How Conditional Access Works
The process begins with the collection of key signals such as:- User and Location: Identifies who is accessing and where the access is coming from.
- Device Security: Confirms that the device complies with security standards.
- Application Type: Determines whether the access is through browsers like Safari or Edge.
- Real-Time Risk Evaluation: Spots any suspicious behaviors or deviations from typical usage patterns.
- Grant access if all conditions are met.
- Request Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
- Block access if the risk is deemed too high.
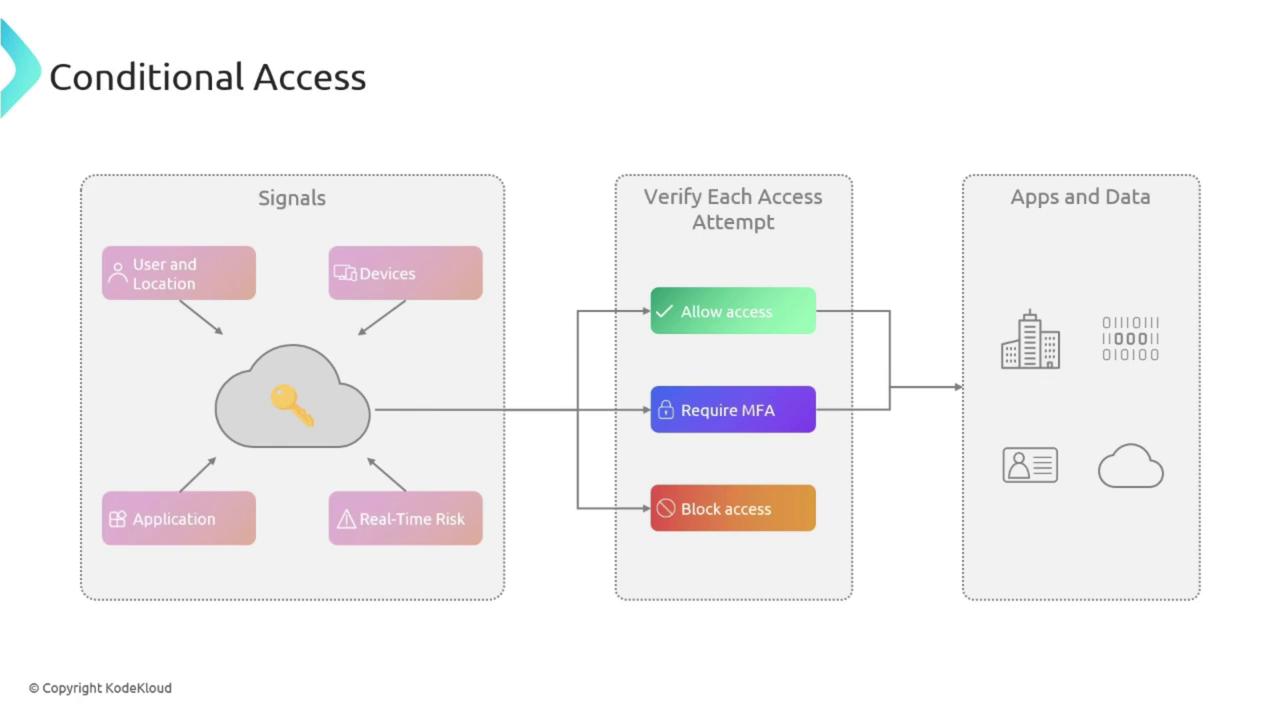
Understanding the flow of signals and verification steps is crucial. Each step reinforces your organization’s security posture by ensuring that only the appropriate users gain access.
Key Features of Conditional Access
Conditional Access incorporates several features that contribute to a robust security framework:User and Group-Based Policies
Think of this as issuing tailored entry passes for different areas within a building. User and group-based policies let you assign access controls to individual users or specific groups, ensuring that restrictions apply precisely where needed.Location-Based Policies
Just as some documents may only be accessible in certain offices, location-based policies restrict access based on where a user is trying to sign in. For instance, you might allow access to critical applications only when users are on the corporate network.Device-Based Policies
Like verifying a security badge before entry, device-based policies ensure that access is only granted from devices that meet your organization’s security requirements. This includes compliance with operating system standards, antivirus protection, and other security protocols.Risk-Based Policies
Risk-based policies work alongside Azure Risk Detection. If Azure notices a deviation from the established usage pattern—such as an unexpected login location—it can immediately escalate the response by blocking access or demanding additional verification.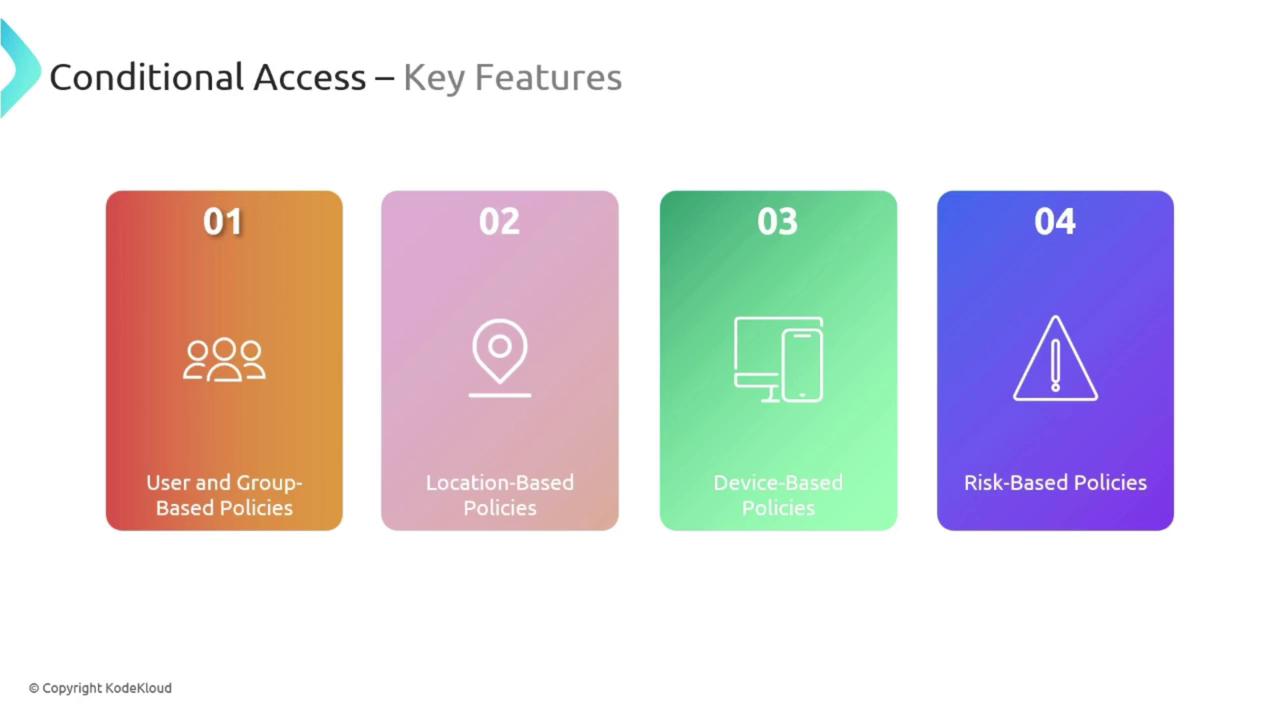
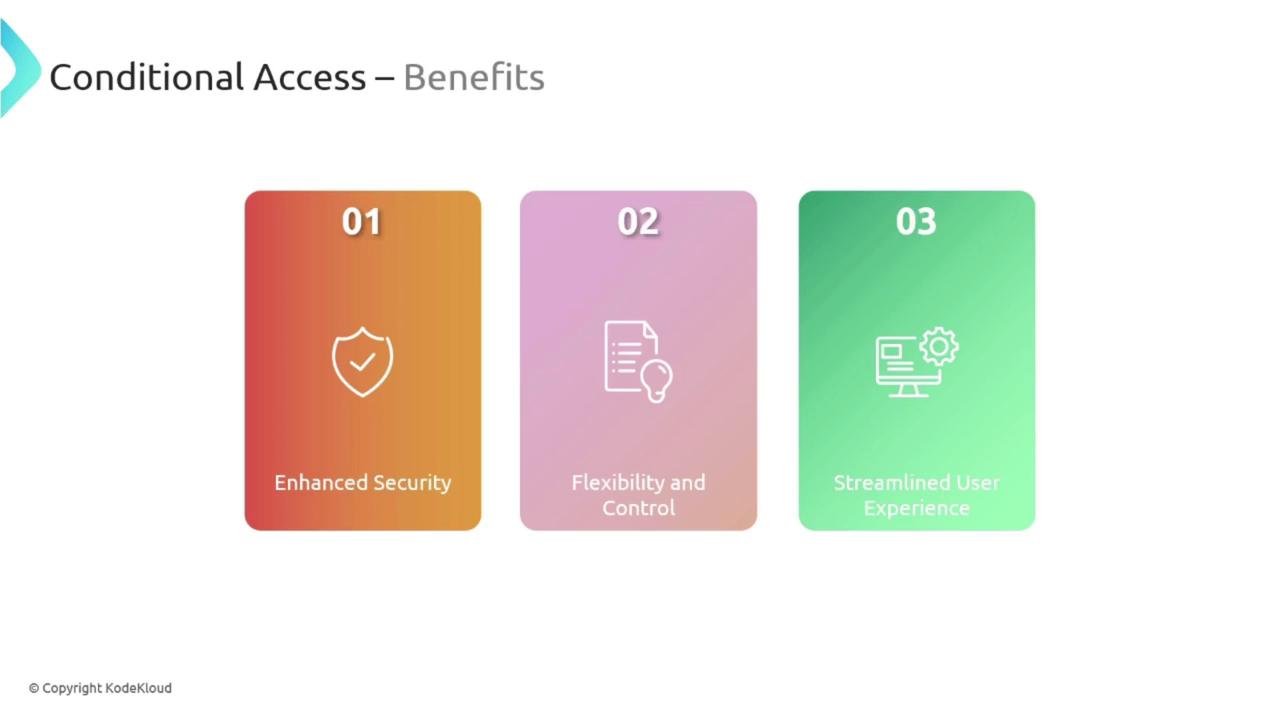
Benefits of Conditional Access
Implementing Conditional Access in your organization offers a range of benefits:- Enhanced Security: Only authorized users meeting the appropriate conditions can access sensitive resources.
- Flexibility and Control: Policies can be finely tuned for specific applications, users, or devices, similar to instituting customizable locks for different doors.
- Improved User Experience: By minimizing unnecessary obstacles for legitimate users while effectively keeping out unauthorized access attempts, Conditional Access supports a smooth workflow.
Conditional Access is especially beneficial in remote work or Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) environments, where securing access from various locations and devices is critical.
