Azure Redis Cache
Azure Redis Cache allows you to cache frequently accessed data so that your application retrieves information quickly without repeatedly querying the underlying database. For instance, rather than having web applications query a SQL database or Cosmos DB for every user request, commonly requested data is cached in Redis. If the data is missing, the application then queries the database for the most recent information. Azure Redis Cache integrates seamlessly with various Azure databases, including SQL DB, Cosmos DB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MariaDB.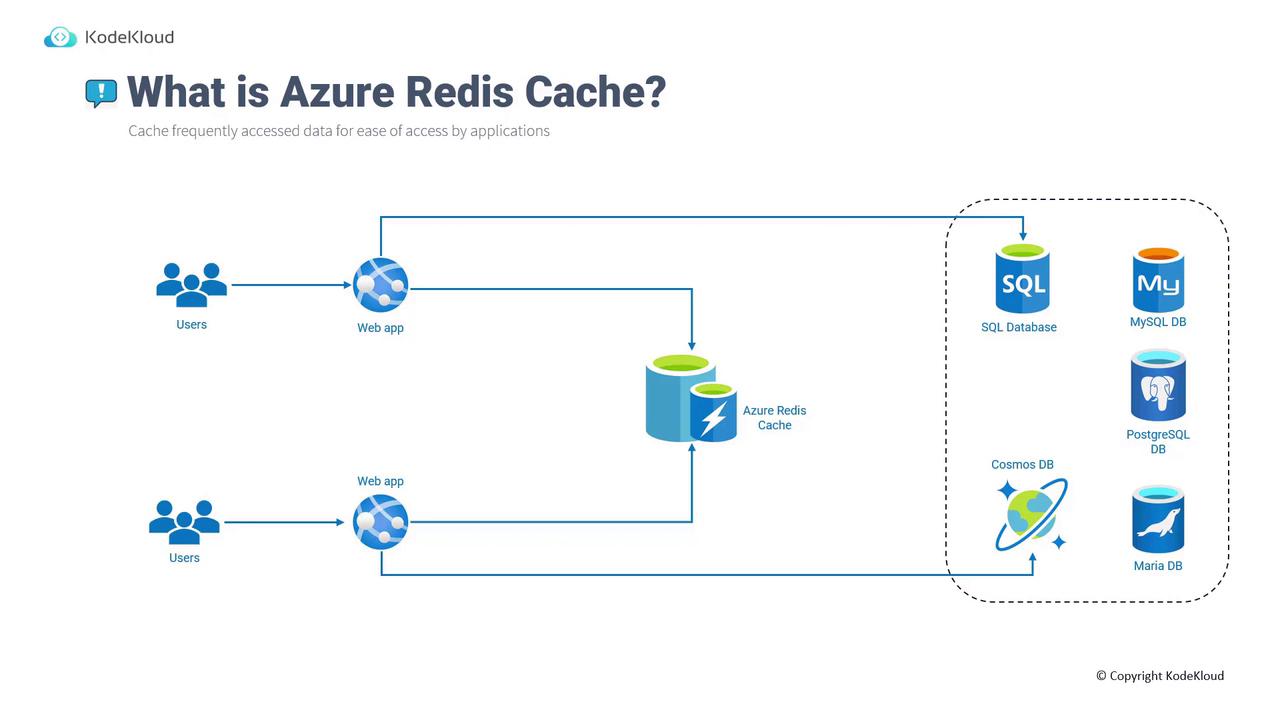
When to Use Redis Cache
Caching
Caching is a typical use case for Redis Cache. Since loading an entire database into the cache is impractical, the cache-aside pattern is recommended: load only the data required, on demand. To handle database updates and ensure data consistency, you can update the relevant cache entries or set a time-to-live (TTL) so that stale data is refreshed automatically.Content Cache
Static web content such as headers, footers, and banners can benefit significantly from caching. For example, in ASP.NET applications, the Redis output cache provider caches static content, reducing page load times substantially.Session Persistence
Instead of enlarging cookie sizes to store session data, you can store session information in Redis Cache. A cookie acts as a reference key, enabling quick retrieval of user session details from the cache, which is much faster than querying a relational database directly.Task Queuing
Azure Redis Cache can also be used for task queuing. When facing operations that require extended processing time, you can enqueue tasks to be processed sequentially. This prevents blocking the main execution flow of your application.Distributed Transactions
For scenarios requiring multiple operations to be executed as a single transaction, Redis Cache supports atomic execution of multiple commands. This ensures that if any step fails, the entire set of operations can be rolled back to maintain data consistency.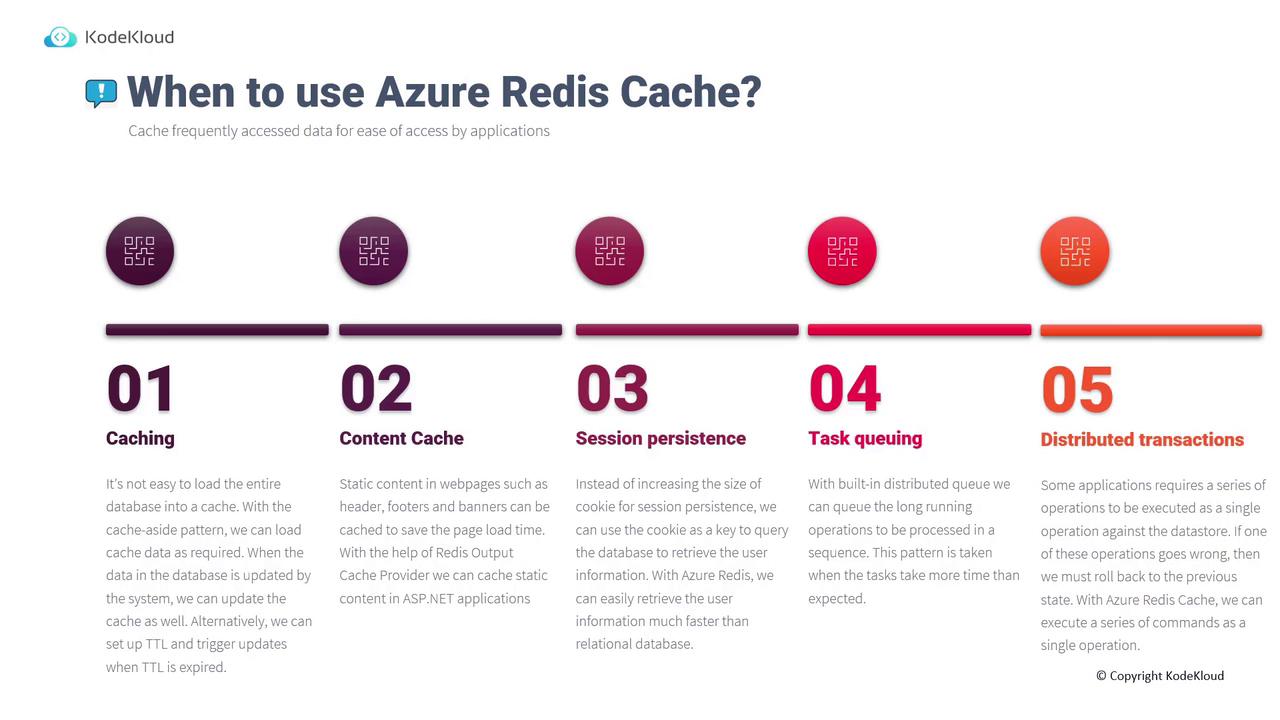
When implementing Redis Cache, consider the cache-aside pattern to minimize memory usage and maintain data integrity.
API Management
Azure API Management is a fully managed service that enables you to publish, manage, secure, maintain, and analyze your APIs. Acting as a gateway, it ensures that API calls from a vast array of clients—such as mobile applications, business partners, developers, employees, IoT devices, and web applications—are properly routed to the appropriate backend servers.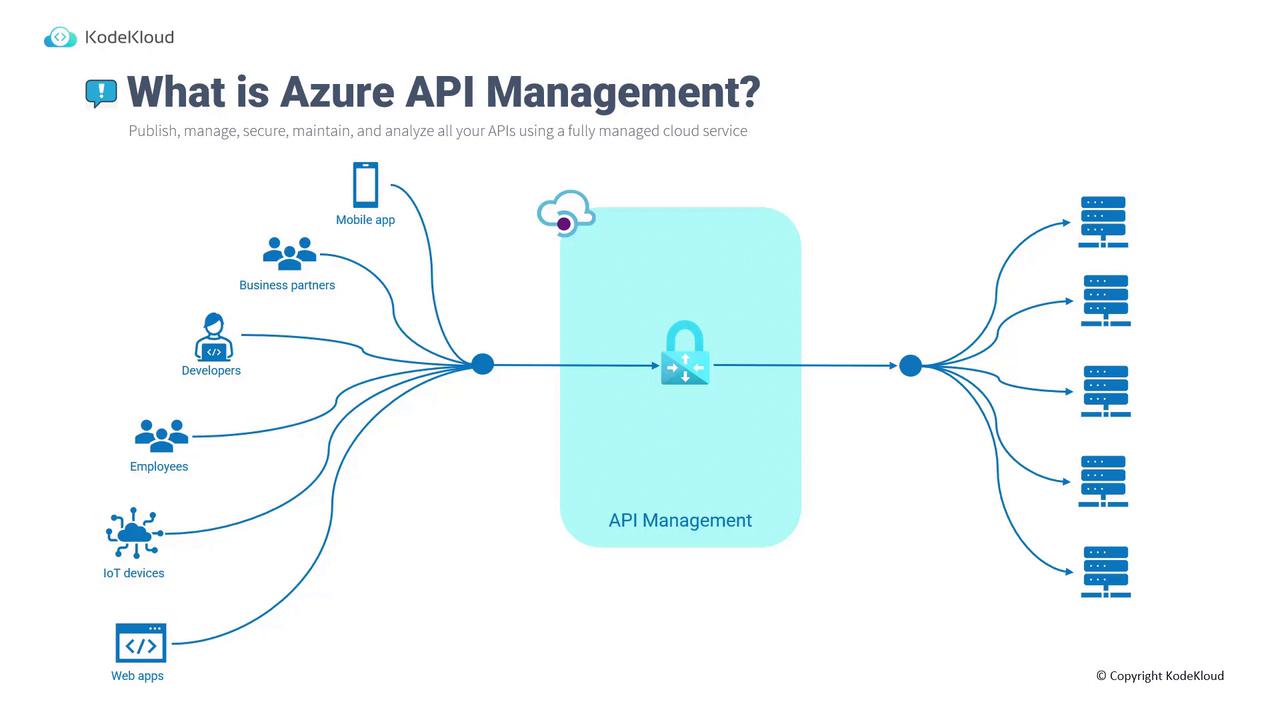
When to Use API Management
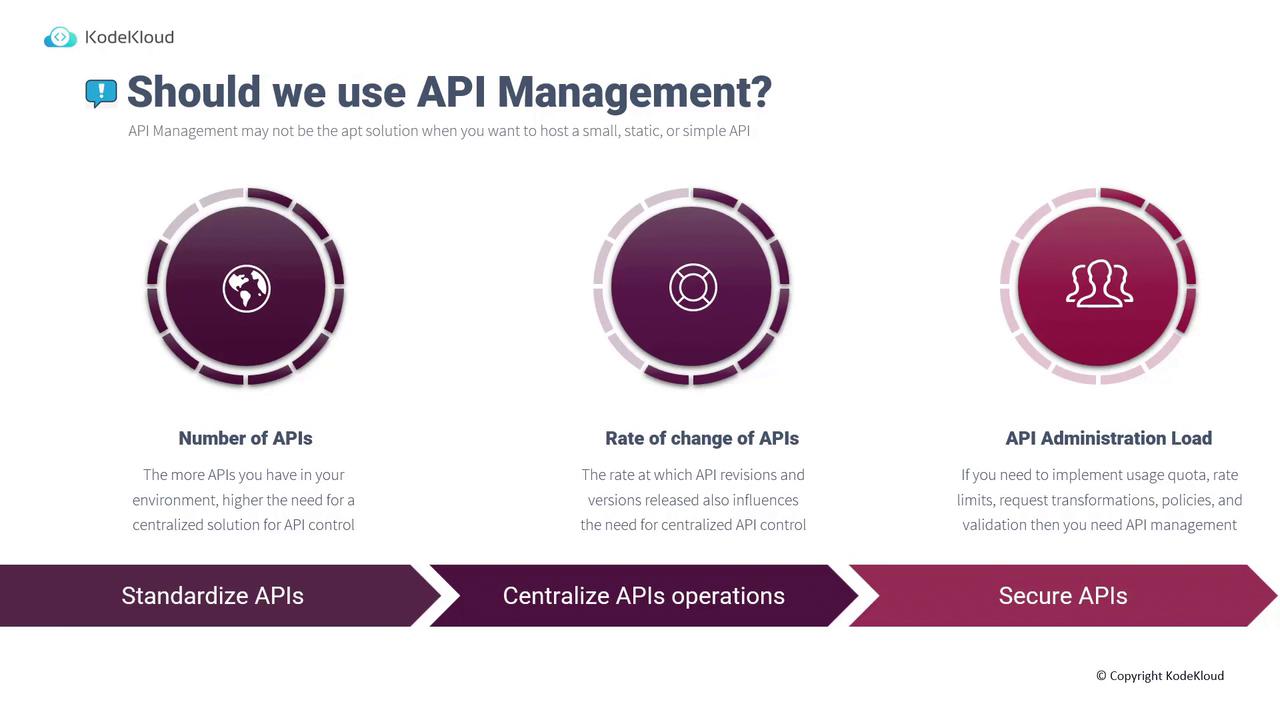
API Management is ideal for environments that require centralized control over a large number of APIs. It is particularly beneficial when you face the following conditions:- Numerous APIs: A centralized system is essential when managing many APIs.
- Rapid API Evolution: Frequent updates and new versions of your APIs demand a robust management system.
- High Administration Overhead: Centralized enforcement of policies such as usage quotas, rate limiting, request transformations, and validations is crucial.
Consider using API Management to gain centralized control and enforce uniform policies across your API ecosystem, especially if you handle a large number of APIs or require frequent updates.