Building on Jenkins’ extensible agent model, this guide demonstrates how to refactor an existing Solar System Pipeline so that all Node.js–based steps run inside a single Kubernetes Pod, while Docker builds and security scans execute on the controller node.
1. Current Jenkinsfile Using agent any The legacy Jenkinsfile relies on agent any, which executes every stage on the default executor. Here’s a simplified snippet:
pipeline { agent any tools { // e.g., nodejs 'node-18' } environment { MONGO_URI = "mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData" MONGO_DB_CREDS = credentials( 'mongo-db-credentials' ) MONGO_USERNAME = credentials( 'mongo-db-username' ) MONGO_PASSWORD = credentials( 'mongo-db-password' ) SONAR_SCANNER_HOME = tool 'sonarqube-scanner-610' GITEA_TOKEN = credentials( 'gitea-api-token' ) } options { timestamps() buildDiscarder(logRotator( daysToKeepStr : '7' )) } stages { stage( 'Installing Dependencies' ) { options { timestamps() } steps { sh 'npm install' } } // ...additional stages... } }
This approach can lead to inconsistent environments across stages and requires pre-installed tools on every Jenkins agent.
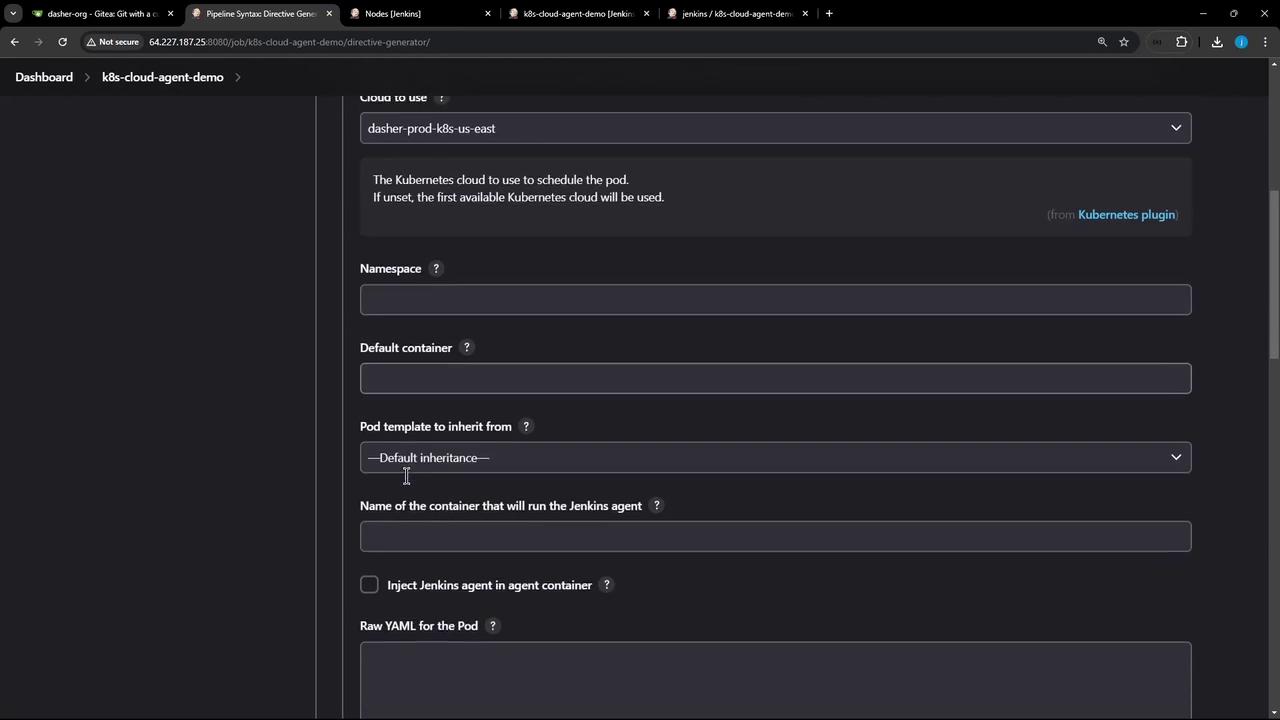
2. Defining a Kubernetes Pod Template Create a Pod definition file named k8s-agent.yaml at the repository root. This template spins up two Node.js containers, defaulting to node-18:
apiVersion : v1 kind : Pod spec : containers : - name : node-18 image : node:18-alpine command : [ "cat" ] tty : true - name : node-19 image : node:19-alpine command : [ "cat" ] tty : true
The command: ["cat"] and tty: true settings keep the container alive for Jenkins to execute steps interactively.
3. Referencing the Pod in Your Jenkinsfile Update your Jenkinsfile header to leverage the Kubernetes cloud and point to the Pod template:
pipeline { agent { kubernetes { cloud 'dasher-prod-k8s-us-east' yamlFile 'k8s-agent.yaml' defaultContainer 'node-18' } } tools { // e.g., nodejs 'node-18' } environment { MONGO_URI = "mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData" MONGO_DB_CREDS = credentials( 'mongo-db-credentials' ) MONGO_USERNAME = credentials( 'mongo-db-username' ) MONGO_PASSWORD = credentials( 'mongo-db-password' ) SONAR_SCANNER_HOME = tool 'sonarqube-scanner-610' GITEA_TOKEN = credentials( 'gitea-api-token' ) } options { timestamps() timeout( time : 1 , unit : 'HOURS' ) } stages { // Defined next... } }
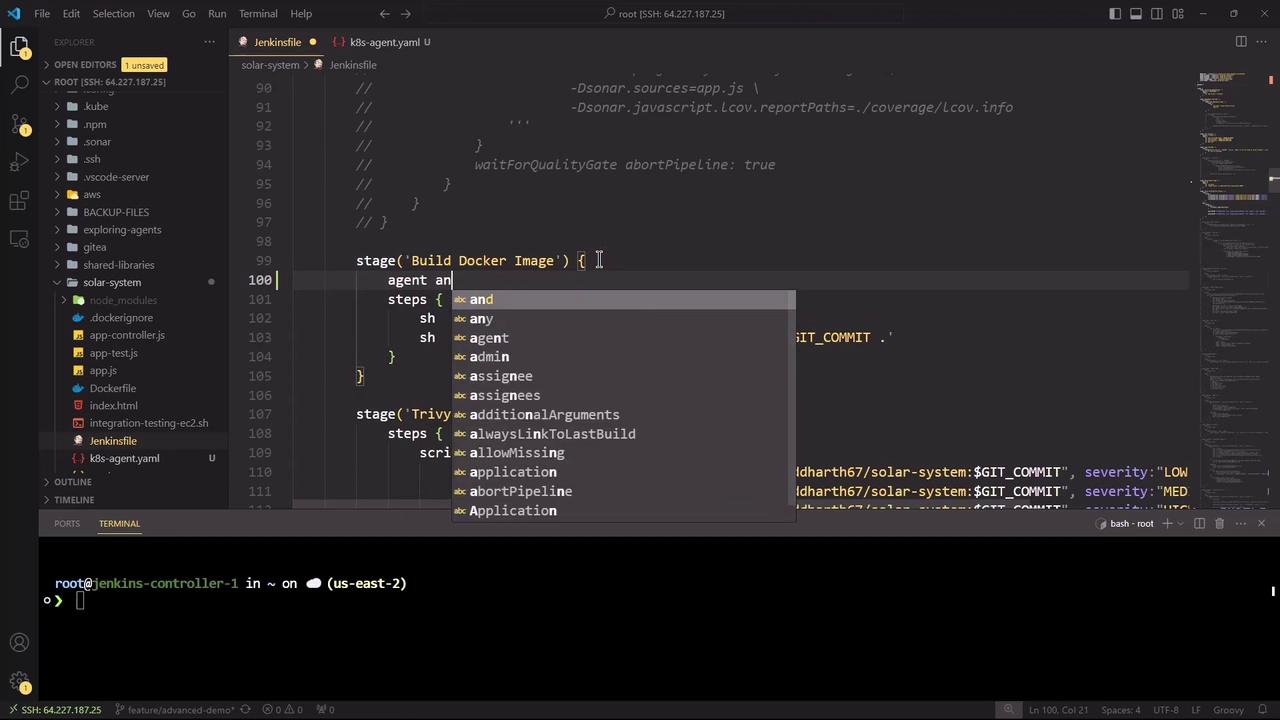
4. Configuring Node.js–Based Stages With the Kubernetes Pod in place, all Node.js stages execute inside node-18:
stages { stage( 'Installing Dependencies' ) { options { timestamps() } steps { sh 'node -v' sh 'npm install --no-audit' } } stage( 'Dependency Scanning' ) { parallel { stage( 'NPM Dependency Audit' ) { steps { sh ''' node -v npm audit --audit-level=critical echo $? ''' } } } } stage( 'Unit Testing' ) { options { retry( 2 ) } steps { sh 'node -v' sh 'npm test' } } stage( 'Code Coverage' ) { steps { catchError( buildResult : 'SUCCESS' , message : 'Coverage issues will be fixed later' ) { sh 'node -v' sh 'npm run coverage' } } } stage( 'Build Docker Image' ) { agent any steps { sh 'printenv' sh 'docker build -t siddharth67/solar-system:$GIT_COMMIT .' } } stage( 'Trivy Vulnerability Scanner' ) { agent any steps { script { trivyScanScript . vulnerability( imageName : "siddharth67/solar-system: $GIT_COMMIT " , severity : "LOW" ) trivyScanScript . vulnerability( imageName : "siddharth67/solar-system: $GIT_COMMIT " , severity : "MED" ) trivyScanScript . vulnerability( imageName : "siddharth67/solar-system: $GIT_COMMIT " , severity : "HIGH" ) } } } }
Push your changes to trigger the updated pipeline automatically.
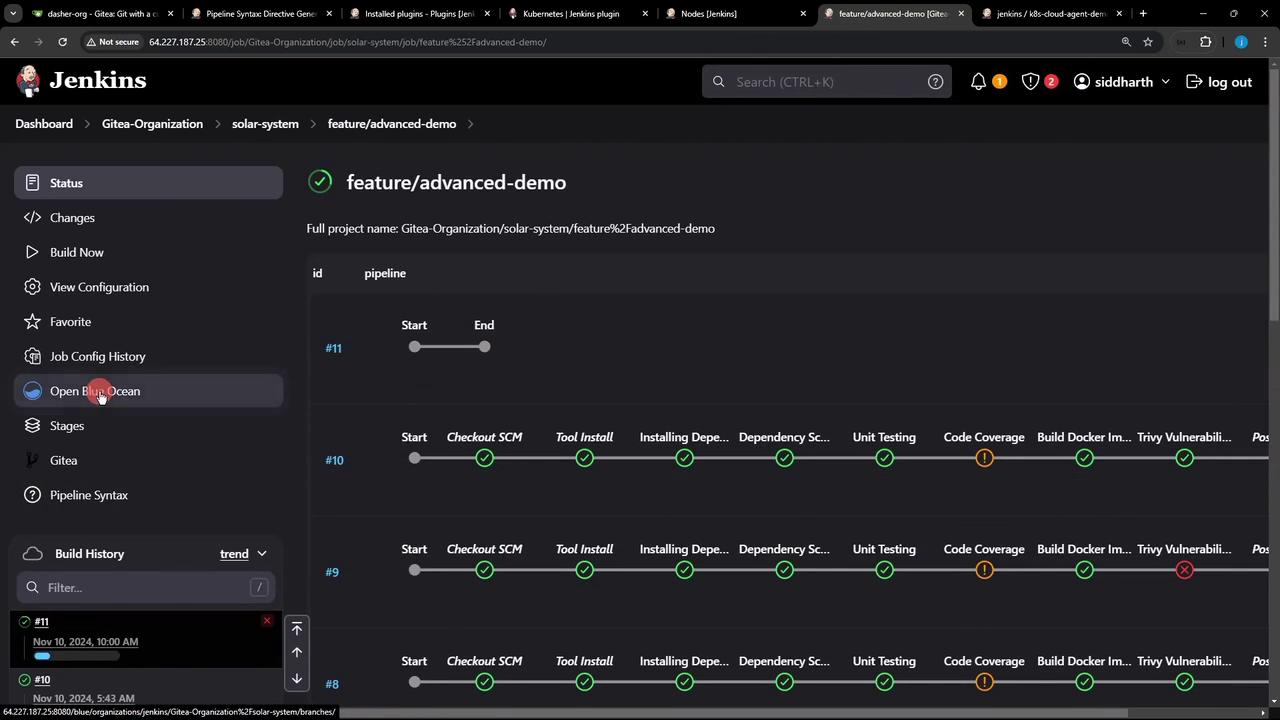
5. Observing the Refactored Pipeline In Blue Ocean or the classic Jenkins UI, the run displays each Kubernetes-backed stage:
Once execution completes, the full pipeline view confirms success across all stages:
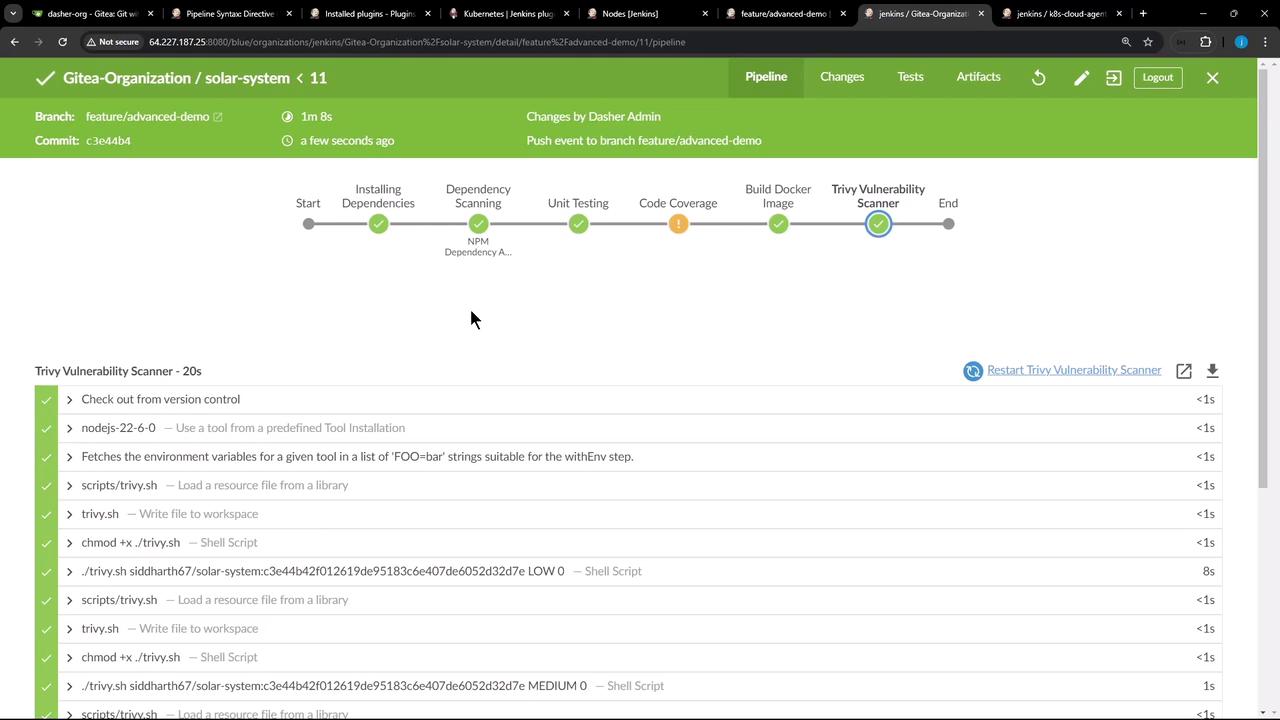
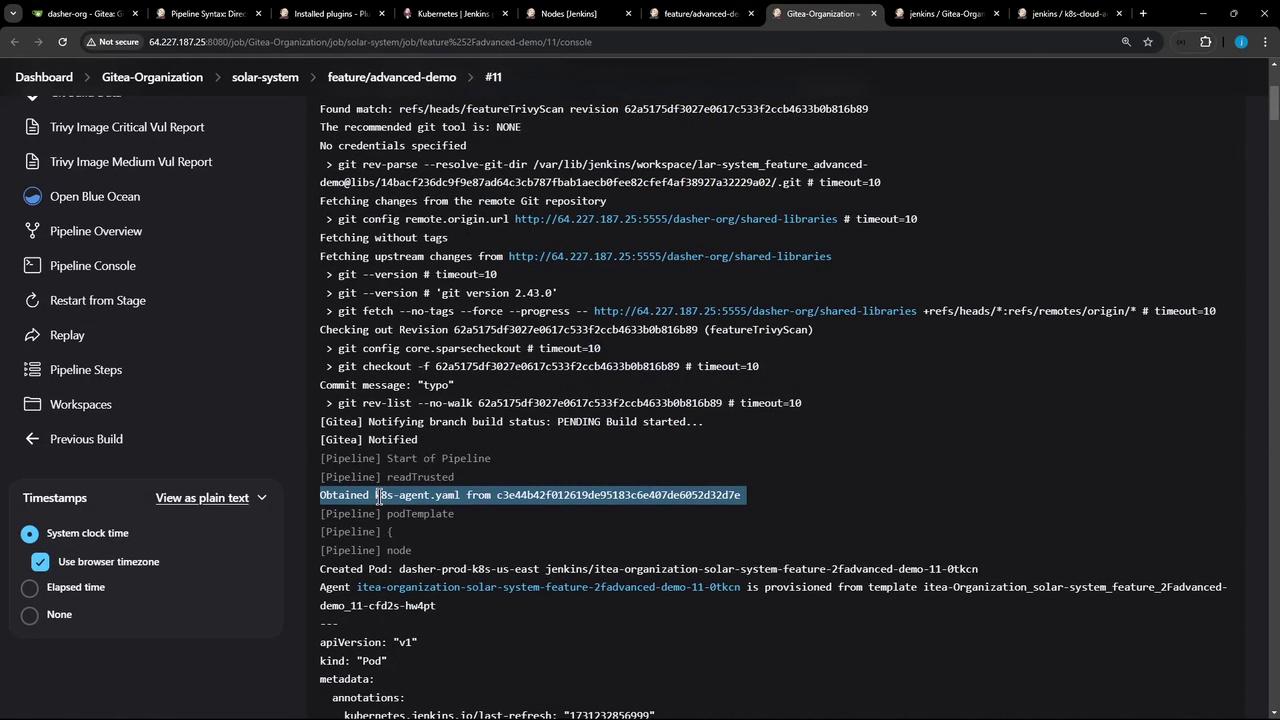
6. Verifying the Console Output The Jenkins console log provides details on Pod creation and step execution:
> git --version # git version 2.30.2 > git fetch --no-tags --force --progress https://gitea-server/credentials > git checkout -f 5ea4402af016919de95183e847d60b321d2fe8d > git rev-list --no-walk 5ea4402af016919de95183e847d60b321d2fe8d
Inside the node-18 container:
+ node -v v18.20.4 + npm install --no-audit added 358 packages in 4s + npm audit --audit-level=critical # (audit results) + echo 0 0 + node -v v18.20.4 + npm test + node -v v18.20.4 + npm run coverage # (coverage report)
All Node.js stages share an emptyDir volume, so dependencies persist across steps without reinstallation.
By consolidating Node.js workloads into a single Kubernetes Pod and delegating Docker builds and vulnerability scans to the controller, this solution ensures consistency, reduces setup time, and leverages cloud-native best practices.
Links and References