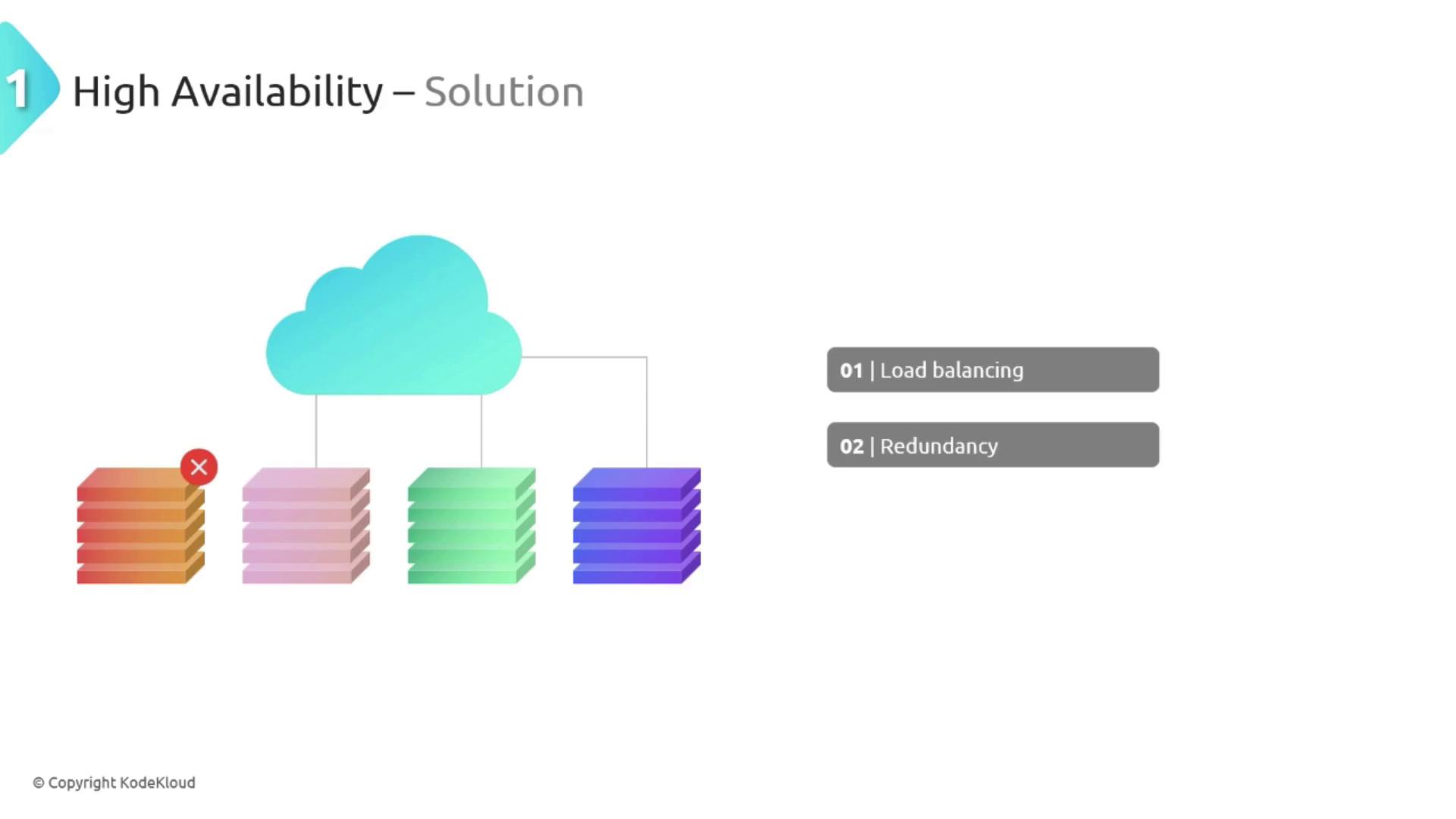
High Availability
High availability is crucial for delivering robust and continuously operational customer-facing services—even during an outage. Many organizations rely on on-premises setups that often include a single data center. When a server fails in such environments, the entire application may become unavailable, resulting in downtime, revenue loss, and diminished customer trust.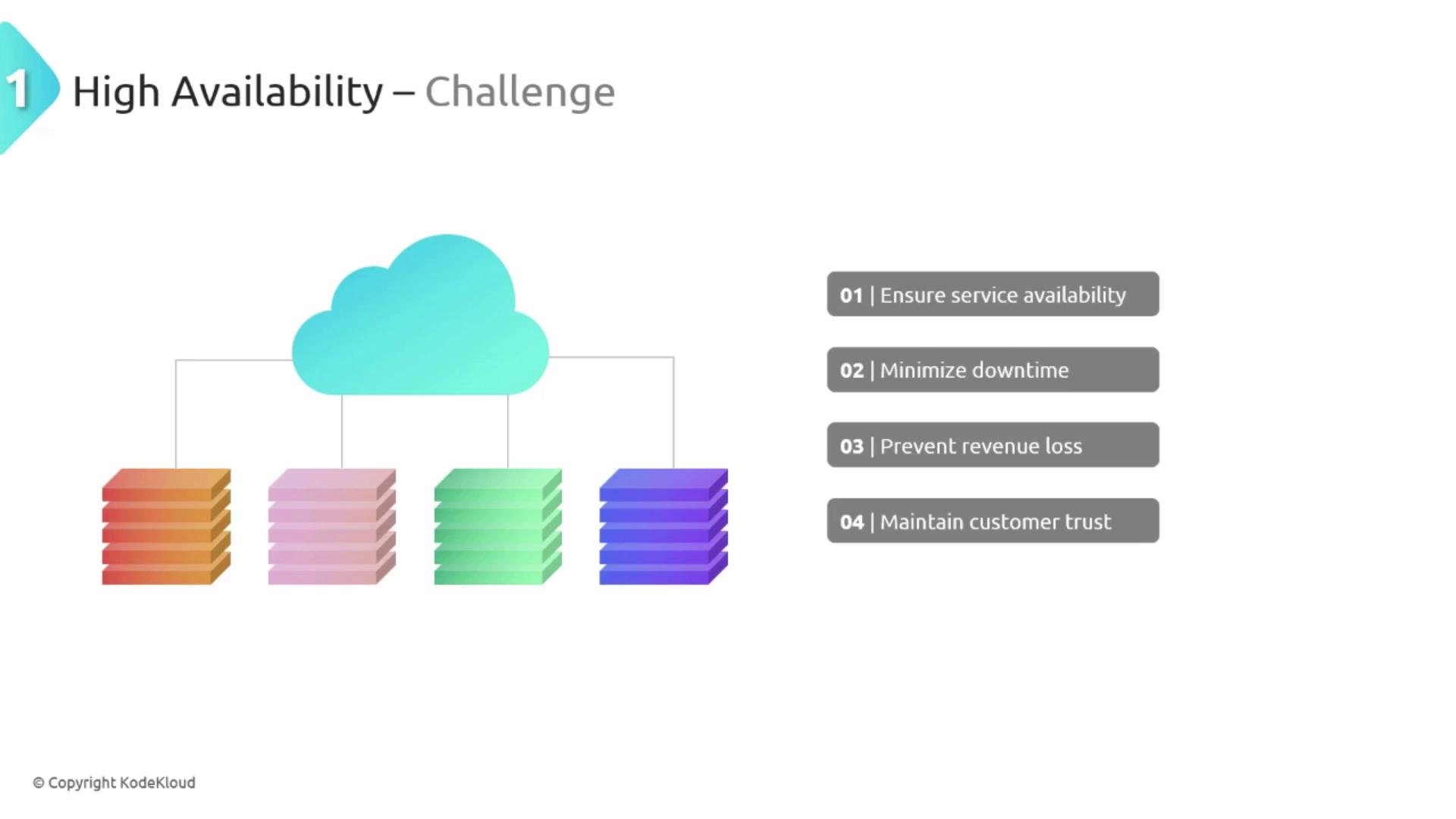
Scalability
As your business expands, so does the need for an IT infrastructure that can seamlessly handle increasing loads and adapt rapidly to changing demands. Traditional on-premises systems often require manual hardware upgrades, which can lead to downtime and high capital expenses. This can result in resource wastage during off-peak periods and shortages during demand spikes, such as major sales events.
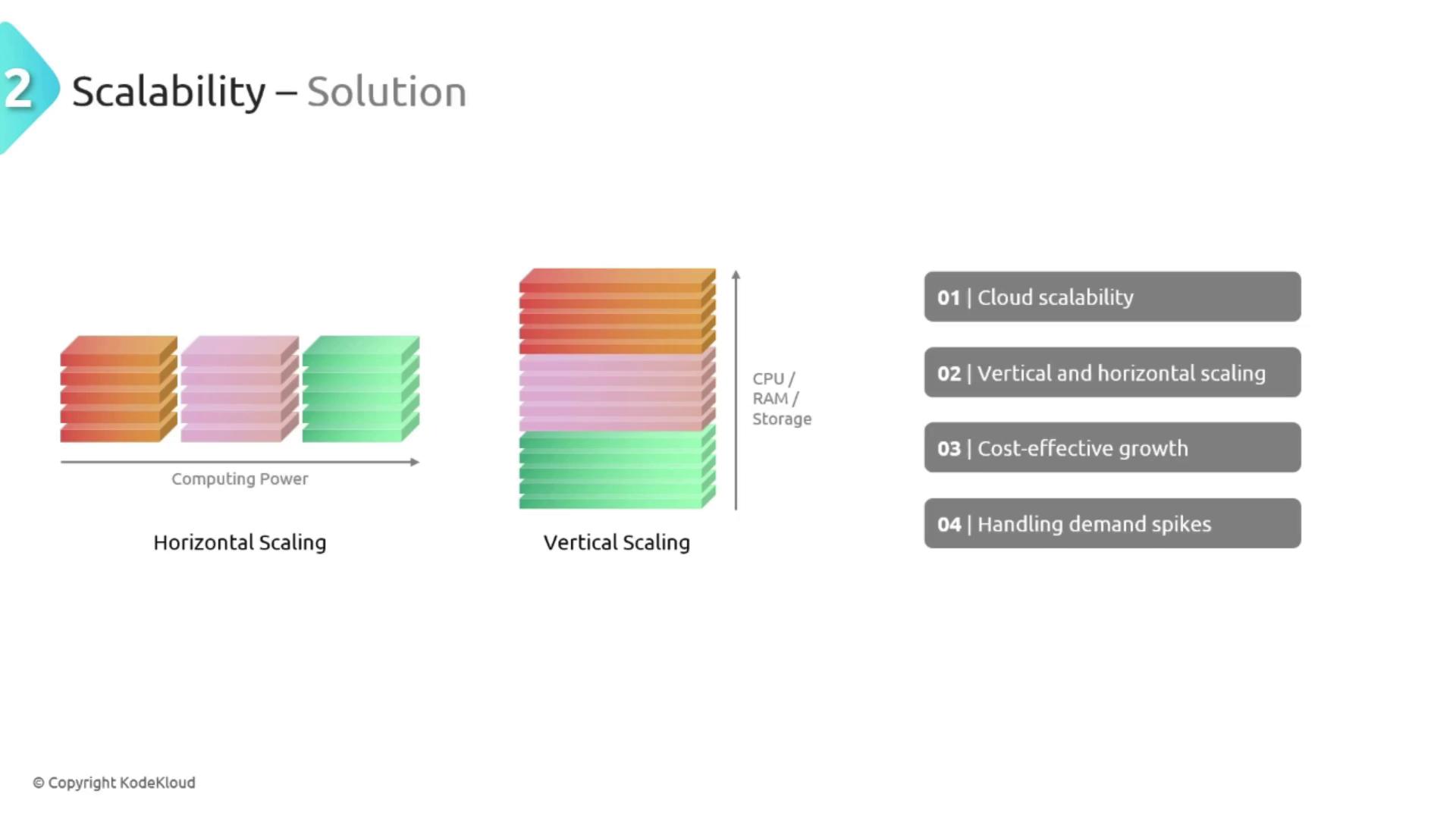
- Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up): Boosts the power of existing machines by increasing CPU, RAM, or storage capacity.
- Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out): Expands the system by adding additional machines to manage increased load.
Predictability
Predictability in cloud computing enables organizations to plan budgets and allocate resources with greater accuracy. Traditional on-premises infrastructures require companies to estimate future demands and commit capital upfront, leading to either over-investment or capacity shortages. Hardware failures or sudden spikes in usage can further cause unexpected cost increases and performance issues. Key challenges with on-premises setups include:- Budgeting Challenges: Risk of over-investment or resource deficiencies due to inaccurate forecasts.
- Cost Spikes: Unanticipated expenses stemming from hardware failures or rapid expansion.
- Performance Impact: Potential slowdowns or outages during peak usage periods.
- Resource Allocation: Uneven resource distribution across different departments.
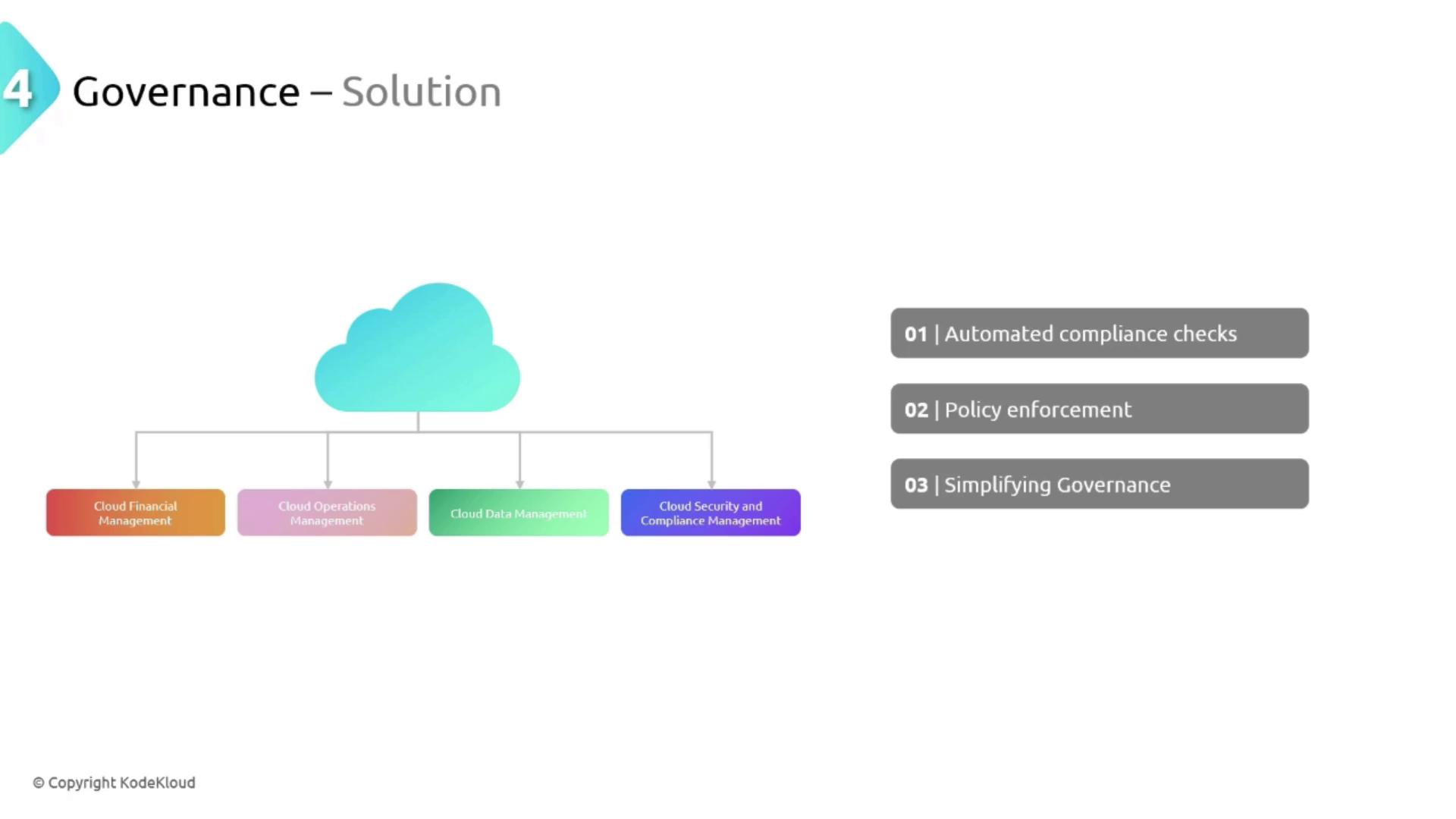
Governance
Effective governance is vital for ensuring that IT operations comply with internal policies and regulatory requirements. Managing consistent governance in a fragmented on-premises environment can be especially challenging. Common issues include:- Governance Policy Consistency: Enforcing uniform policies across decentralized systems.
- Environment Compliance: Achieving cost-effective compliance with industry regulations.
- Data Protection Assurance: Implementing consistent security protocols across fragmented infrastructures.
- Operational Integrity Maintenance: Managing regular updates, patches, and maintenance without disruption.
Cloud providers often integrate tools that allow organizations to implement and enforce policies with a few clicks, reducing the need for extensive manual intervention.