Advanced Jenkins
Shared Libraries in Jenkins
Introduction to Shared Libraries
Jenkins Shared Libraries enable teams to centralize reusable Groovy scripts and pipeline logic in a single, version-controlled repository. By defining common steps—such as notifications, build commands, or deployment tasks—you can apply the DRY principle, reduce duplication, and ensure consistency across all your CI/CD pipelines.

Consider a typical Jenkinsfile for a Node.js project:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
sh 'npm install'
sh 'npm run build'
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
sh 'npm test'
}
}
}
}
Without a Shared Library, you’d copy and paste this snippet into every repository—leading to:
| Problem | Impact |
|---|---|
| Duplication | Hard to maintain multiple Jenkinsfiles |
| Inconsistency | Different pipelines drift over time |
| Complexity | Updates become error-prone |

By extracting common logic—like setup, notifications, or deployment—into a central repository, you get:
- Better maintainability
- Unified pipeline behavior
- Easier on-boarding for new team members
Example: Centralizing a Welcome Message
Imagine your DevOps team wants every pipeline to greet developers:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Welcome') {
steps {
sh 'echo Welcome to the DevOps team from Dasher Organization'
}
}
// ...
}
}
When “Dasher” rebrands to “KodeKloud,” updating dozens of Jenkinsfiles is labor-intensive. Instead, create a welcome.groovy step in your Shared Library:
// vars/welcome.groovy
def call() {
sh 'echo Welcome to the DevOps team from KodeKloud Organization'
}
Then, load and invoke this function in your Jenkinsfile:
@Library('kode-kloud-shared-library') _
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Welcome') {
steps {
welcome()
}
}
// ...
}
}
Now, editing one file in the Shared Library updates every pipeline automatically.
Setting Up a Shared Library in Jenkins
To configure a Shared Library:
- Create a Git repository dedicated to your shared steps and utilities.
- In Jenkins, go to Manage Jenkins → Configure System → Global Pipeline Libraries.
- Click Add and specify:
- Name: A unique identifier (e.g.,
kode-kloud-shared-library) - Default Version: Branch or tag (e.g.,
main) - Retrieval Method: Modern SCM → Git URL
- Advanced Options: Allow overriding the default version, load implicitly, etc.
- Name: A unique identifier (e.g.,
Note
Make sure Jenkins has read access to your Git repository. If you use credentials, add them under Manage Jenkins → Credentials.
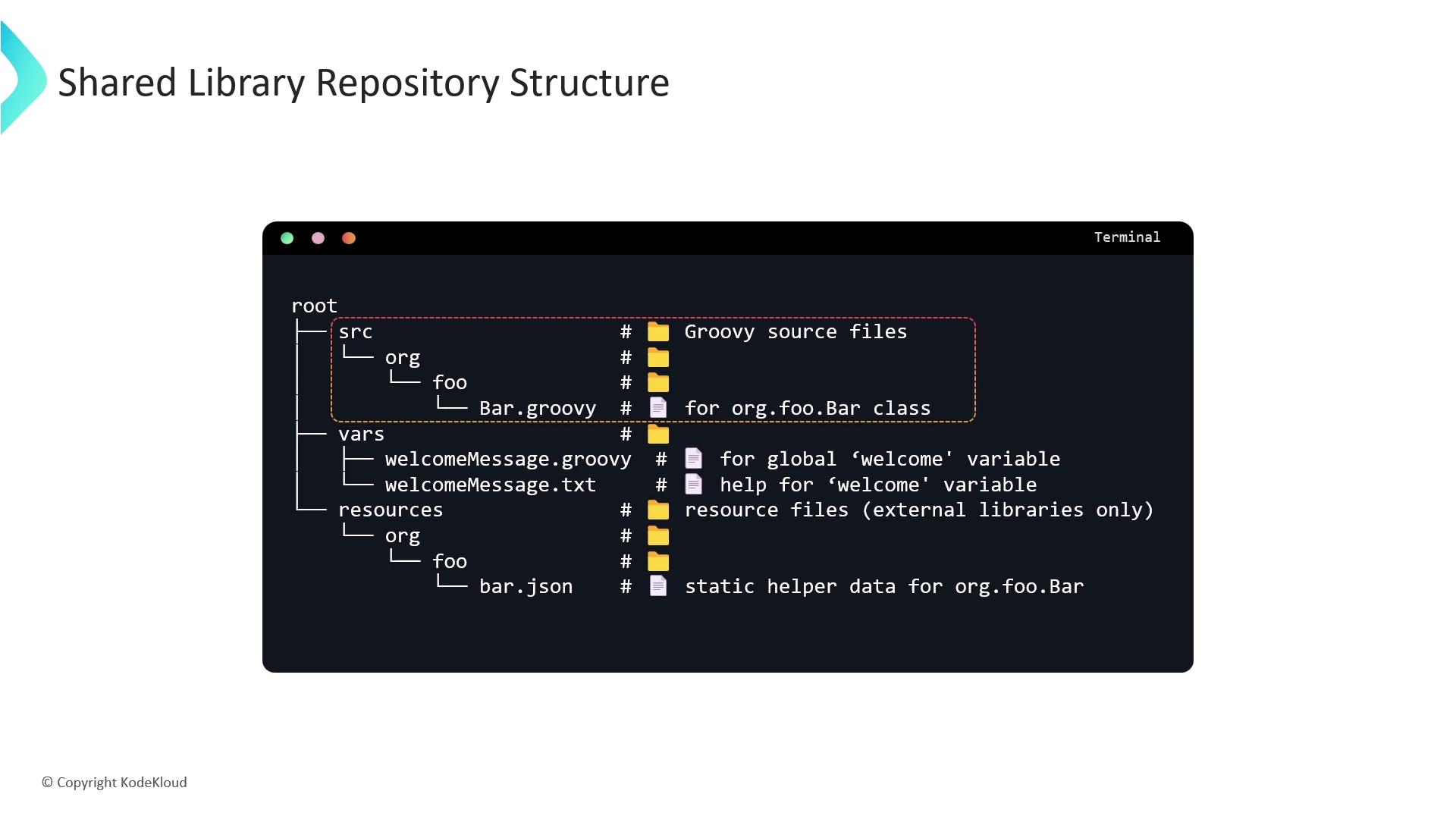
Repository Structure
A clear directory layout helps Jenkins locate your scripts:
(root)
├── src
│ └── org
│ └── foo
│ └── Bar.groovy # Optional: compiled Groovy classes
├── vars
│ ├── welcome.groovy # Defines the 'welcome' pipeline step
│ └── welcome.txt # Documentation for 'welcome'
└── resources
└── org
└── foo
└── bar.json # Optional: static resource files
| Directory | Purpose |
|---|---|
| src | (Optional) Groovy/Java classes |
| vars | Required: global pipeline steps (camelCase) |
| resources | (Optional) static files accessed via libraryResource |
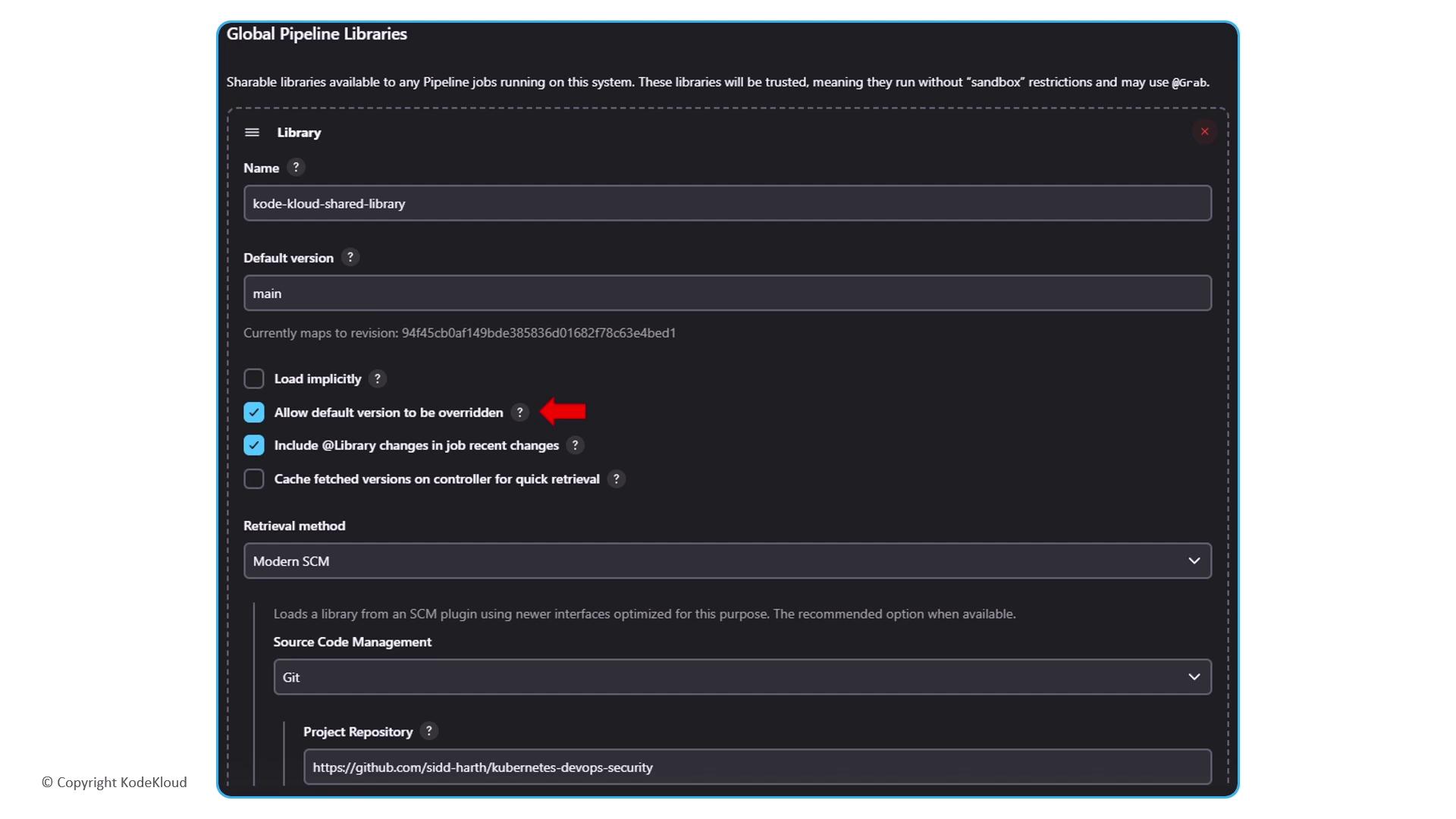
Configuring Global Pipeline Libraries
Once your repo is ready:
- Manage Jenkins → Configure System → Global Pipeline Libraries.
- Add Library with:
- Name:
kode-kloud-shared-library - Default Version:
main - Load implicitly (optional)
- SCM: Git URL and credentials
- Name:
Using Your Shared Library
In each Jenkinsfile, include the @Library annotation to load your shared code:
@Library('kode-kloud-shared-library') _
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Welcome') {
steps {
welcome()
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
// your build steps...
}
}
}
}
The welcome() step now references vars/welcome.groovy from your Shared Library, keeping pipelines concise and maintainable.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content