AWS Networking Fundamentals
Core Networking Services
Internet Gateway Demo
In this tutorial, you’ll convert a private subnet into a public subnet by attaching an Internet Gateway and updating the route table. After completing these steps, any EC2 instance launched in your public subnet will have Internet access.
Overview
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Create a VPC & Subnet |
| 2 | Launch an EC2 instance in the public subnet |
| 3 | Verify default connectivity (should fail) |
| 4 | Create & attach an Internet Gateway |
| 5 | Configure the route table for Internet access |
| 6 | Test Internet connectivity (should succeed) |
Prerequisites
- An AWS account with permissions to manage VPCs and EC2.
- A generated SSH key pair (for example,
aws-demo.pem).
Note
You can refer to the AWS VPC Documentation for more details on VPC components.
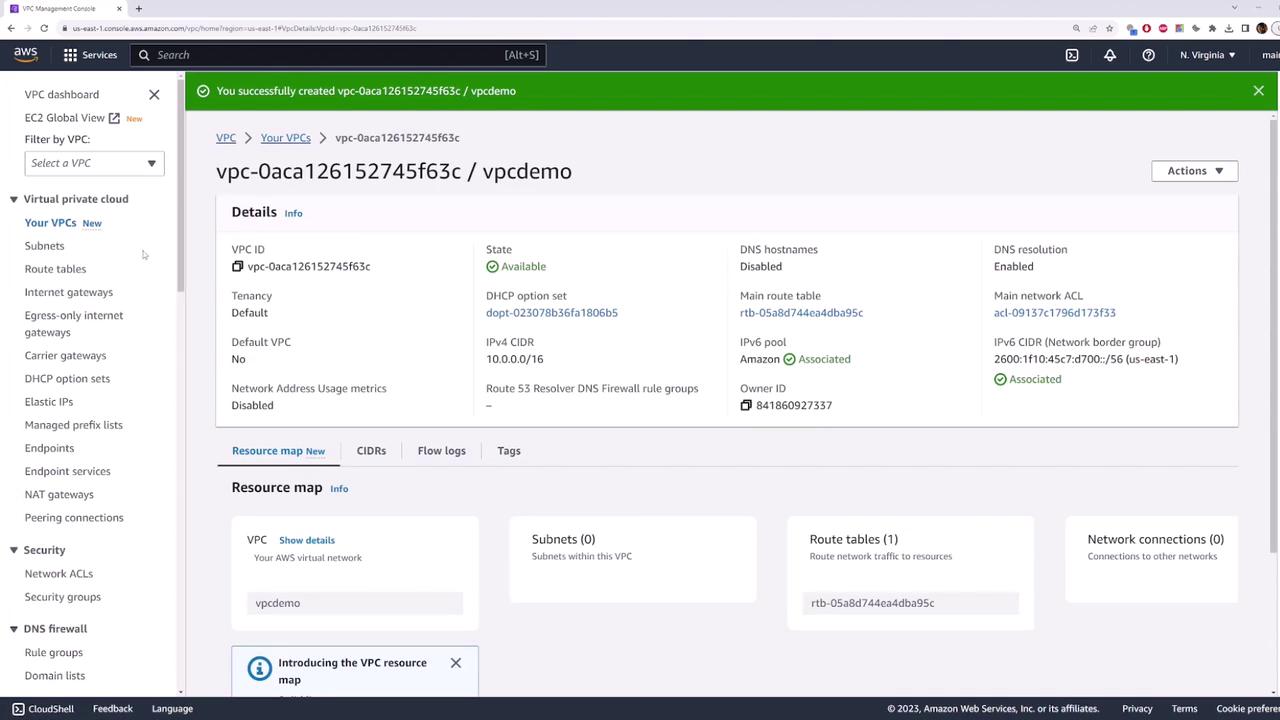
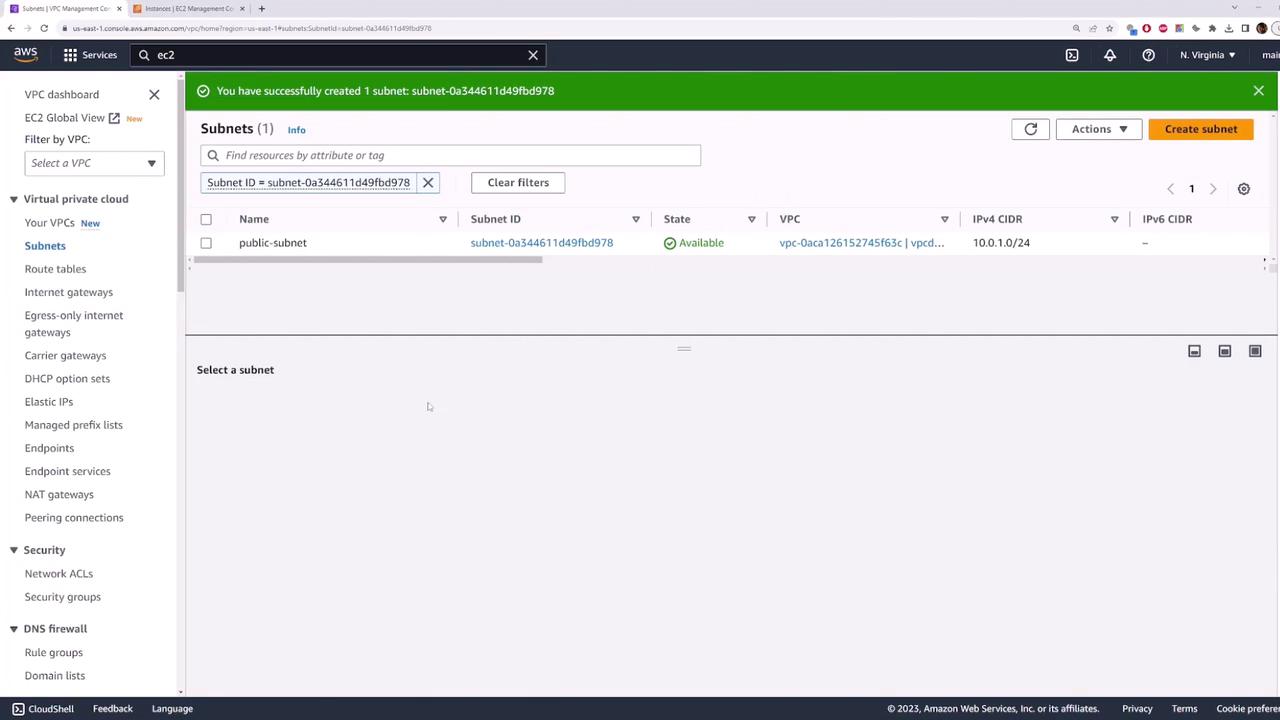
1. Create a VPC and Public Subnet
- In the AWS Console, go to VPC > Your VPCs and click Create VPC.
- Set the IPv4 CIDR block to
10.0.0.0/16. Optionally add an IPv6 block. - Click Create VPC.
- Navigate to Subnets > Create subnet:
- Name tag:
public-subnet - VPC: your newly created VPC
- IPv4 CIDR block:
10.0.1.0/24
- Name tag:
- Click Create subnet.
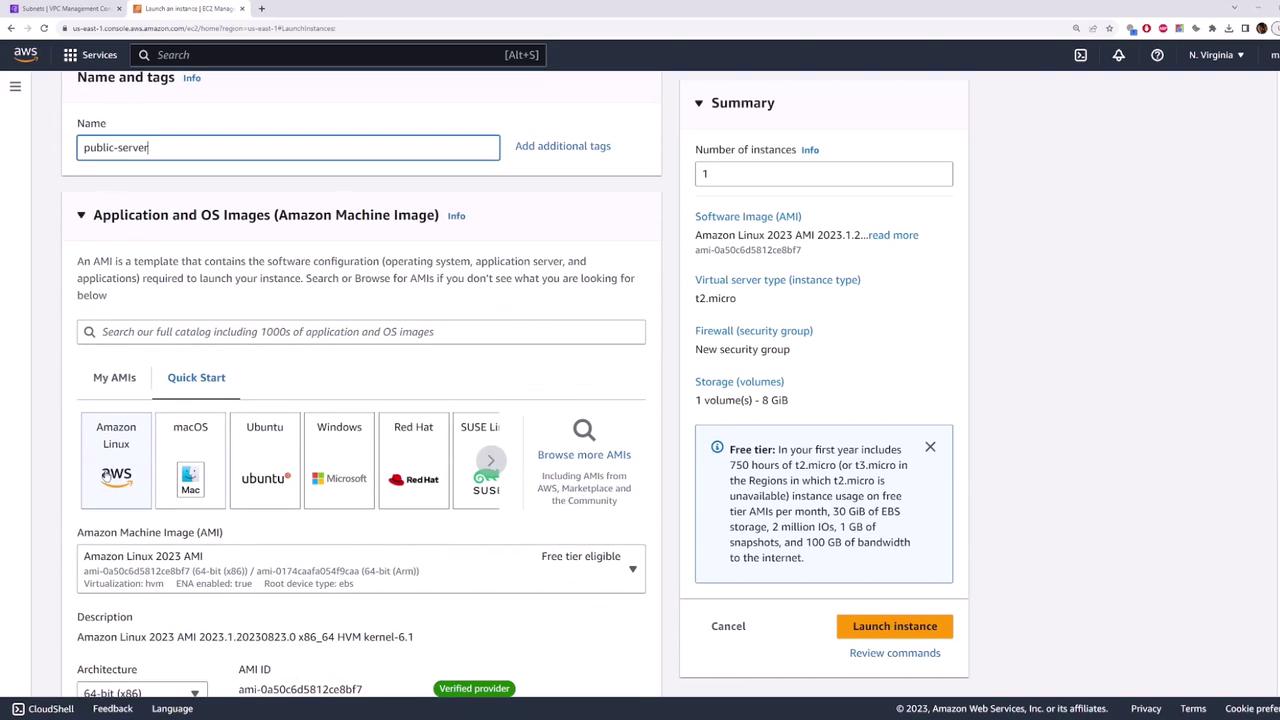
2. Launch an EC2 Instance in the Public Subnet
- Open EC2 Console > Instances > Launch instances.
- For Name, enter
my-public-server. - Choose Amazon Linux 2023 under Application and OS Images (AMI).
- Select the t2.micro instance type (free tier).
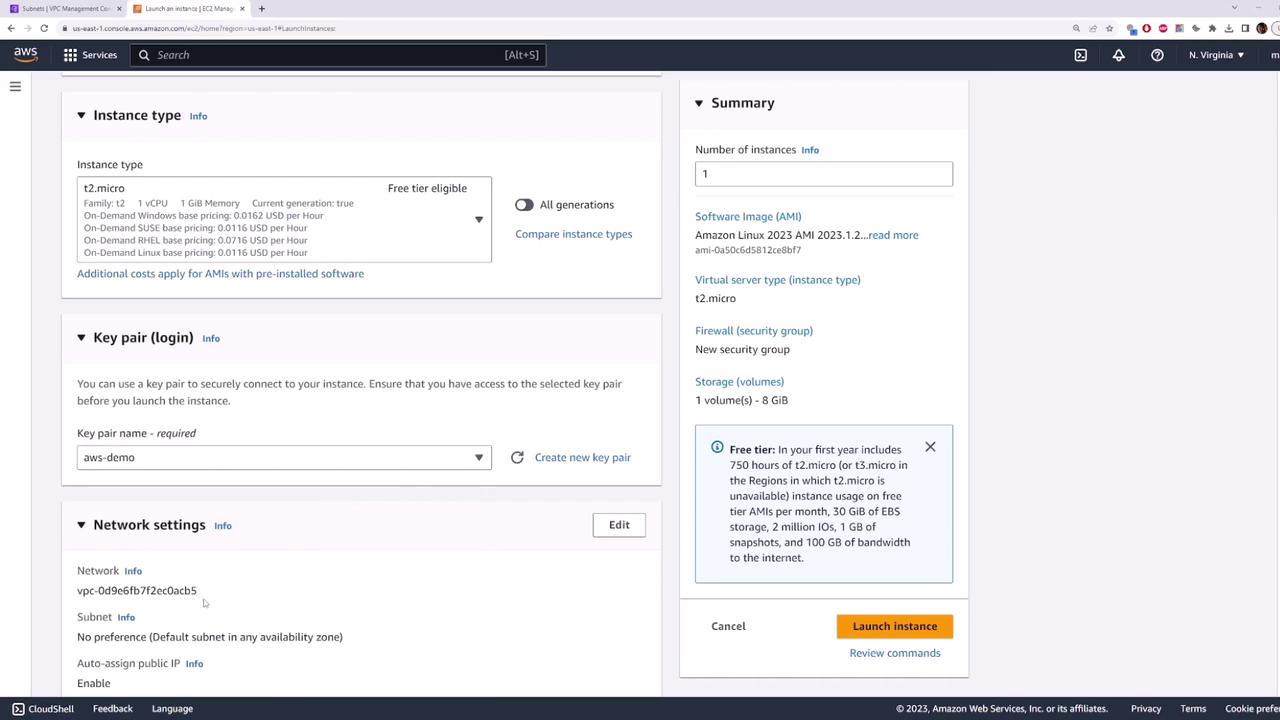
- Under Key pair, choose
aws-demo.pem. - Expand Network settings > Edit and configure:
- VPC: your new VPC
- Subnet:
public-subnet - Auto-assign public IP: Enable
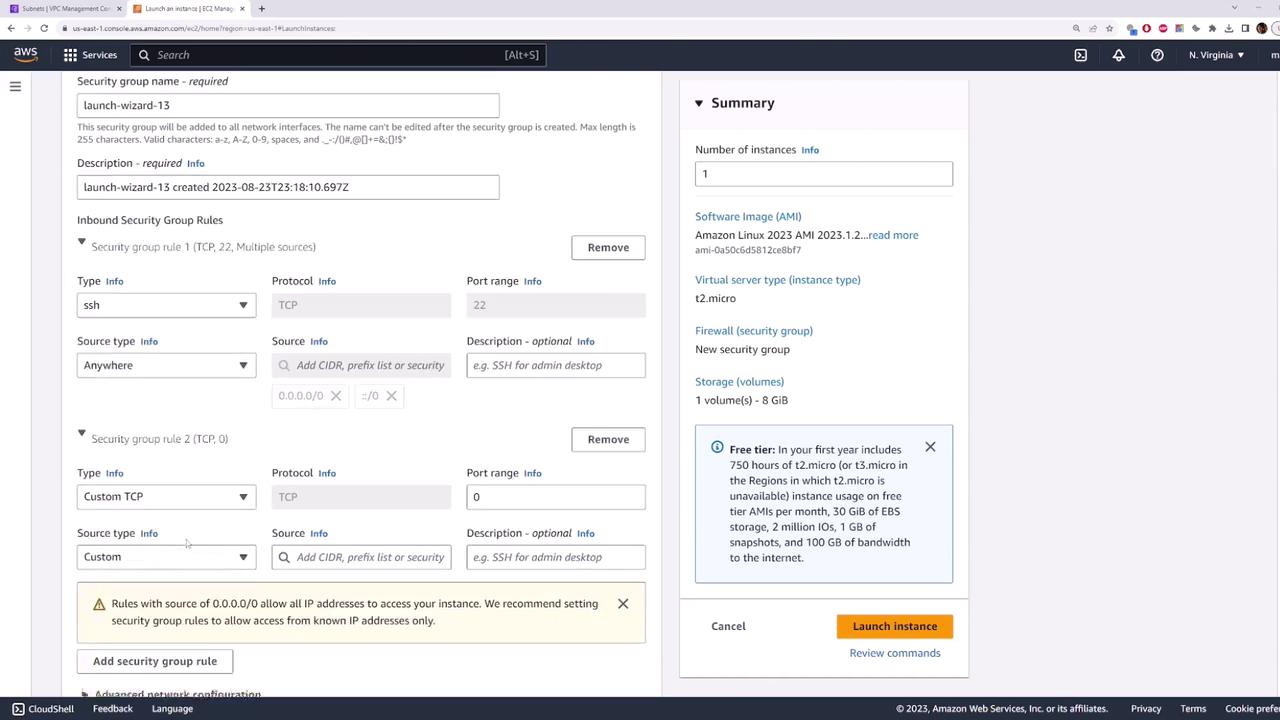
- Under Security group, allow SSH (port 22) from
0.0.0.0/0. Optionally add ICMP for ping.
- Click Launch instance and wait for it to switch to running.
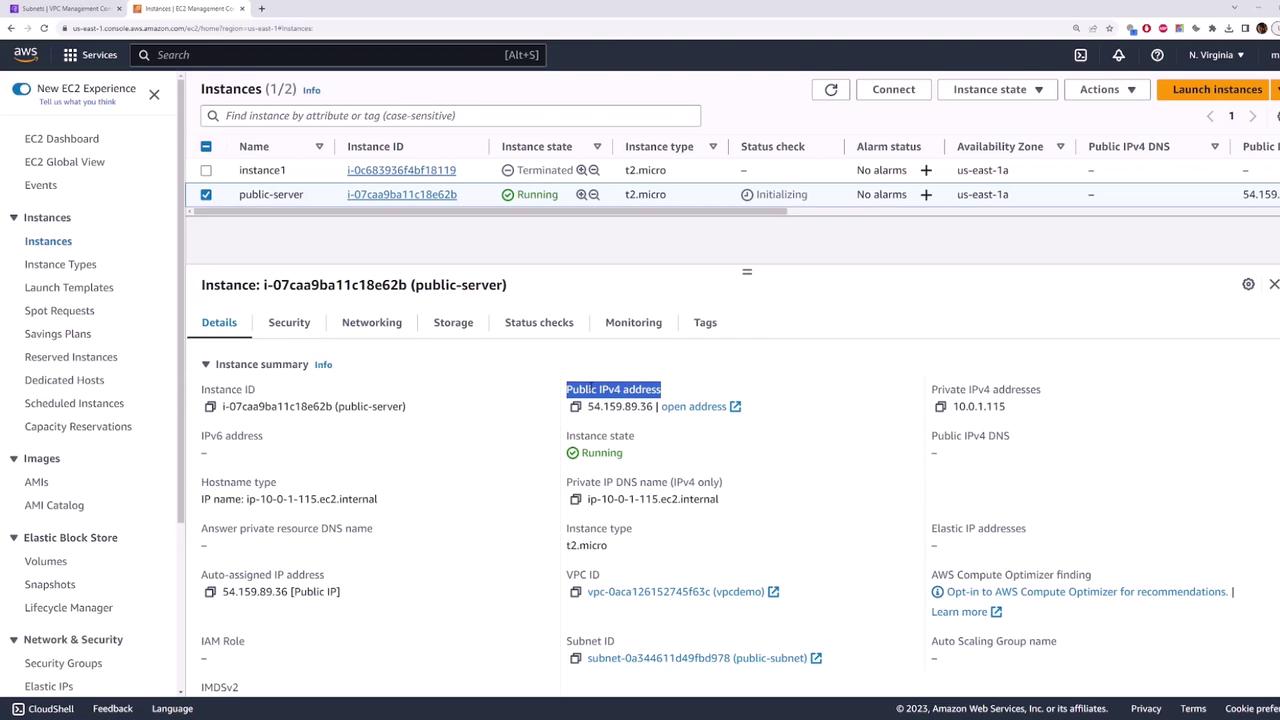
3. Verify Default Connectivity (Should Fail)
After your instance is running, copy its public IP (example: 54.159.89.36) and test connectivity:
ping 54.159.89.36
ssh -i aws-demo.pem [email protected]
# Connection hangs.
By default, there’s no Internet route, so the instance remains unreachable despite having a public IP.
4. Create and Attach an Internet Gateway
- In the VPC Console, select Internet Gateways and click Create internet gateway.
- Name tag:
my-internet-gateway
- Name tag:
- Click Create internet gateway.
- Select the newly created gateway, choose Actions > Attach to VPC, and select your VPC.
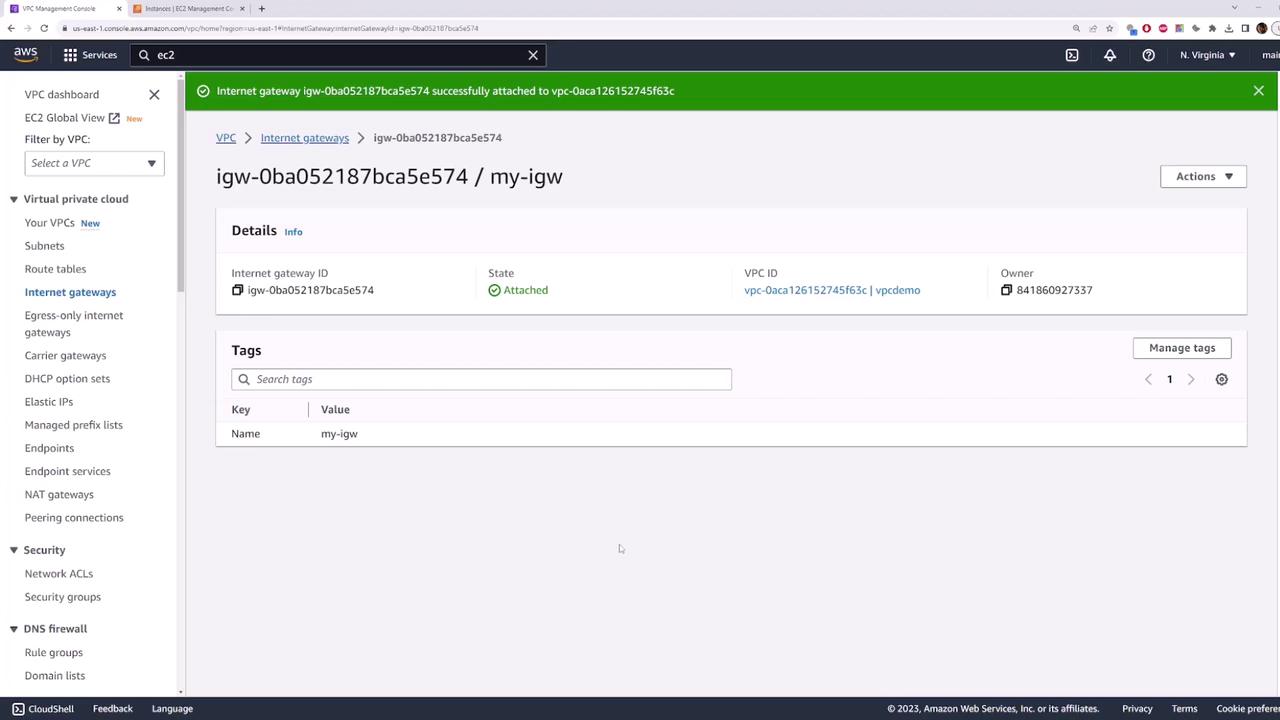
Pinging still fails because the route table isn’t updated yet.
5. Configure the Route Table for Internet Access
- Go to VPC > Route Tables and click Create route table.
- Name tag:
public-route-table - VPC: your demo VPC
- Name tag:
- Click Create route table.
- Select the new route table, open Subnet associations, click Edit subnet associations, check
public-subnet, and save.
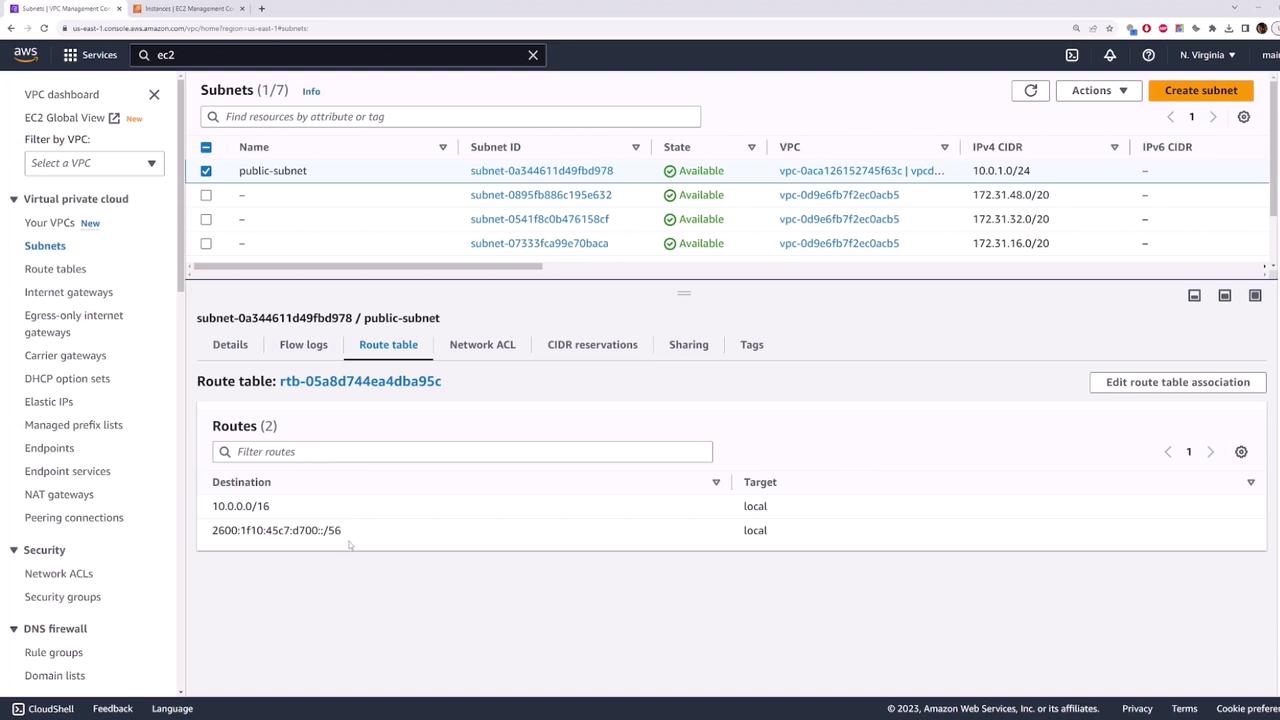
- In the Routes tab, click Edit routes > Add route:
- Destination:
0.0.0.0/0 - Target:
my-internet-gateway
- Destination:
- Save the route.
6. Test Internet Connectivity (Should Succeed)
Now retry ping and SSH using the public IP:
ping 54.159.89.36
ssh -i aws-demo.pem [email protected]
# Welcome to your public EC2 instance!
Congratulations! Your public-subnet is now internet-enabled, and any EC2 instances launched into it can be accessed from the Internet.
Additional Resources
Watch Video
Watch video content