AWS CloudWatch
Introduction to Observability in AWS
Monitoring strategy and Categories of insights
Building on proactive problem reduction, this guide shows how to design a monitoring strategy and leverage the FCAPS model to gain actionable insights in AWS CloudWatch and other IT environments.
Monitoring Strategies
Imagine your IT ecosystem as a dynamic organism—complex, interconnected, and requiring constant vigilance.
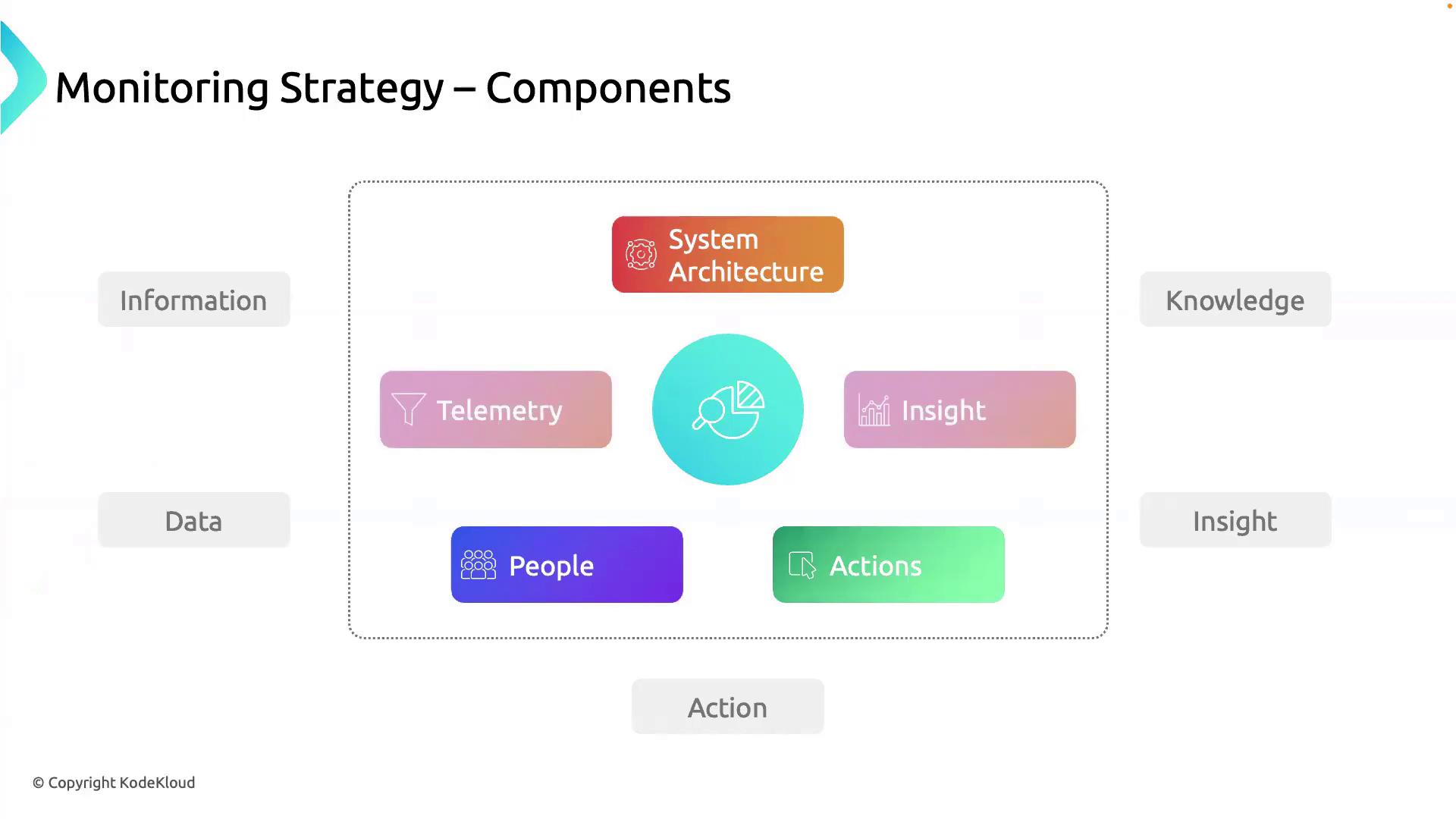
A comprehensive monitoring strategy converts raw data into operations-ready guidance:
- Telemetry: Your system’s sensory network—collects logs, metrics, traces, and events in real time.
- System Architecture: The topology map—defines data sources, dependencies, and expected behaviors.
- Insights: Actionable intelligence—derived by correlating telemetry with architectural baselines.
- People: DevOps engineers and operators—interpret insights to make informed decisions.
- Actions: Automated or manual responses—alerts, auto-scaling, remediation, and optimizations.
Together, these elements form a feedback loop that moves you from Information → Knowledge → Insight → Action.
Note
A successful strategy integrates with tools like AWS CloudWatch for unified observability across logs, metrics, and alarms.
Categories of Insights: The FCAPS Framework
The FCAPS model (Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, Security) organizes monitoring into five key areas. Each category provides a unique lens on system health, helping you stay ahead of issues and drive continuous improvement.
FCAPS Overview
FCAPS originated in network management standards and remains invaluable for holistic IT operations.
| Category | Purpose | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Fault Management | Detect, isolate, and remedy errors | Server crash alerts & root-cause logs |
| Configuration Management | Track and enforce system settings | AMI version control & change audits |
| Accounting Management | Monitor resource usage and cost allocation | EC2 instance billing & usage charts |
| Performance Management | Analyze and optimize system efficiency | CPU/memory forecasting & auto-scaling |
| Security Management | Protect data integrity, confidentiality, availability | IAM policy compliance & threat detection |
1. Fault Management
Fault management acts like an on-demand diagnostic system:
- Continuously scans for errors—network outages, service failures, or unexpected restarts.
- Triggers alerts and runs automated remediation playbooks.
- Reduces mean time to repair (MTTR) by pinpointing root causes.
2. Configuration Management
Configuration management ensures settings and changes are versioned, documented, and enforceable.
Use IaC tools (Terraform, CloudFormation) and drift detection to maintain a single source of truth and meet compliance requirements.
3. Accounting Management
Accounting management functions like a utility meter—tracking compute, storage, and network consumption.
- Enables precise cost allocation and chargeback models.
- Drives budget forecasting and capacity planning.
- Integrates with billing dashboards in AWS Cost Explorer or third-party platforms.
4. Performance Management
Performance management focuses on resource utilization and end-user experience:
- Leverages historical metrics and trend analysis.
- Implements SLO/SLI tracking to uphold service levels.
- Automates scaling policies based on thresholds or predictive models.
Warning
Ignoring performance baselines can lead to cost overruns and degraded user experience. Always define realistic thresholds.
5. Security Management
Security management underpins trust and resilience:
- Monitors IAM policy changes, suspicious API calls, and vulnerability scans.
- Enforces encryption, MFA, and network segmentation.
- Integrates with SIEM tools for real-time threat detection.
By mapping your observability tools and processes to the FCAPS framework, you can move from reactive firefighting to proactive optimization. This structured approach aligns DevOps, SecOps, and FinOps teams, driving efficiency, security, and cost control across the IT lifecycle.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content