Kubernetes Cluster Architecture
A standard Kubernetes cluster consists of two main layers:-
Control Plane
- etcd (the key/value store)
- API Server
- Scheduler
- Controller Manager
-
Data Plane
- Worker nodes (EC2 instances or AWS Fargate)
- Pods and containers
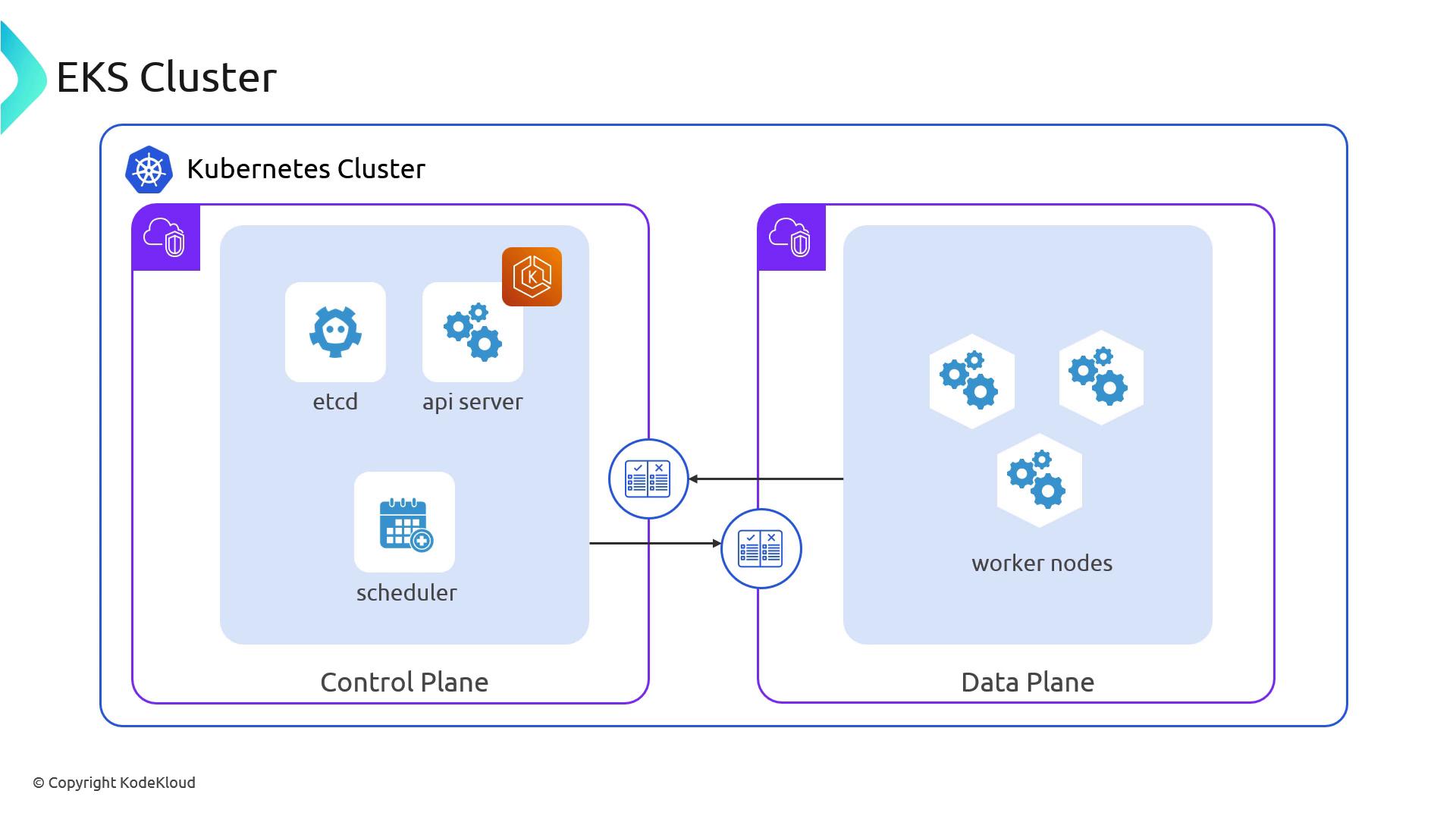
EKS Shared Responsibility Model
With Amazon EKS, AWS takes care of the highly available, secure control plane, while you manage your worker nodes and application workloads.| AWS Manages (Control Plane) | You Manage (Data Plane) |
|---|---|
| etcd, API Server, Scheduler | Worker Nodes (EC2 instances or Fargate) |
| Controller Manager | Operating System patches & node upgrades |
| Control Plane VPC networking & HA | Kubernetes workloads, Namespaces, RBAC, CRDs |
| Automatic backups, updates & scaling | Pod configuration, Security Groups, IAM roles |
AWS provisions a dedicated VPC for the control plane and connects it to your VPC using cross-account Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs).
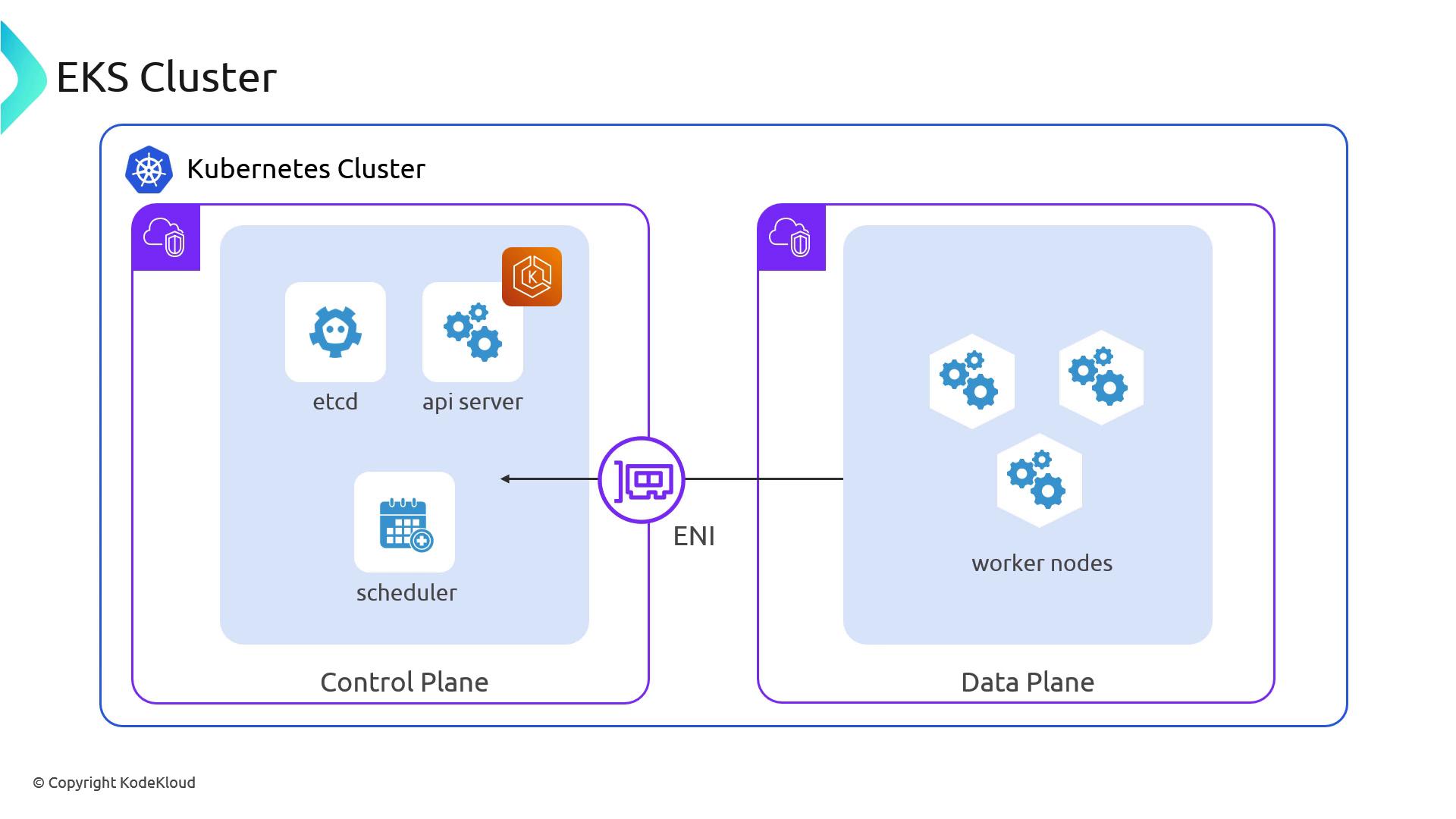
Control Plane ↔ Data Plane Communication
Under the hood, your worker nodes in one VPC communicate with the managed control plane in another VPC. AWS uses cross-account ENIs to bridge the two, similar to connecting two physical network switches with a cable:- Your Network: Worker nodes plugged into your VPC.
- AWS’s Network: Control plane components housed in AWS’s VPC.
Make sure your VPC subnets, route tables, and security groups allow traffic between your nodes and the control plane ENIs. Misconfigured rules can cause API connectivity failures.