1. Confirm Your EKS Cluster
Start by verifying which EKS cluster is active:2. Inspect VPCs and Subnets
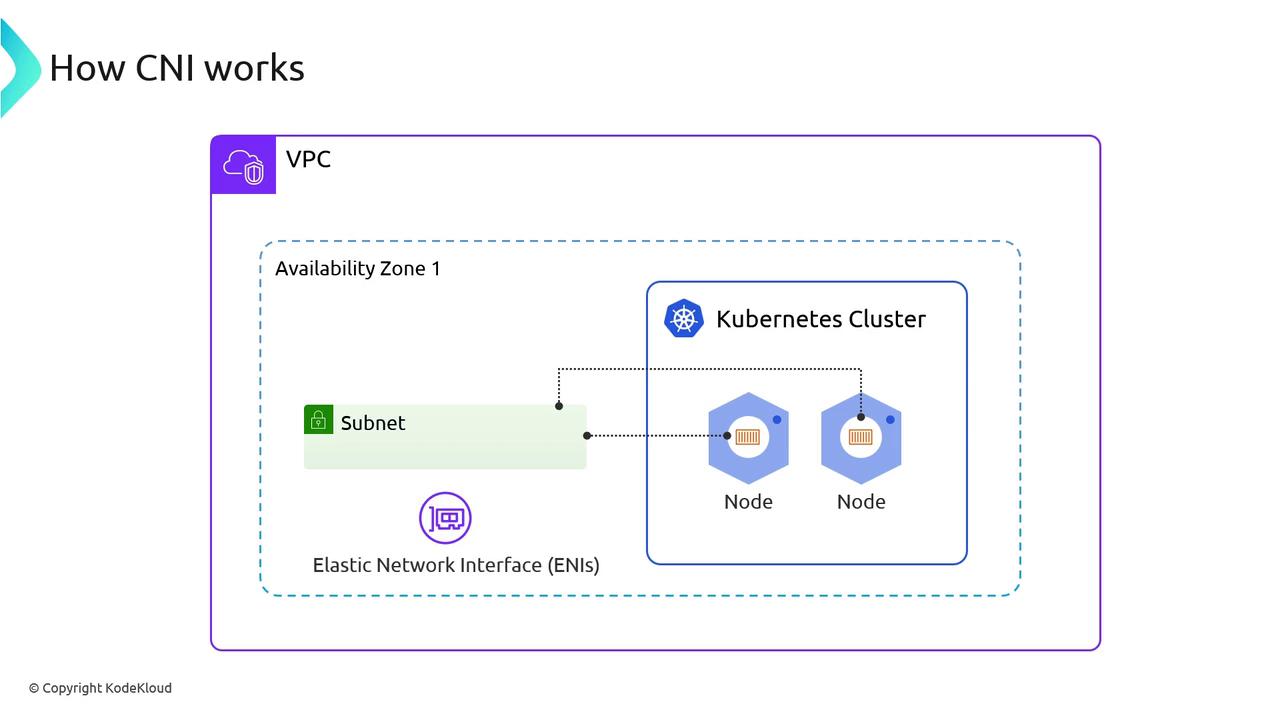
It’s recommended to dedicate one VPC per EKS cluster to simplify IP management:/16 VPC block yields ~65,000 IPv4 addresses—enough for control plane, nodes, pods, and endpoints.
Running multiple clusters in a single VPC can lead to IP exhaustion. Always project your pod and node scale before choosing CIDR sizes.
3. List ENIs in the VPC
AWS attaches ENIs for both control-plane interfaces and worker-node networking. Use this table to distinguish primary vs. secondary ENIs:| ENI Type | Description | Attached To | IPs per ENI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary ENI | eth0, node’s main interface | EC2 instances (nodes) | 1 |
| Secondary ENI | eth1, eth2… for pod traffic | EC2 instances (nodes) | Up to 12 |
| Control-Plane | Managed by AWS for the EKS API endpoints | eks_control_plane | 1 |
4. Kubernetes Data Plane: Nodes & Pods
Verify that your nodes are Ready and system pods are running:- aws-node DaemonSet (VPC CNI plugin)
- kube-proxy
- coredns for DNS resolution
5. Examine the aws-node DaemonSet
Describe the DaemonSet to view replicas and container images:- Desired / Current / Ready pod counts
- Init Container:
aws-vpc-cni-init - Main Container:
aws-node(configures ENIs, warm IP pools) - Sidecar:
aws-eks-nodeagent(eBPF network policies)
6. aws-node Pod Spec Breakdown
Below is a trimmed excerpt of the DaemonSet pod spec:Adjust environment variables like
WARM_ENI_TARGET and WARM_PREFIX_TARGET to control how many spare IPs the plugin keeps ready.7. View Init Container Logs
The init container seeds CNI binaries and tunes sysctls:8. Inspect Node Network Interfaces
SSH into any worker node to see eth0 (primary) and secondary ENIs:- eth0: Node’s primary IP
- eni…: Pod IPs handled by the CNI
9. Review Host CNI Configuration
The init container writes/etc/cni/net.d/10-aws.conflist on each node:
"type": "aws-cni"plugin"vethPrefix": "eni""mtu": "9001"- Egress CNI stub
10. List CNI Plugin Binaries
CNI executables live under/opt/cni/bin on each node:
- aws-cni
- egress-cni
- bridge, dhcp, host-local, bandwidth, firewall