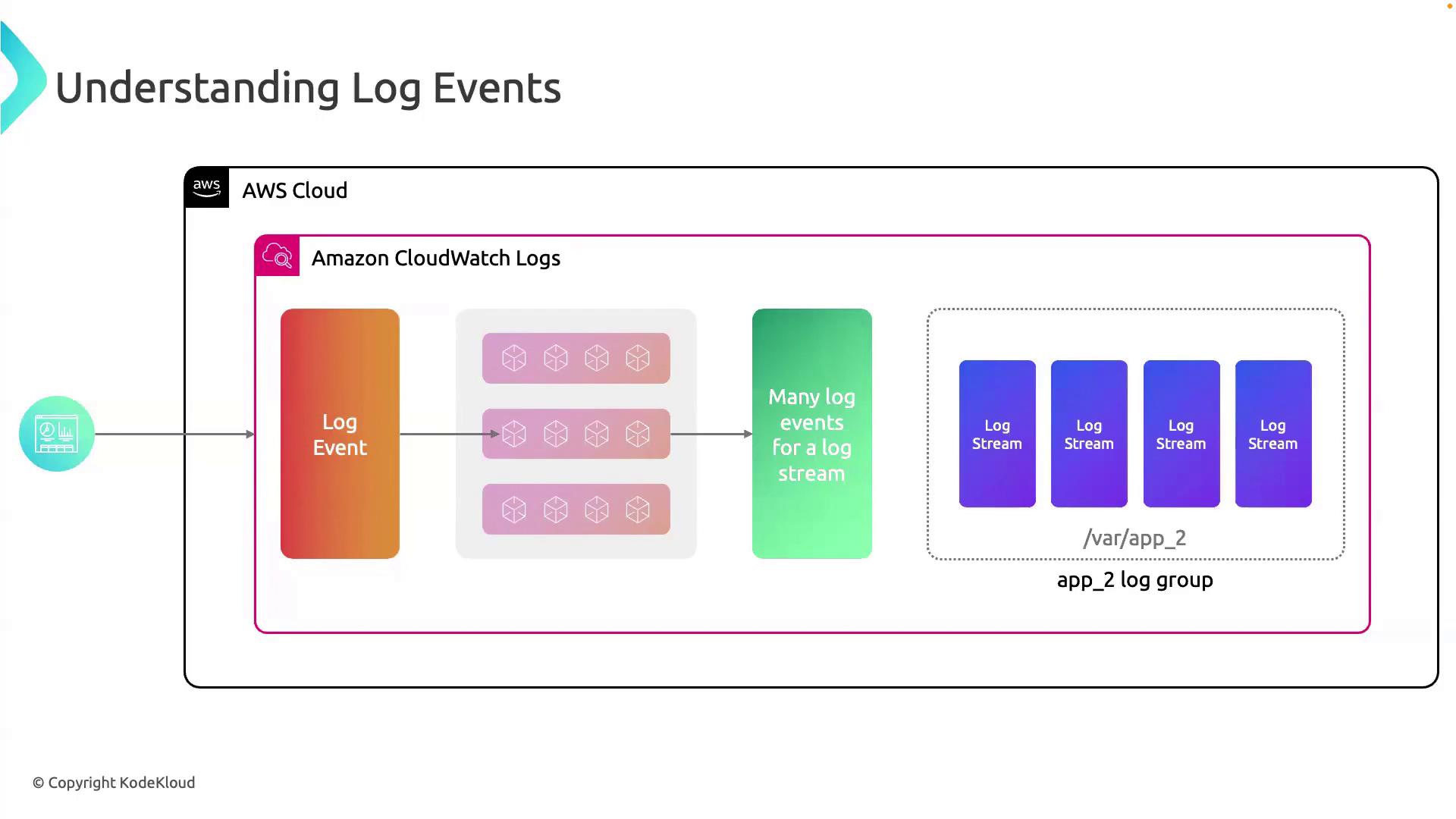
Anatomy of a Log Event
Each log event in CloudWatch Logs is usually a JSON object with the following core attributes:eventType is UserLogin, indicating a successful login. Other common event types might include PasswordReset, LoginFailure, or AccountLockout.
Structured vs. Unstructured Log Events
CloudWatch Logs supports both structured and unstructured log data:| Log Type | Format | Benefits | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured | JSON, key–value | Easy search & parse, consistent schema | API request logs, audit trails, metrics |
| Unstructured | Plain text | Flexible, minimal setup | Error stack traces, debug output |
Structured logs simplify querying with CloudWatch Logs Insights and help maintain consistent event schemas.
Immutability of Log Events
Once ingested, log events in CloudWatch Logs are immutable—you cannot alter or delete individual records. To remove data, you must delete the entire log stream or log group.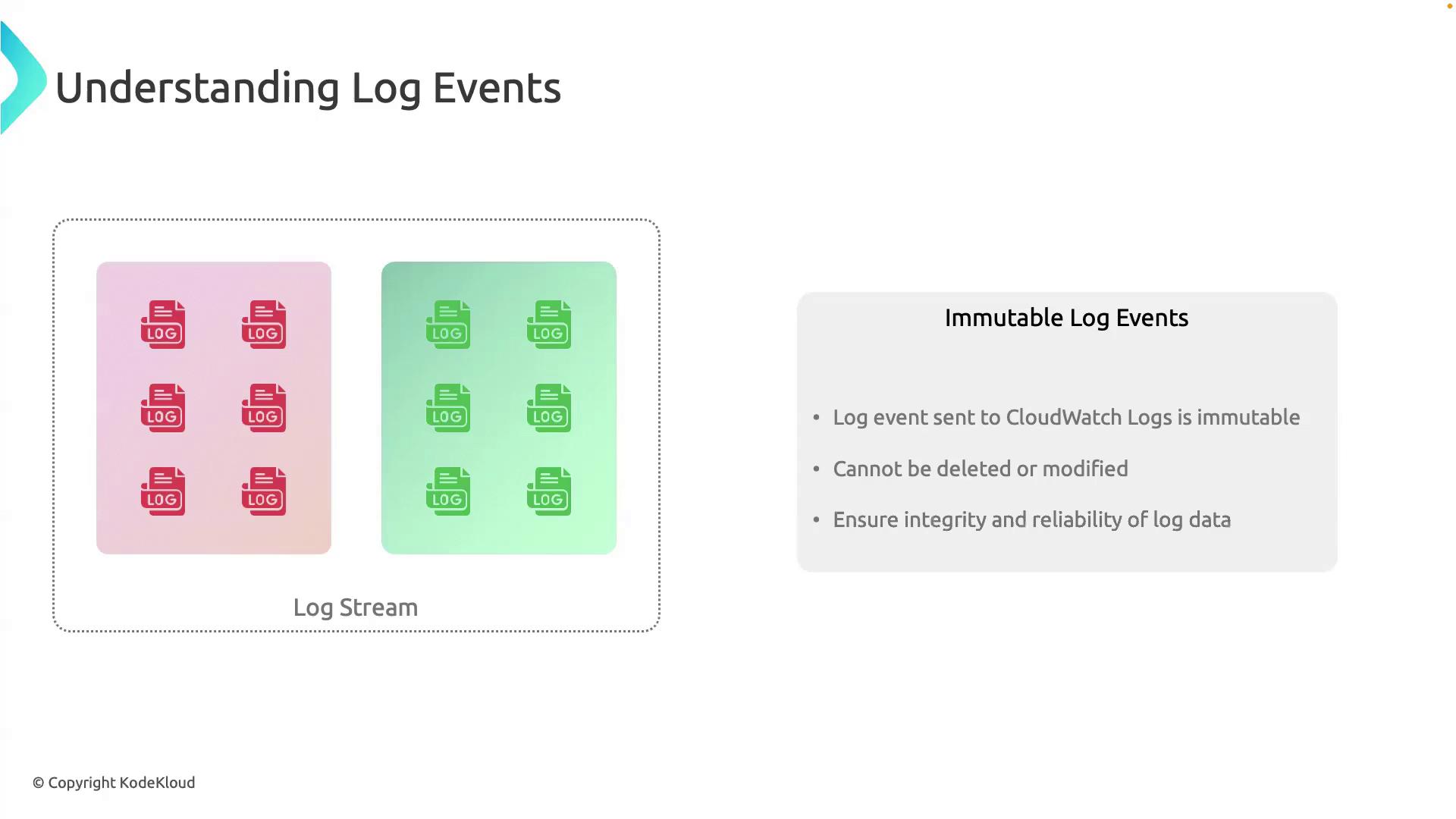
Immutable logs ensure data integrity and compliance. Plan your retention policies carefully: removing sensitive data requires deleting the whole stream or group.
Pre-Ingestion Filtering
To reduce costs and enhance signal-to-noise in your logs, apply pre-ingestion filtering. This lets you filter, transform, or drop unwanted log data on the client side before sending to CloudWatch Logs.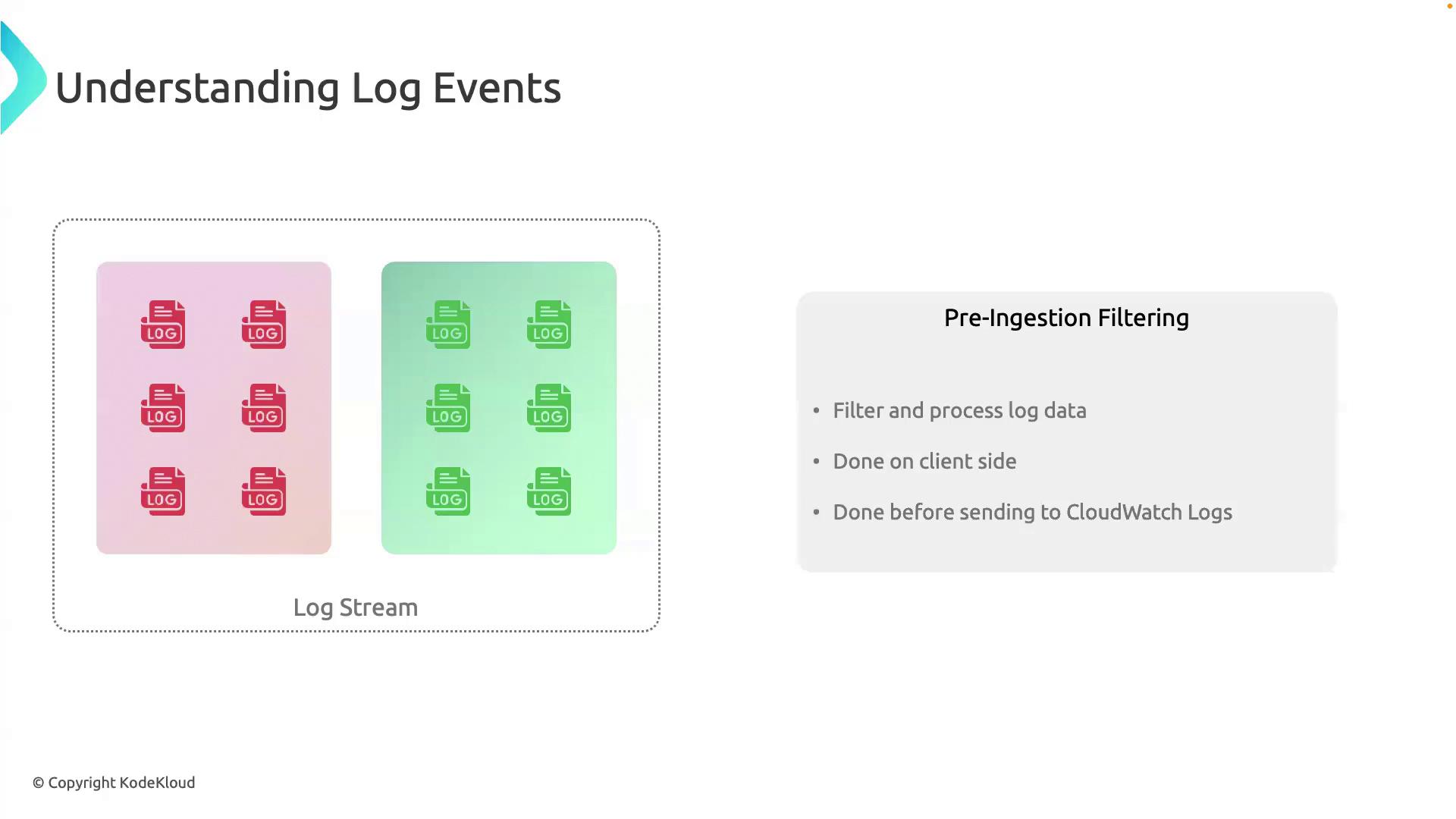
- Lower storage and ingestion costs
- Focus on critical events
- Improved performance when querying
Use the AWS SDK or CloudWatch Logs Agent to configure filters before data is sent.