Initializing a New Module with go.mod
Use thego mod init command to create a new module. This command initializes a new go.mod file in the current directory, establishing the module’s root. You can optionally provide a module path as an argument if needed.
Tidying the Module with go.mod tidy
Thego mod tidy command ensures that your go.mod file accurately reflects the dependencies used in your source code. It automatically adds any missing module requirements and removes those that are no longer relevant.
Running Go Code with go run
Thego run command facilitates quick testing of your Go code. It compiles and runs your program by creating an executable binary in a temporary location. Once the program completes execution, Go cleans up the temporary binary, similar to running a script in other languages.
Building and Installing Executables
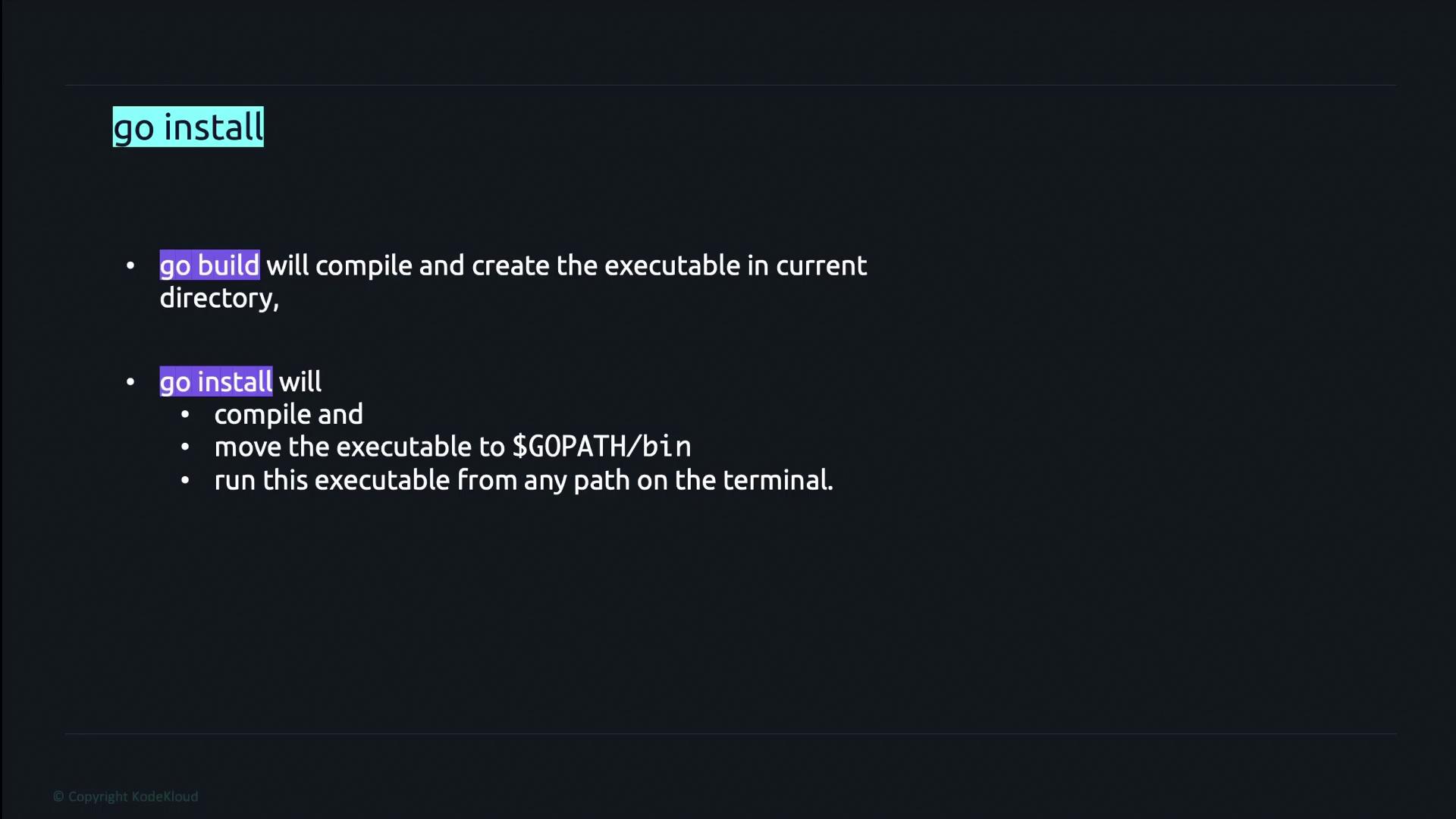
go build
Thego build command compiles the packages specified by the import paths along with their dependencies into an executable. The resulting binary is created in the current source directory.
go install
Thego install command compiles your code and installs the executable into the GOPATH/bin directory. This makes it accessible from any terminal session. To find your GOPATH, execute the following command:
go build and go install:
Managing Dependencies with go get
Thego get command helps manage dependencies by resolving package arguments to specific module versions. It updates the go.mod file with the necessary versions and downloads the source code into the module cache. Use this command to add, upgrade, or downgrade a dependency.
Keep your modules organized by regularly using
go mod tidy after adding or updating dependencies to ensure that your go.mod file stays clean and up-to-date.