EC2 Instance States
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| Pending | AWS reserves capacity, initializes the instance, and performs setup operations. |
| Running | The instance is fully provisioned. You can connect via SSH/RDP, serve traffic, and access instance-store volumes. |
| Stopping | Triggered by a stop command; the OS shuts down gracefully and compute resources prepare for release. |
| Stopped | The instance is shut down. Compute charges stop, but EBS volumes, private IPs, and Elastic IPs remain allocated. |
| Shutting-down | Initiated by termination; AWS deallocates CPU, memory, and networking before deletion. |
| Terminated | The instance is permanently removed. All resources flagged for deletion (instance-store, default EBS) are cleaned up. |
Stopping an instance does not delete attached EBS volumes or Elastic IP addresses—you will continue to incur charges for those resources until you release them.
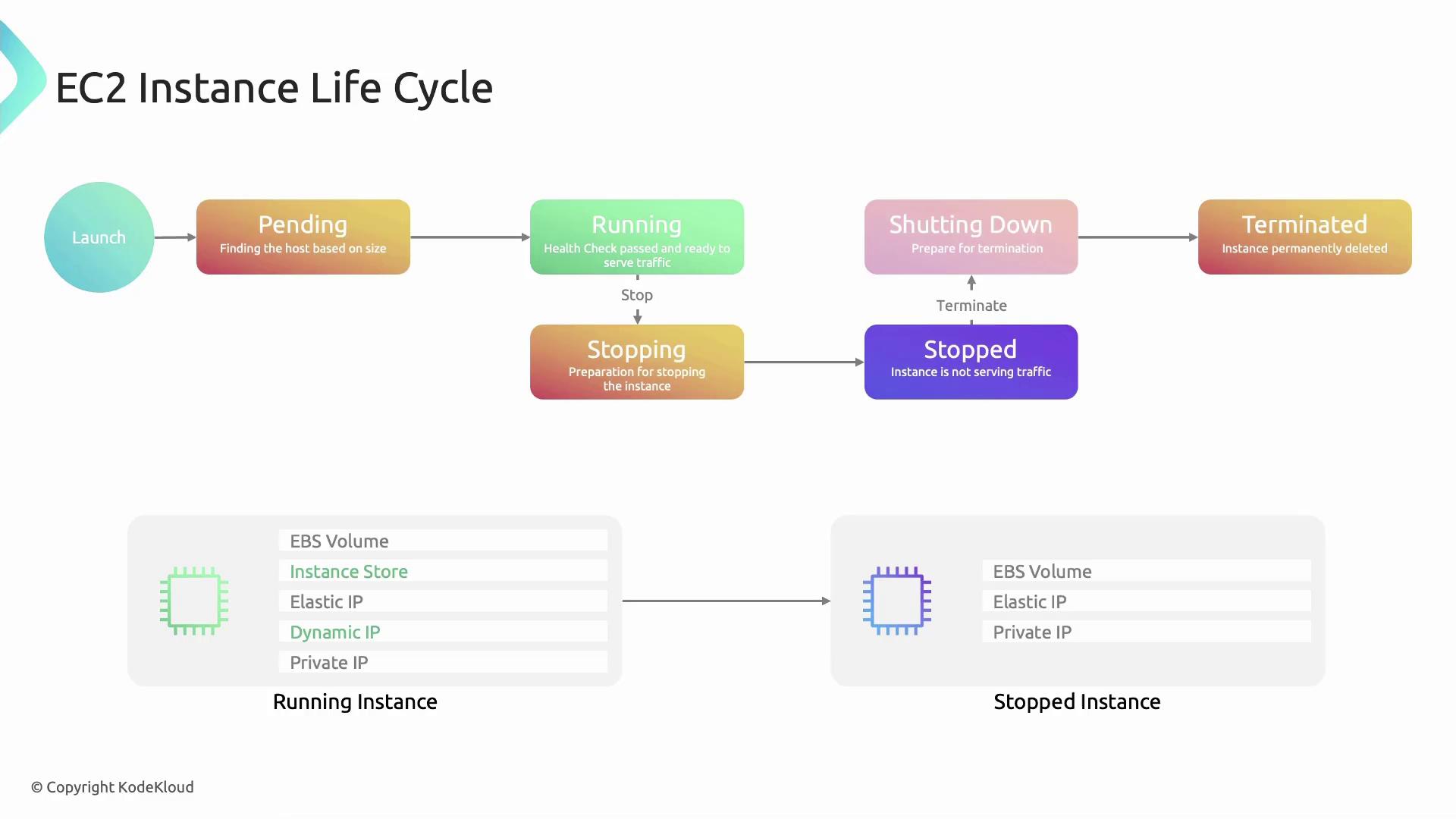
Detailed State Transitions
-
Pending
- AWS locates capacity for your chosen instance type.
- Resources are reserved, networking is configured, and the hypervisor initializes the VM.
-
Running
- Health checks complete and instance-store volumes attach.
- A public IP is assigned (if enabled at subnet level).
- Your applications can now serve traffic.
-
Stopping
- Issued via Console, AWS CLI (
aws ec2 stop-instances), or within the guest OS. - The guest OS performs a clean shutdown; the hypervisor marks resources for release.
- Issued via Console, AWS CLI (
-
Stopped
- Compute resources are released, halting billing for CPU and memory.
- Storage (EBS), private IP, and Elastic IP remain allocated.
-
Shutting-down
- Occurs when you terminate an instance from either the
runningorstoppedstate. - AWS deallocates virtual hardware; cleanup operations begin.
- Occurs when you terminate an instance from either the
-
Terminated
- The instance record is removed from your account.
- Instance-store volumes and default EBS volumes flagged for deletion are erased.
Edge Cases and Best Practices
Sending a terminate command is irreversible. Ensure you’ve backed up any critical data on instance-store volumes or unencrypted EBS volumes before terminating.
| Scenario | Behavior |
|---|---|
Termination issued during stopping or stopped | Instance immediately moves to shutting-down |
Health check failure in pending | AWS automatically issues a terminate signal |