AZ900: Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
Identity Access and Security
Zero Trust
In today's rapidly evolving cyber threat landscape, traditional security measures are often insufficient. This article delves into the Zero Trust model—a strategic security framework that operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." Unlike conventional network security that assumes internal users are safe, Zero Trust mandates continuous authentication for every access request, regardless of the user's location.
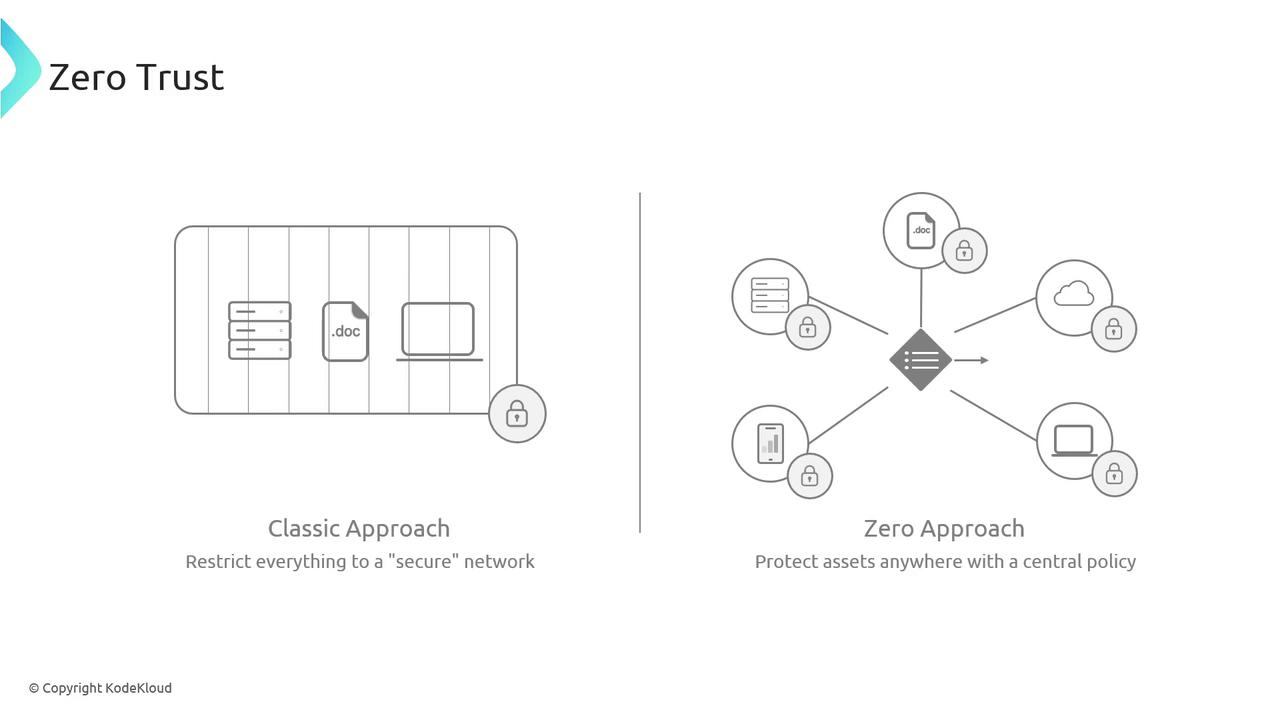
With Zero Trust, every access request is treated as a potential threat until it is verified. Picture a VIP event: regardless of whether you are a staff member or a guest, you must show your invitation to gain entry. Similarly, Zero Trust requires digital interactions to undergo stringent checks before access is granted.
The core tenets of Zero Trust are:
- Verify Explicitly
- Use Least Privilege Access
- Assume Breach
Key Principles Explained
The three principles work together to create a layered defense. Verifying explicitly ensures comprehensive validation of all access requests, least privilege limits access only to essential functions, and assuming breach means preparing to detect and mitigate threats in real time.
Verify Explicitly
Every access request must be verified, similar to checking each guest's credentials at a secure event. Decisions regarding authentication and authorization rely on multiple data points, including user identity, location, device health, and the nature of the workload. This multi-factor verification process guarantees that only legitimate requests gain access.
Use Least Privilege Access
Consider a secure event where staff members are only allowed in areas required for their duties. Zero Trust follows the same logic by confining user access to the minimum necessary level. Advanced strategies like just-in-time (JIT) and just-enough-access (JEA) policies dynamically adjust permissions according to the context of each request.

Adaptive Access Control
By enforcing adaptive policies, organizations ensure users receive only the necessary permissions—and just for as long as needed—minimizing the potential impact of any security compromise.
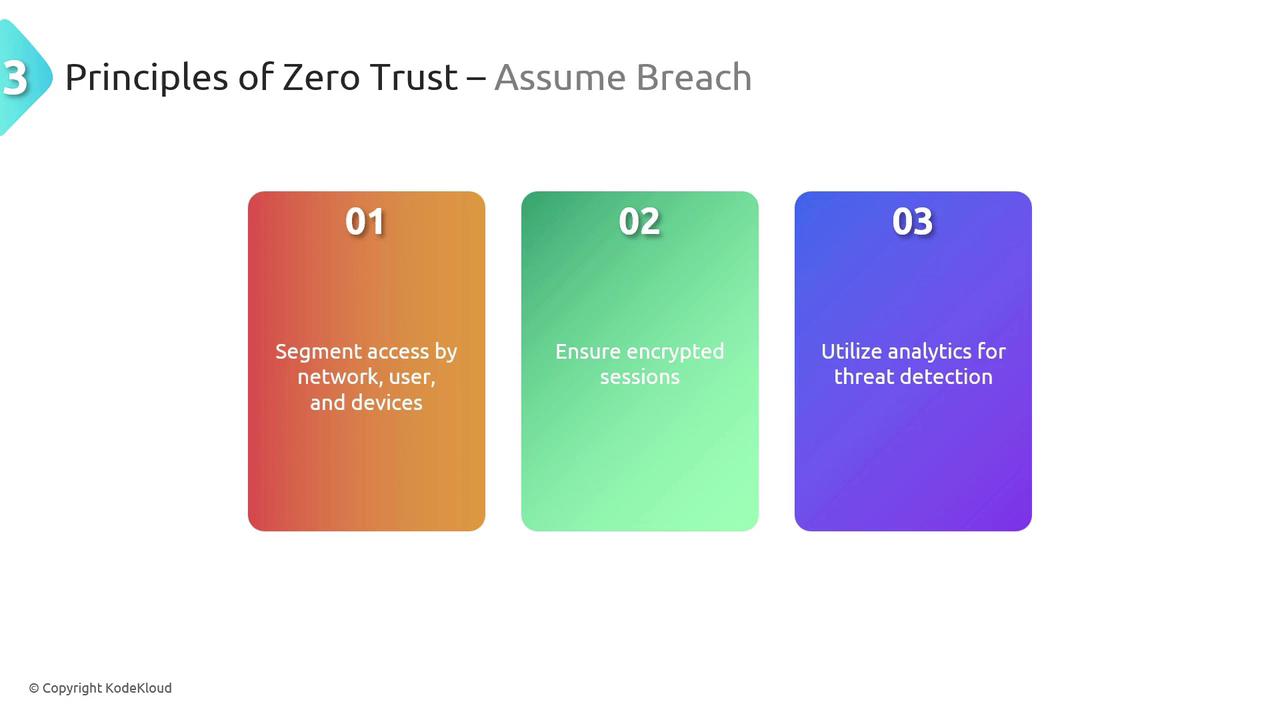
Assume Breach
Rather than solely focusing on prevention, the "assume breach" mindset emphasizes rapid detection and response. This approach is similar to having undercover security at an event: continuously monitoring, swiftly identifying threats, and reacting immediately to any suspicious activity.
To further reduce risks, access is tightly segmented across networks, users, devices, and applications. Should a breach occur, these granular boundaries help contain the fallout. Additionally, continuous session encryption and advanced analytics significantly enhance an organization's capability to identify and respond to threats in real time.
Proactive Security Measures
Adopting a Zero Trust strategy means that organizations must be prepared to not only prevent attacks but also detect and respond to them as they happen. This proactive stance is crucial in today’s dynamic security environment.
By integrating explicit verification, least privilege access, and a proactive "assume breach" approach, Zero Trust establishes a resilient security framework designed to protect modern digital infrastructures against an ever-changing spectrum of cyber threats.
Watch Video
Watch video content