Advanced Golang
Modules Packages and Imports
Repositories Modules and Packages
In this lesson, we explore library management in Golang by understanding how the language organizes code into repositories, modules, and packages. This foundational knowledge is essential for efficient code management and dependency tracking in Go projects.
A repository is a designated location in a version control system where a project's source code is stored. Within a repository, a module represents the root of a Go library or application. Modules can contain one or more packages, which serve as the building blocks used to organize and structure code. Although it is technically possible to store multiple modules in a single repository, this practice is discouraged. Since all code within a module is versioned together, maintaining separate version histories for different projects in one repository can introduce unnecessary complexity.
Before incorporating code from packages outside the standard library, you must declare your project as a module. Each module is assigned a globally unique identifier—often a GitHub repository URL, a private domain, or another URL—that Go tools use as the download path.
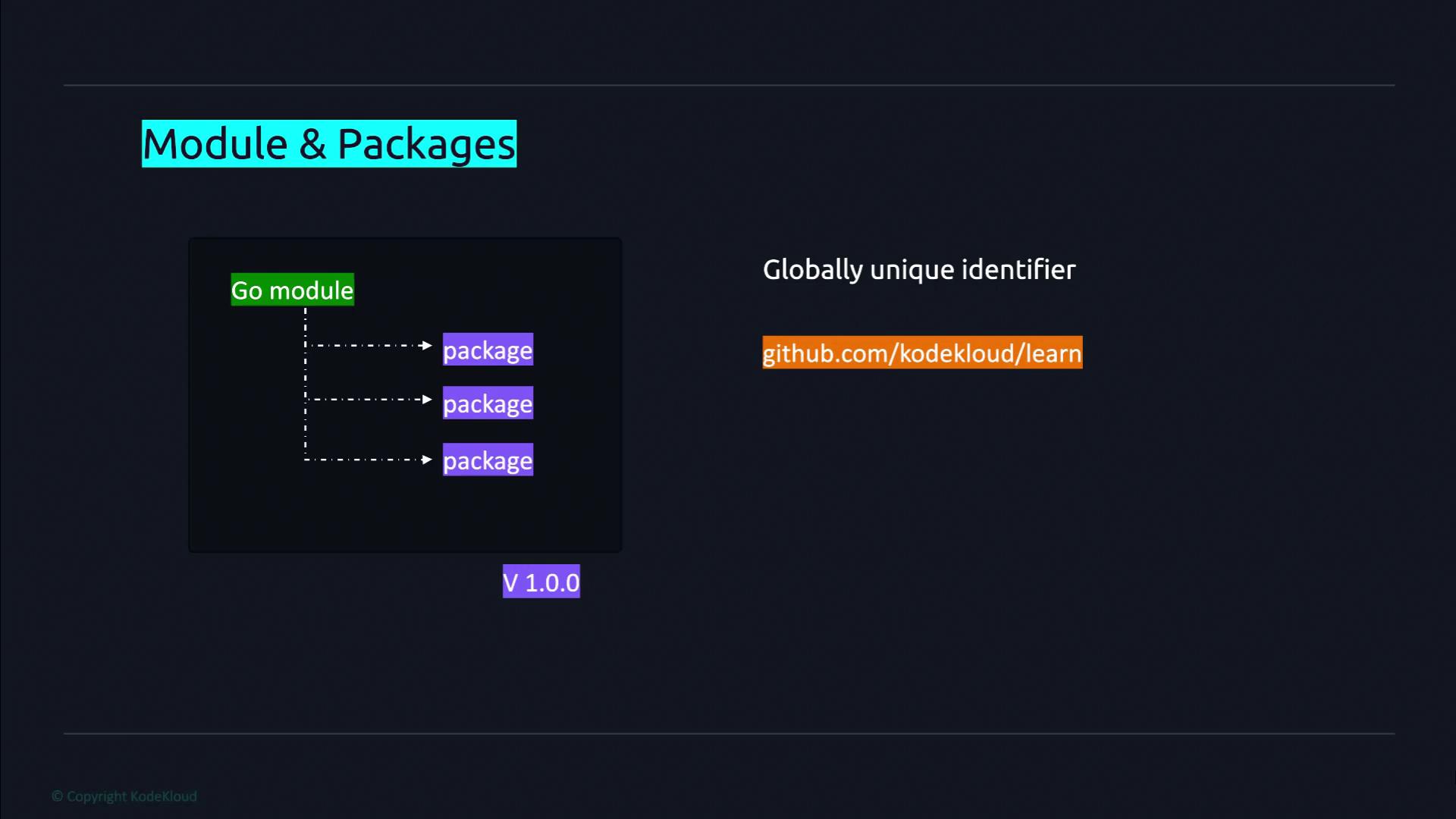
In summary, Go code is structured into packages grouped into modules. A module not only organizes code but also specifies the dependencies needed to run the code, including the Go version and other modules, as recorded in the go.mod file.

Creating a Go Module
Follow these steps to create a new Go module for your project:
Navigate to Your Source Code Directory:
Open your terminal and change to the directory where your source code is stored.Create a New Project Directory:
For this lesson, we name the project "learn". Execute the following command:mkdir learnEnter the Project Directory:
Change into the newly created directory:cd learnInitialize the Go Module:
Declare the directory as a Go module by runninggo mod initwith a globally unique module path. While paths likegithub.com/yourusername/yourrepositoryare common, we will useexample.com/learnfor this lesson:go mod init example.com/learnThe output should confirm the creation of the
go.modfile:go: creating new go.mod: module example.com/learn
Now, your learn directory is configured as a Go module, complete with a go.mod file. This file will later help manage dependencies and specify the Go version required for your project.
Next Steps
In upcoming lessons, we will dive deeper into the structure and functionalities of the go.mod file, exploring how it manages dependencies and versioning for Go projects.
Thank you for learning with us!
Watch Video
Watch video content