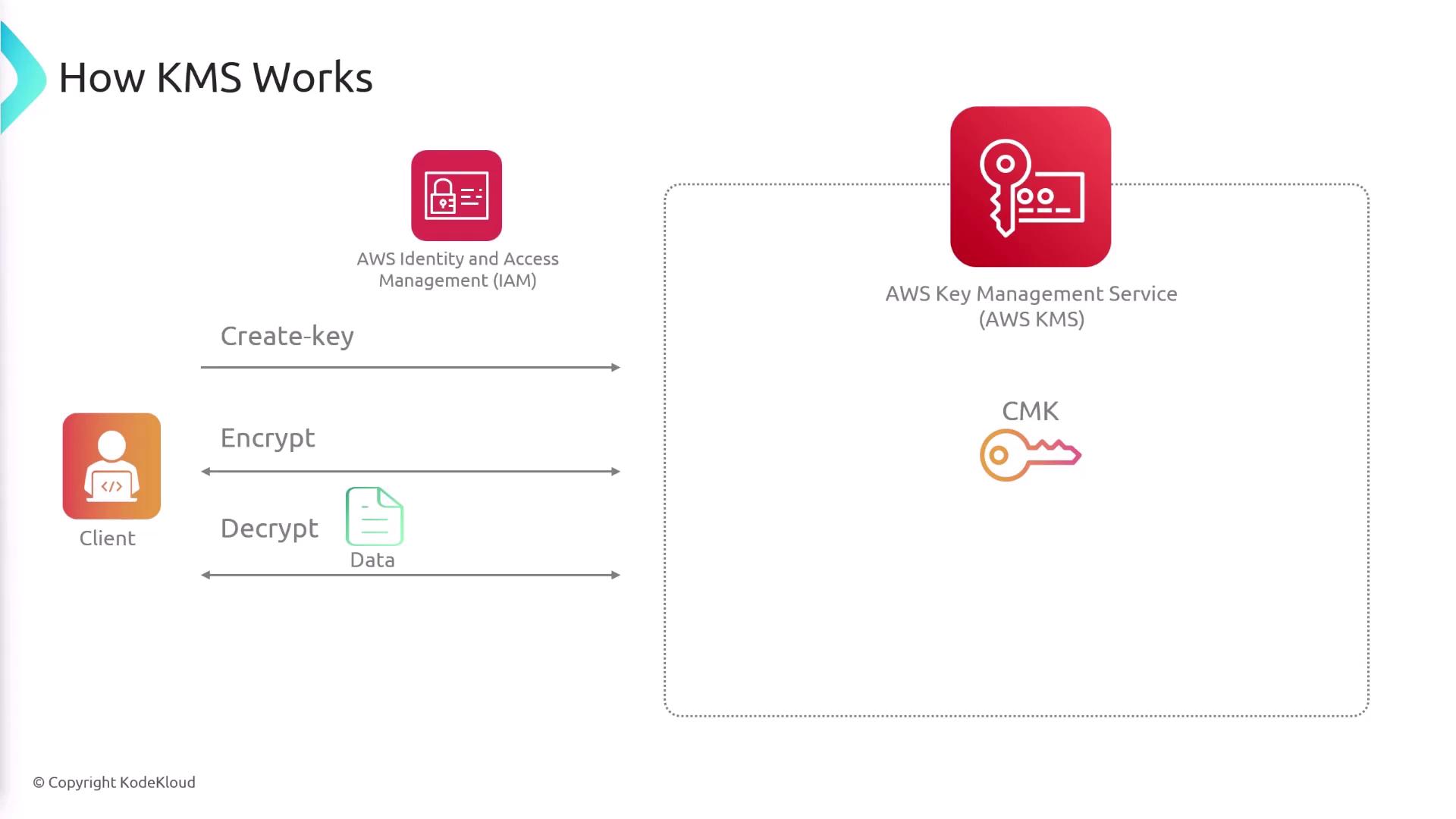
How AWS KMS Works
AWS KMS follows a streamlined workflow to enhance security:-
Key Creation:
Use the CreateKey API to generate a customer managed key, which is securely stored in KMS and never directly exposed. -
Encryption:
Invoke the Encrypt API to send your data to KMS. The service encrypts your data using the customer managed key and returns the ciphertext. -
Decryption:
To access encrypted data, the Decrypt API is used with the ciphertext to retrieve the original plaintext.
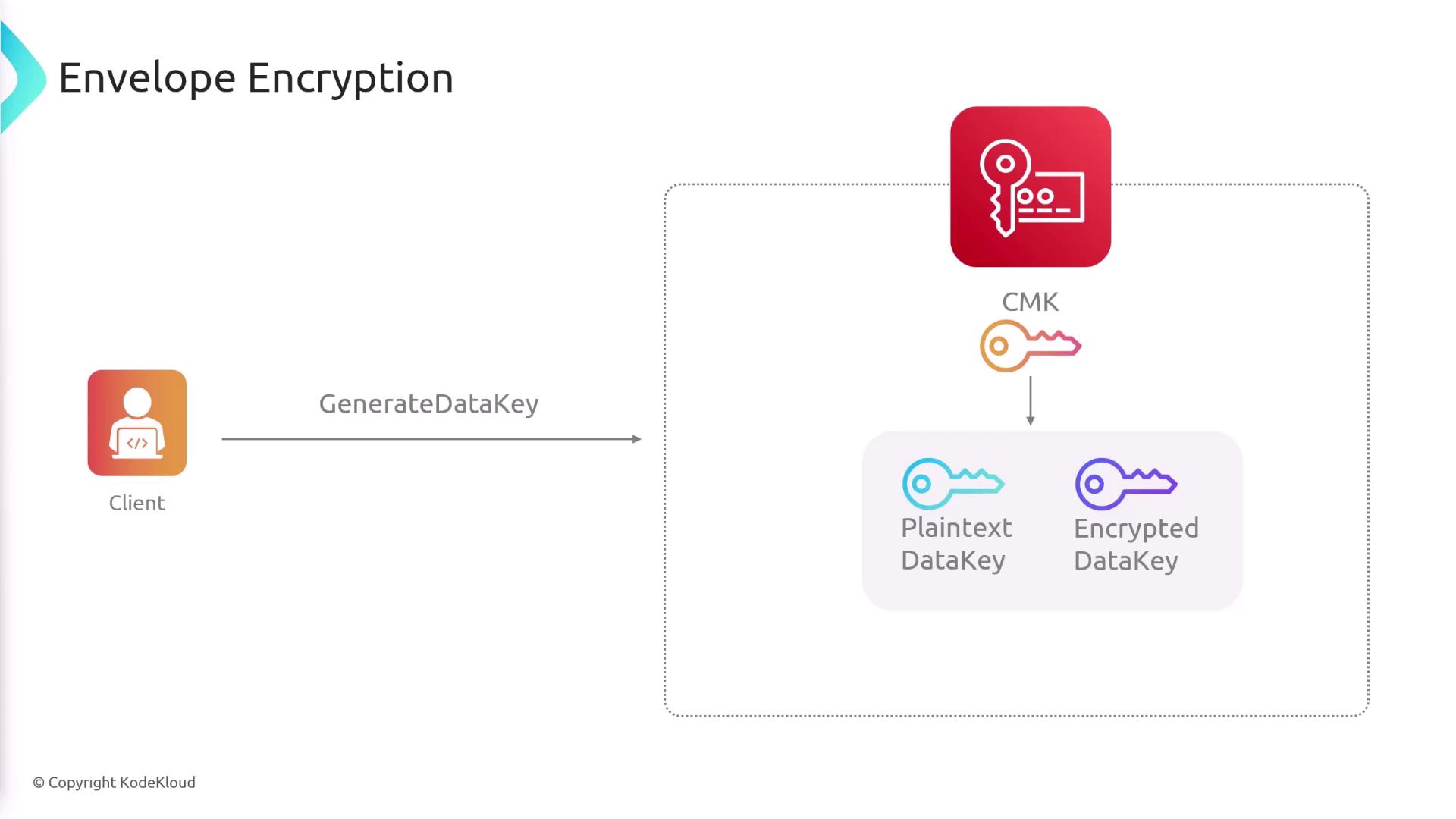
File Size Limitations and Envelope Encryption
AWS KMS has a limitation where the Encrypt API can only handle files up to 4 kilobytes. For larger files, envelope encryption is the recommended approach. The process involves the following steps:- Call the GenerateDataKey API with your customer managed key. KMS returns both a plaintext and an encrypted version of the data key.
- Use the plaintext data key to encrypt your larger file.
- Store the encrypted data key along with the encrypted file.
- For decryption, use the Decrypt API by sending the encrypted data key to obtain the plaintext key, and then decrypt your file.
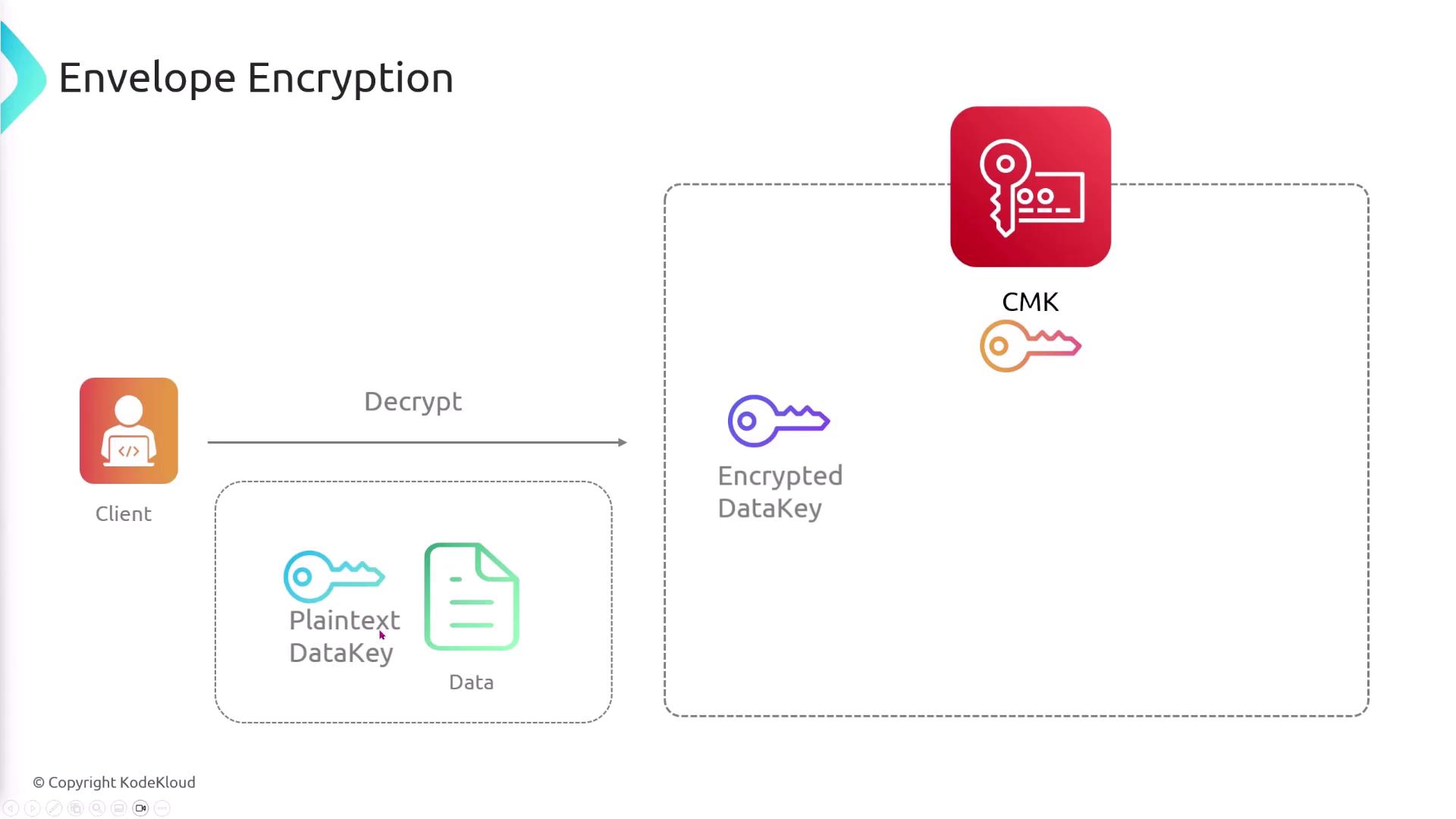
For a simplified implementation of envelope encryption, consider using the AWS Encryption SDK. It automates key generation, encryption, and decryption in a single command.
KMS Resource and Request Quotas
AWS KMS enforces both resource and request quotas to ensure optimal performance and security.Resource Quotas
By default, you can have up to 100,000 customer managed KMS keys and 50 aliases per key, among other quotas. If you exceed these quotas, AWS returns a “LimitExceededException” error. These limits may be adjusted by AWS based on your needs.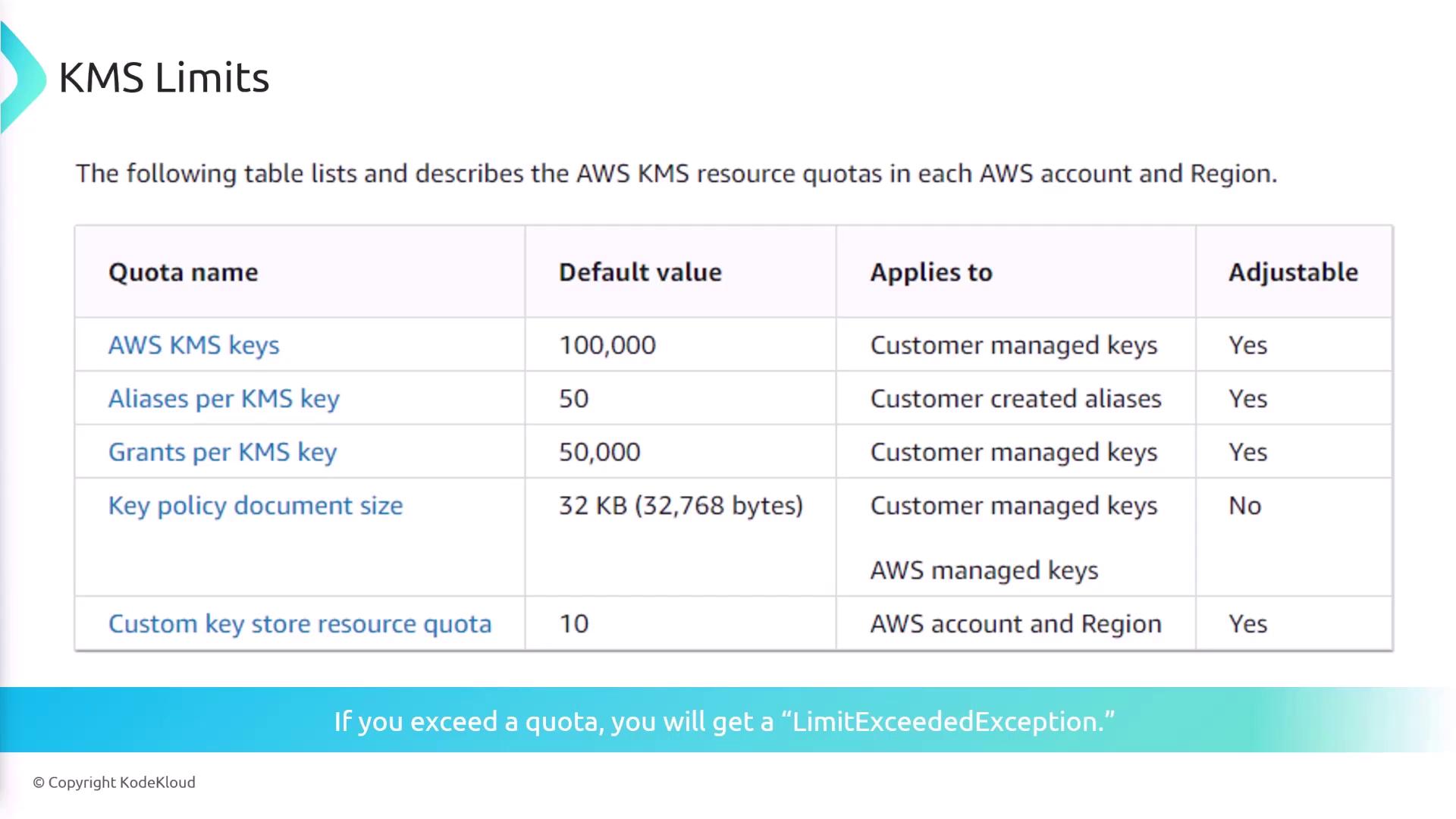
Request Quotas
Request quotas regulate the number of API operations you can perform per second. Exceeding these limits leads to throttling, and KMS returns relevant error messages. For example, exceeding the allowed rate may produce an error similar to the one shown below: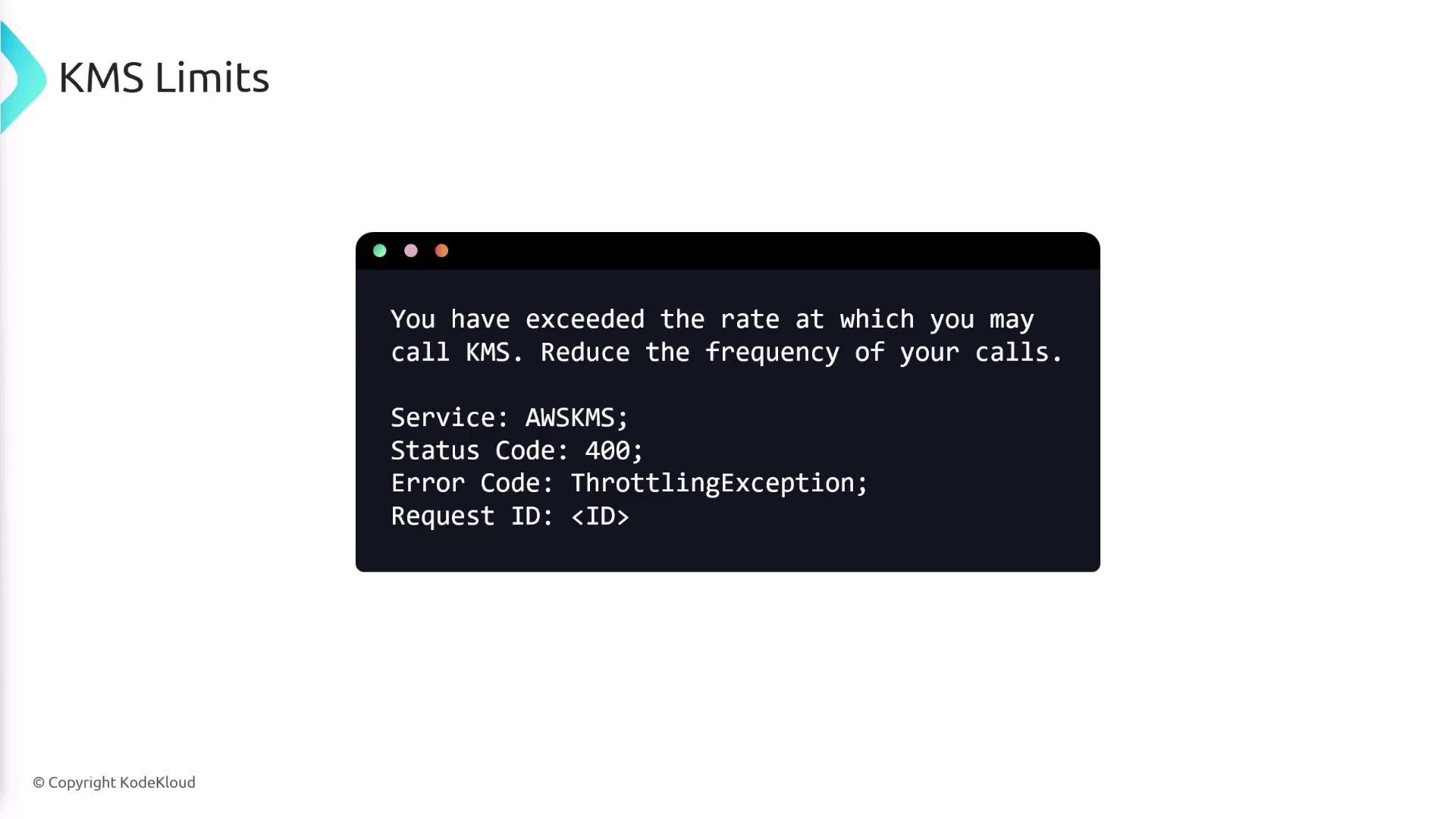
Mitigating Throttling
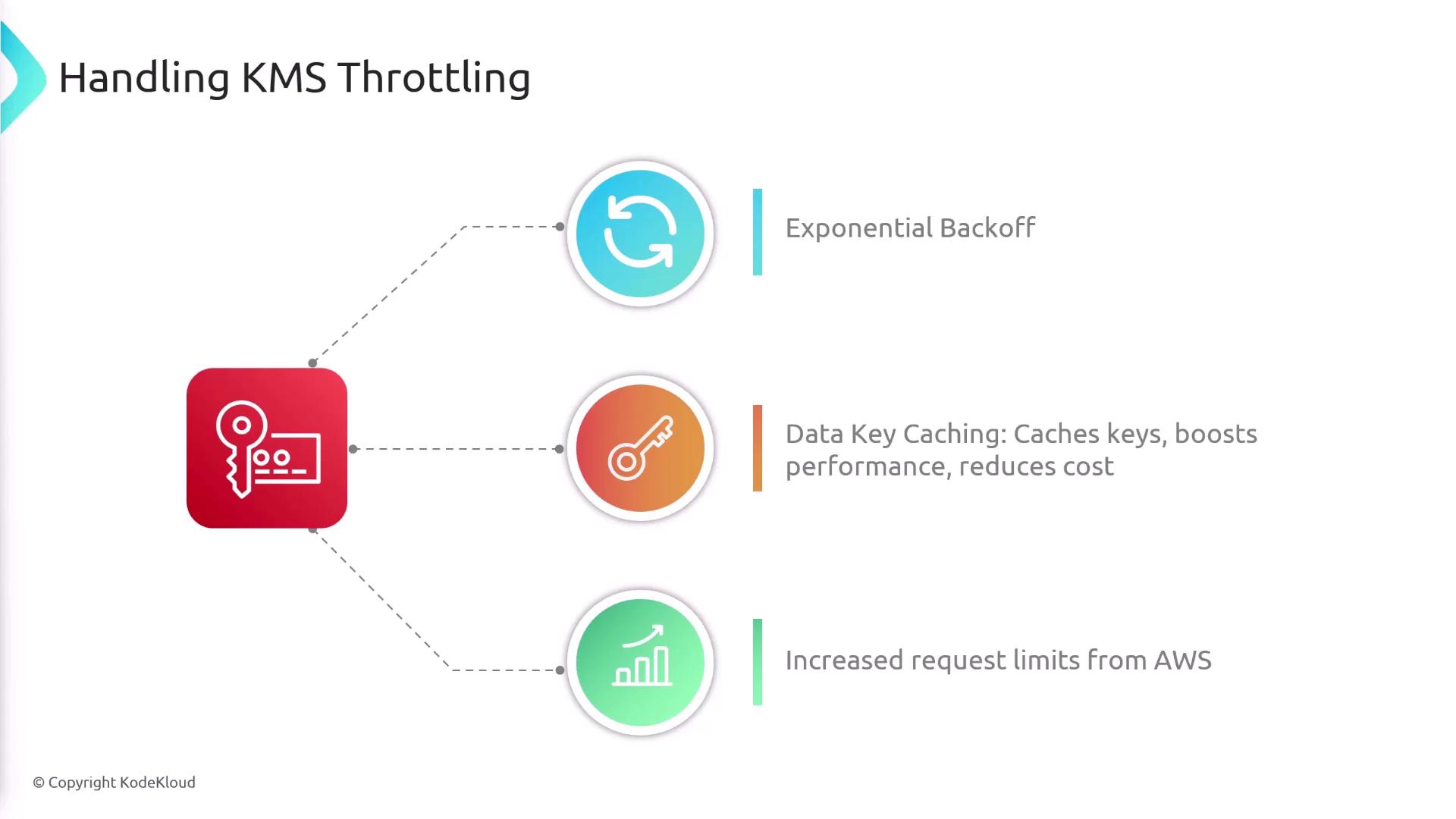
Managing throttling can be achieved through several strategies:- Exponential Backoff: Retry failed requests with progressive delays.
- Data Key Caching: Cache decrypted data keys to reduce repeated API calls.
- Request a Limit Increase: Contact AWS support to increase your request quotas.
KMS Key Policies
Key policies in AWS KMS dictate who can perform various operations. Typically, administrators are granted permissions to create, disable, or delete keys, while regular users might only be allowed to encrypt or decrypt data. Below is an example of a key policy designed for administrators:Summary
AWS KMS simplifies the management of cryptographic keys and provides robust solutions for data encryption and decryption. Key takeaways include:- AWS KMS integrates seamlessly with many AWS services to offer out-of-the-box encryption.
- For data up to 4 KB, KMS supports direct encryption, while the GenerateDataKey API facilitates envelope encryption for larger files.
- Two key types are available: AWS managed keys, which are fully managed by AWS, and customer managed keys, which offer full control over key lifecycle and policies.
- Both resource quotas and API rate limits are enforced in KMS. Exceeding these may result in throttling or limit errors.
- Implementing robust key policies ensures that only authorized users perform sensitive cryptographic operations.

