AWS EKS
EKS Fundamentals
Architecture
In this lesson/article, we’ll delve into the Amazon EKS control plane and examine every component AWS provisions and manages when you launch an EKS cluster.
Kubernetes Control Plane Components
When you create an Amazon EKS cluster, AWS automatically sets up the core Kubernetes control plane, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| etcd | Distributed key–value store. EKS runs a minimum of three etcd nodes (up to five for extra resilience) to maintain quorum and leader election. |
| API Servers | Multiple instances handle all Kubernetes API requests (e.g., kubectl commands for pods, deployments, services). |
| Controller Managers | Execute control loops to reconcile the desired and current cluster state (for example, maintaining the right number of pod replicas). |
| Schedulers | Assign pods to nodes based on resource requirements, node labels, taints, and affinity rules. |
Note
Amazon EKS automatically manages patching, scaling, and failover for these control plane components so you can focus on deploying applications.
Regional and Availability Zone Distribution
Amazon EKS is a regional service. Each cluster’s control plane is distributed across at least three Availability Zones (AZs) to guarantee high availability:
- Automatic Failover: If one AZ becomes unavailable, etcd maintains quorum (read-only until a new leader is elected), and API servers route traffic through healthy AZs.
- Cross-AZ Replication: AWS handles networking, latency optimization, and data replication between AZs without any additional configuration.
Warning
When deploying your own Kubernetes cluster, you’d need to configure multiple data centers, replicate etcd manually, and set up API servers, controllers, and schedulers across zones. EKS eliminates this operational overhead.
AWS-Specific Control Plane Integrations
Beyond the standard Kubernetes control plane, EKS includes built-in AWS integrations to streamline authentication, logging, and access control:
| Integration | Purpose | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| OIDC Endpoint | Issues tokens for IAM-to-Kubernetes identity mapping | Enabled by default when you create the cluster |
| CloudWatch Logs | Forwards API server, controller manager, and scheduler logs to Amazon CloudWatch | Configure via the EKS console or AWS CLI |
| EKS Authentication API | Defines which IAM principals can access your cluster (replaces aws-auth ConfigMap) | Managed through IAM roles and policies |
For more details, see the Amazon EKS User Guide.
EKS Data Plane Extensions
EKS extends the Kubernetes API with custom resources and services in your AWS account, handling your workloads and cluster add-ons:
| Extension | Description |
|---|---|
| Node Groups | Managed or self-managed EC2 instances (Linux/Windows) where your pods run. Supports Auto Scaling groups. |
| Add-ons | Core cluster services (CoreDNS, kube-proxy, VPC CNI) deployed as pods. Managed via the EKS Add-on API. |
These data plane components reside within your AWS account, giving you control over scaling, updates, and monitoring.
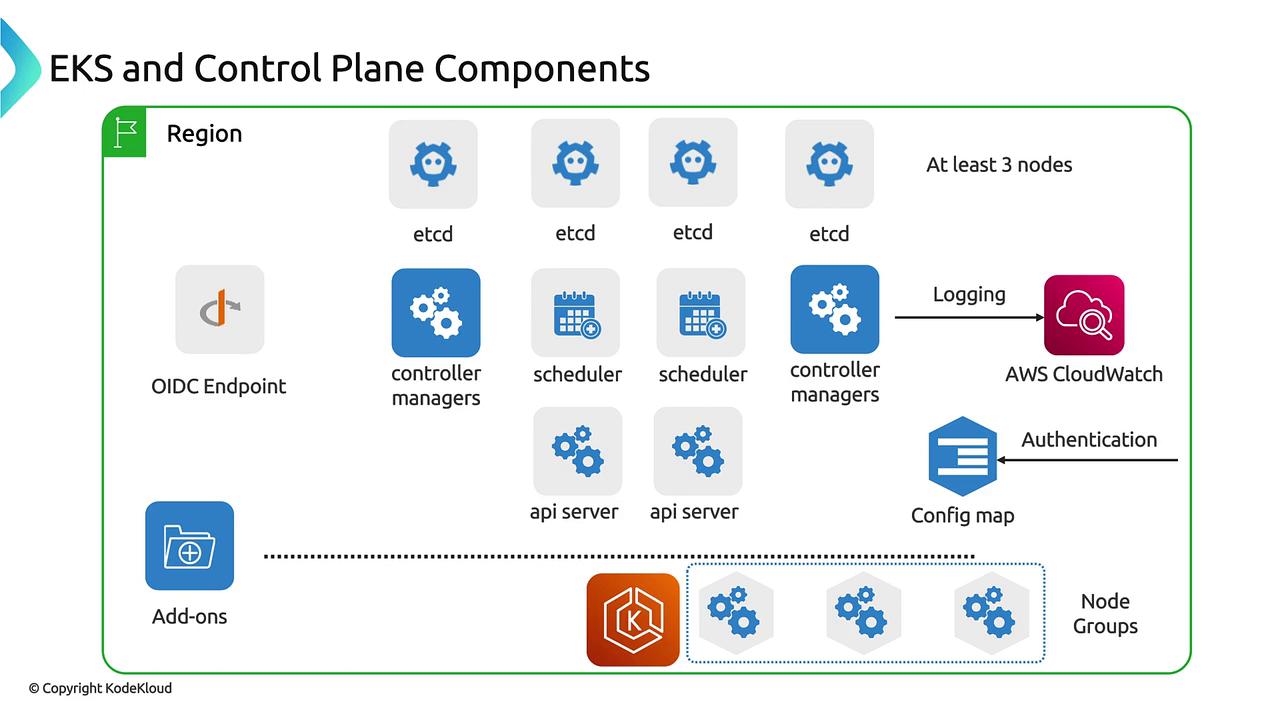
This diagram provides a holistic view of the Amazon EKS control plane services, AWS integrations, and data plane extensions that power a resilient Kubernetes cluster on AWS.
Watch Video
Watch video content