AWS EKS
EKS Networking
Network Policies
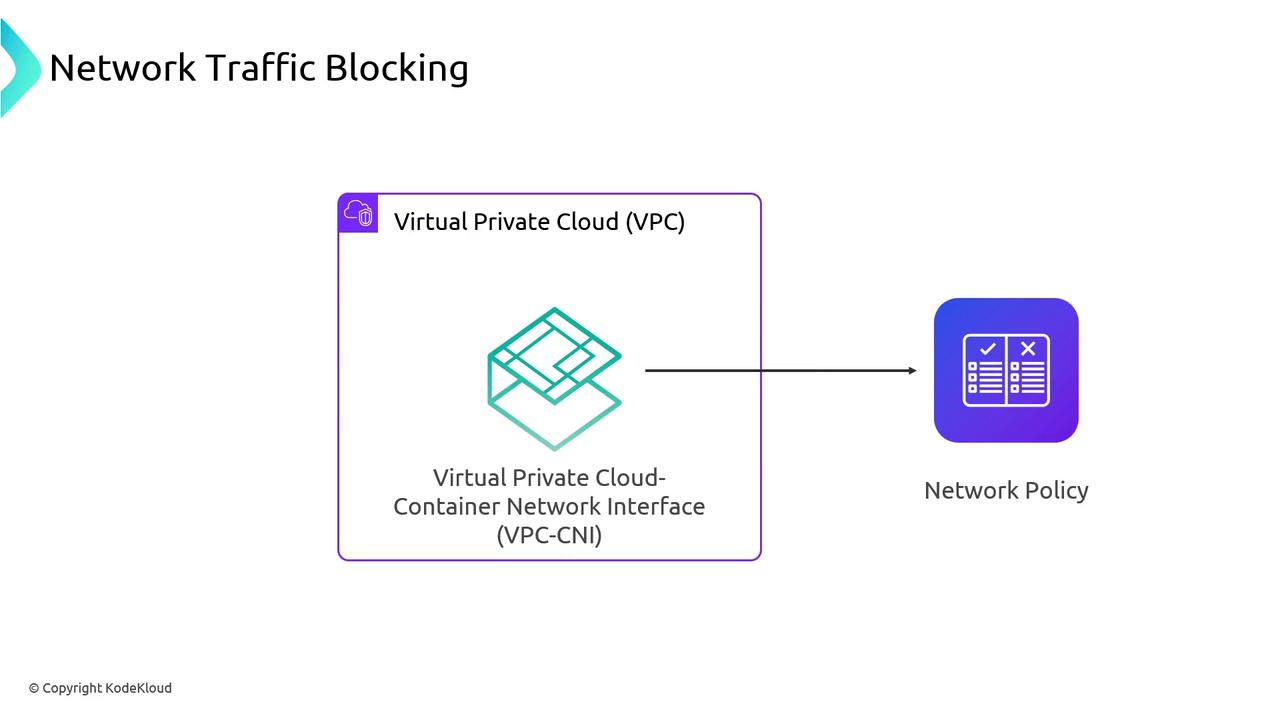
Kubernetes Network Policies enable fine-grained control over Pod-to-Pod traffic (ingress and egress). While some CNI plugins like Calico pioneered policy enforcement, AWS VPC CNI now supports native NetworkPolicies using eBPF in the node kernel—bringing security rules closer to your application manifests.
![]()
By embedding network rules alongside your Deployment YAML, you avoid external firewall tickets or manual IP table edits. As your application stack grows—databases, caches, external services—the same declarative NetworkPolicy objects evolve with it.
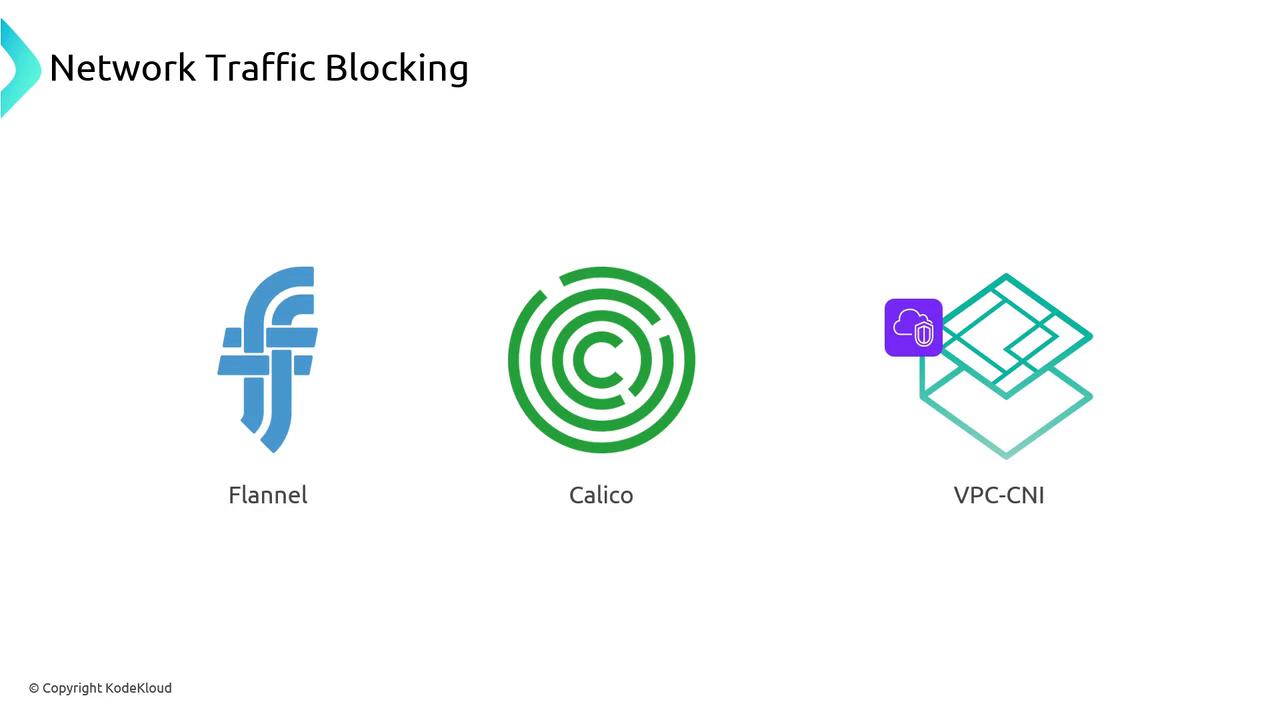
CNI Plugins & Policy Enforcement
| CNI Plugin | Native NetworkPolicy Support | Enforcement Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Calico | Yes | iptables / eBPF |
| AWS VPC CNI | Yes (with flag) | eBPF in Linux kernel |
| Flannel | Requires extension | iptables |
Note
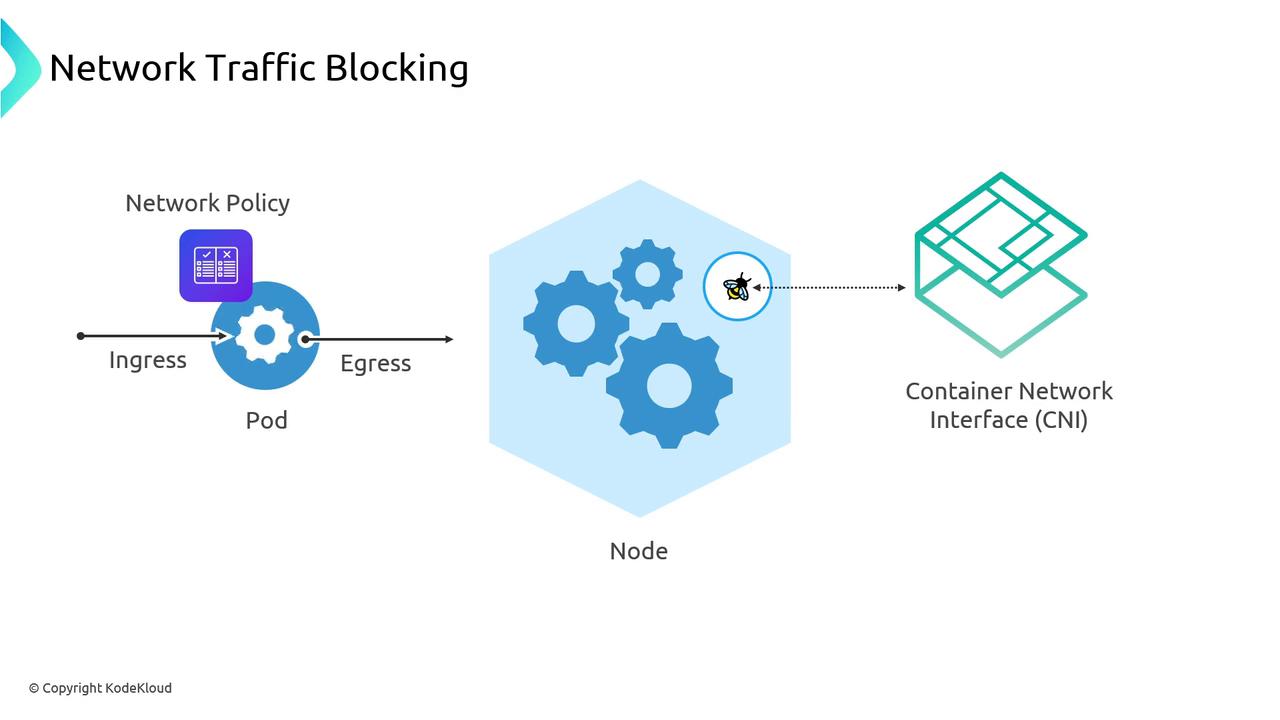
AWS VPC CNI’s eBPF agent installs tiny packet-filter programs on each node. It intercepts traffic before it reaches the container network namespace.
Traffic hits eBPF hooks that enforce ingress and egress rules defined by Kubernetes NetworkPolicy objects:
Demo: Enabling and Testing Network Policies
This walkthrough uses an EKS cluster with AWS VPC CNI and --enable-network-policy=true.
- Verify nodes and pods:
kubectl get nodes kubectl get pods --all-namespaces - Ensure no policies exist:
kubectl get networkpolicies --all-namespaces # No resources found - Inspect the
aws-nodeDaemonSet for policy flags:kubectl get daemonset aws-node -n kube-system -o yaml | grep -A3 enable-network-policy- args: - --enable-network-policy=true image: amazon/aws-network-policy-agent:v1.0.8-eksbuild.1 - Launch an Alpine pod and install
curl:kubectl run alpine --image=alpine --restart=Never -- sleep 1d kubectl exec -it alpine -- apk add --no-cache curl - Test egress connectivity:
kubectl exec alpine -- curl -I https://kubernetes.io - Apply a default-deny egress policy:
# default-deny.yaml apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: default-deny-egress spec: podSelector: {} policyTypes: - Egress
Now all outbound traffic is blocked:kubectl apply -f default-deny.yaml kubectl get networkpolicieskubectl exec alpine -- curl -I https://kubernetes.io # curl: (6) Could not resolve host: kubernetes.io
Warning
A default-deny policy stops all egress. Verify you’ve whitelisted required endpoints before applying to production Pods.
You can then craft allow-rules to permit only specific ports, CIDR ranges, or peer Pods.
Inspecting the eBPF Agent Logs
On any node running aws-node, view the network policy agent logs:
sudo tail -f /var/log/aws-routed-eni/network-policy-agent.log
Typical entries include:
{"level":"info","msg":"Pod has an Ingress hook attached","progFD":16,"mapName":"ingress_map"}
{"level":"info","msg":"Pod has an Egress hook attached","progFD":18,"mapName":"egress_map"}
{"level":"info","msg":"Successfully attached Ingress TC probe","pod":"alpine-xxxxx","namespace":"default"}
{"level":"info","msg":"Successfully attached Egress TC probe","pod":"alpine-xxxxx","namespace":"default"}
These eBPF probes enforce your NetworkPolicy at the kernel level—packets are dropped before reaching the container.
Learn More
By combining Kubernetes Network Policies with AWS VPC CNI’s eBPF enforcement, you achieve an application-centric firewall that lives alongside your manifests—no extra tickets, no manual IP tables, just declarative security.
Watch Video
Watch video content