Azure Kubernetes Service
CICD Workflow for AKS
Pull Based Workflow GitOps
Introduction to GitOps
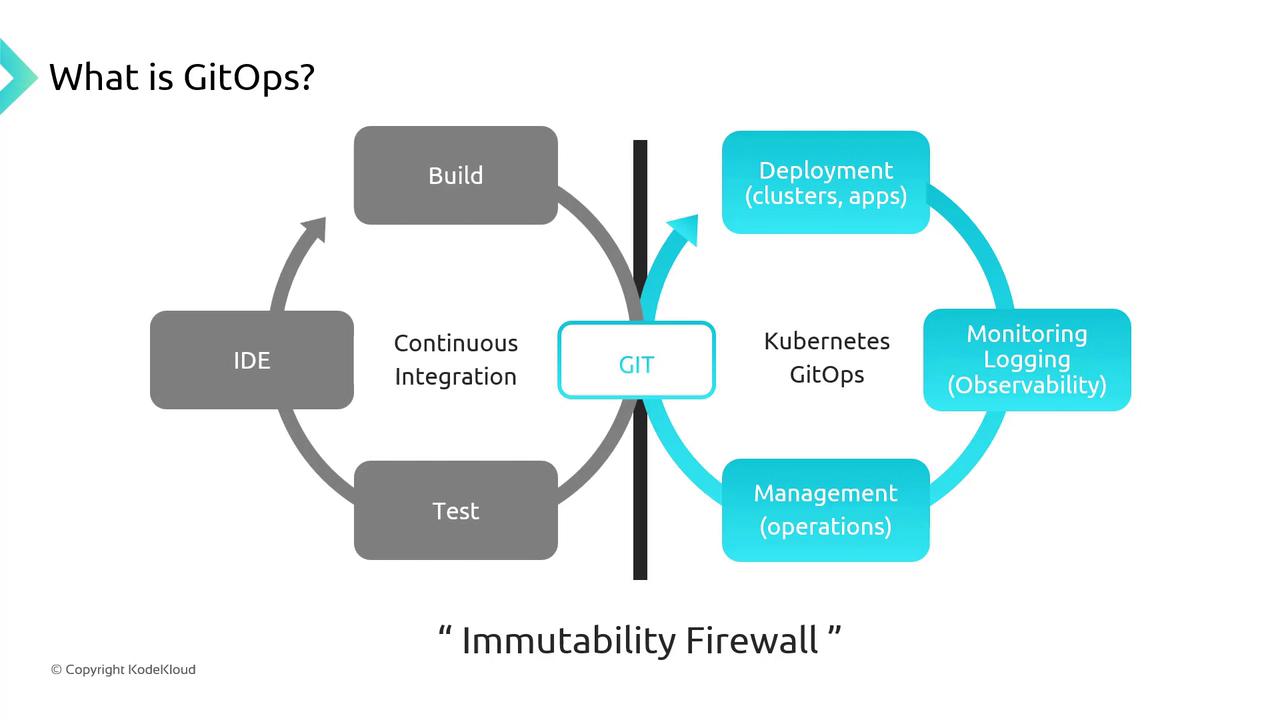
GitOps is a pull-based methodology for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD), where both application and infrastructure configurations are stored as code in a Git repository. Any desired state changes are made via Git commits, ensuring version-controlled deployments, easy auditing, and reliable rollbacks.
Note
The “Immutability Firewall” enforces separation between build artifacts and deployment manifests, guaranteeing consistent, reproducible releases.
When you push commits to your Git repo, a GitOps operator—such as Flux or Argo CD—detects updates and reconciles your AKS cluster to match the declared state automatically.
Push-Based vs. Pull-Based Workflows
In CI/CD, you can choose between push-based or pull-based (GitOps) models.
| Workflow | Trigger | Operator | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Push-Based | CI pipeline pushes to AKS | N/A | Immediate deployments, fast feedback | Harder to track drift, limited audit |
| Pull-Based | GitOps operator polls Git | Flux, Argo CD | Full audit trail, self-healing clusters | Sync interval adds slight delay |
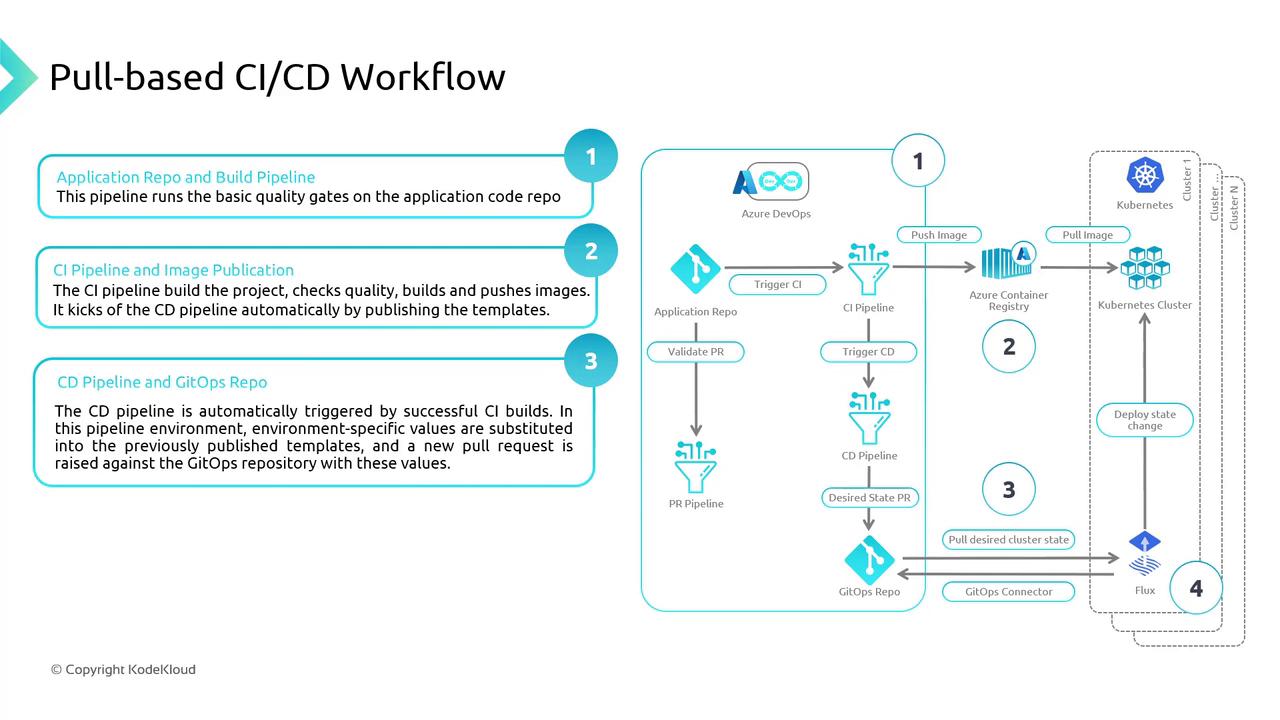
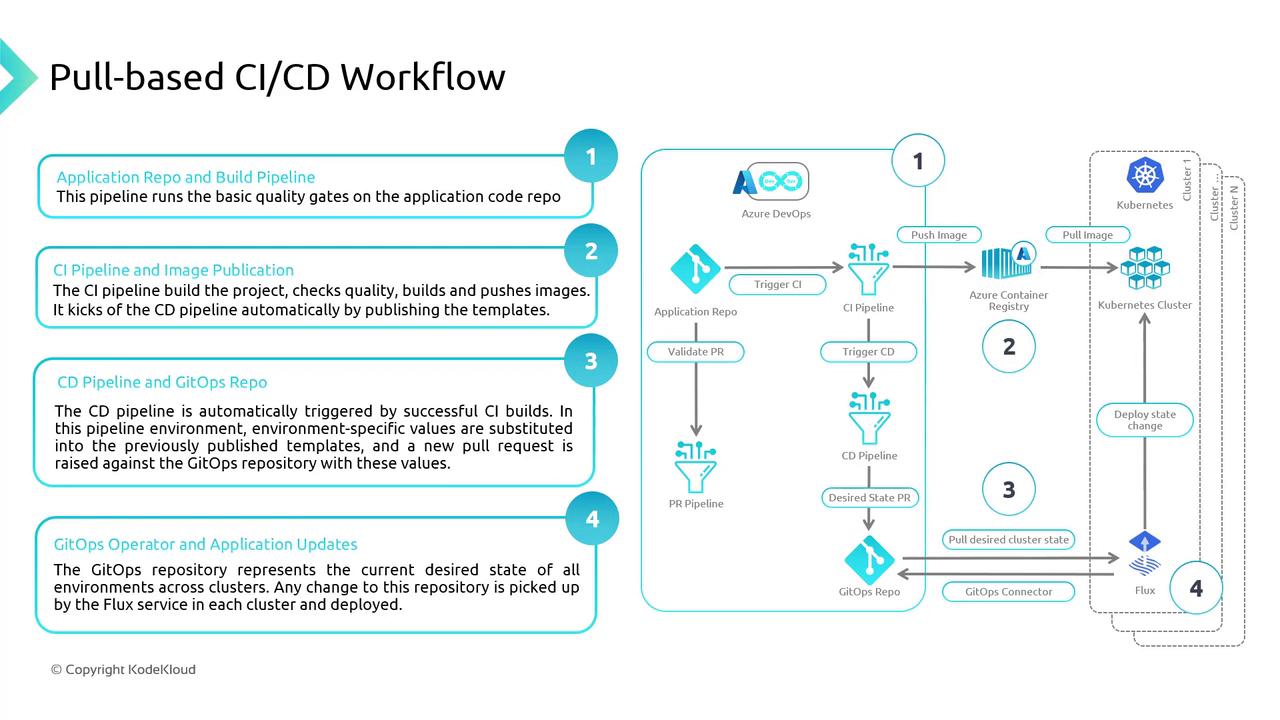
Pull-Based CI/CD Workflow for AKS
A typical GitOps pipeline for Azure Kubernetes Service involves:
- Source Control
Store application code and Kubernetes manifests in a Git repo. - CI Pipeline
Build, test, and push container images to Azure Container Registry (ACR). - CD Pipeline
Generate environment-specific YAMLs (e.g., via Kustomize) and commit them to Git. - GitOps Operator
Flux or Argo CD polls Git, detects changes, and applies the new state to AKS.
| Step | Azure Service | Artifact |
|---|---|---|
| Build & CI | Azure DevOps Pipelines | Docker images (ACR) |
| Configuration CD | Azure DevOps Releases | Kustomize overlays |
| Continuous Sync | Flux / Argo CD on AKS | Deployed Kubernetes resources |
Demonstration: Deploying a New AKS Cluster with GitOps
Follow these steps to provision an AKS cluster and configure GitOps using Azure Portal:
Create AKS Cluster
In the Azure Portal, select Kubernetes services → + Add.
Choose a new resource group, use default settings, then Review + Create → Create.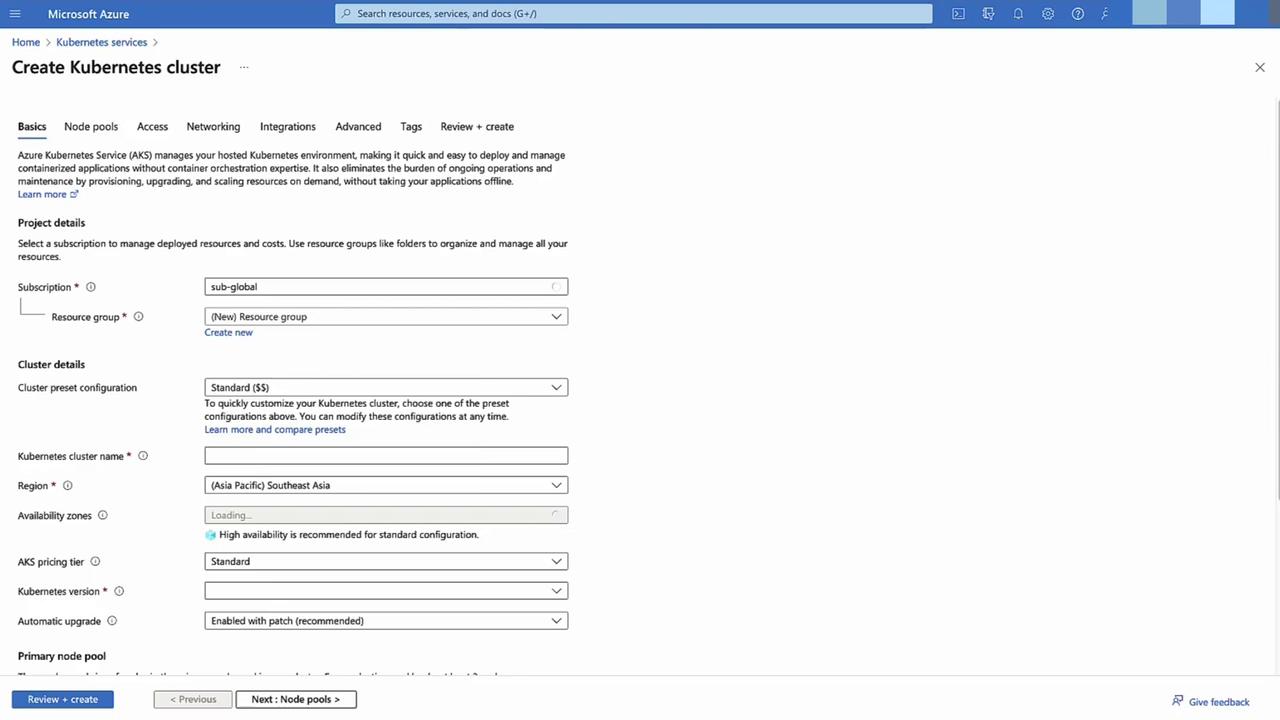
Fork and Prepare Your Git Repository
Open your forked repo (e.g.,aksflux) containing Flux YAMLs. In theinfrastructurefolder, inspectkustomization.yaml:apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization resources: - sources - nginxYou’ll later add
redisto demonstrate dynamic updates. Underapps/staging, maintain environment-specific overlays.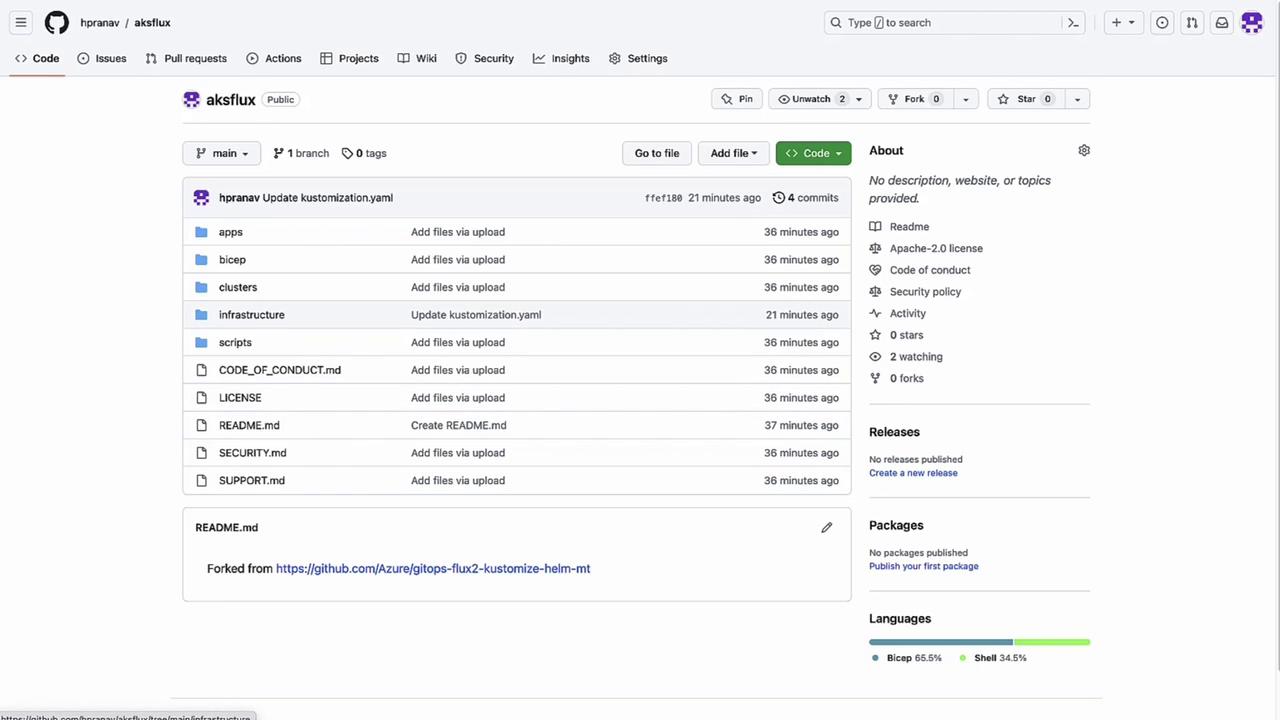
Verify Cluster Deployment
Once provisioning finishes, confirm status in Deployments.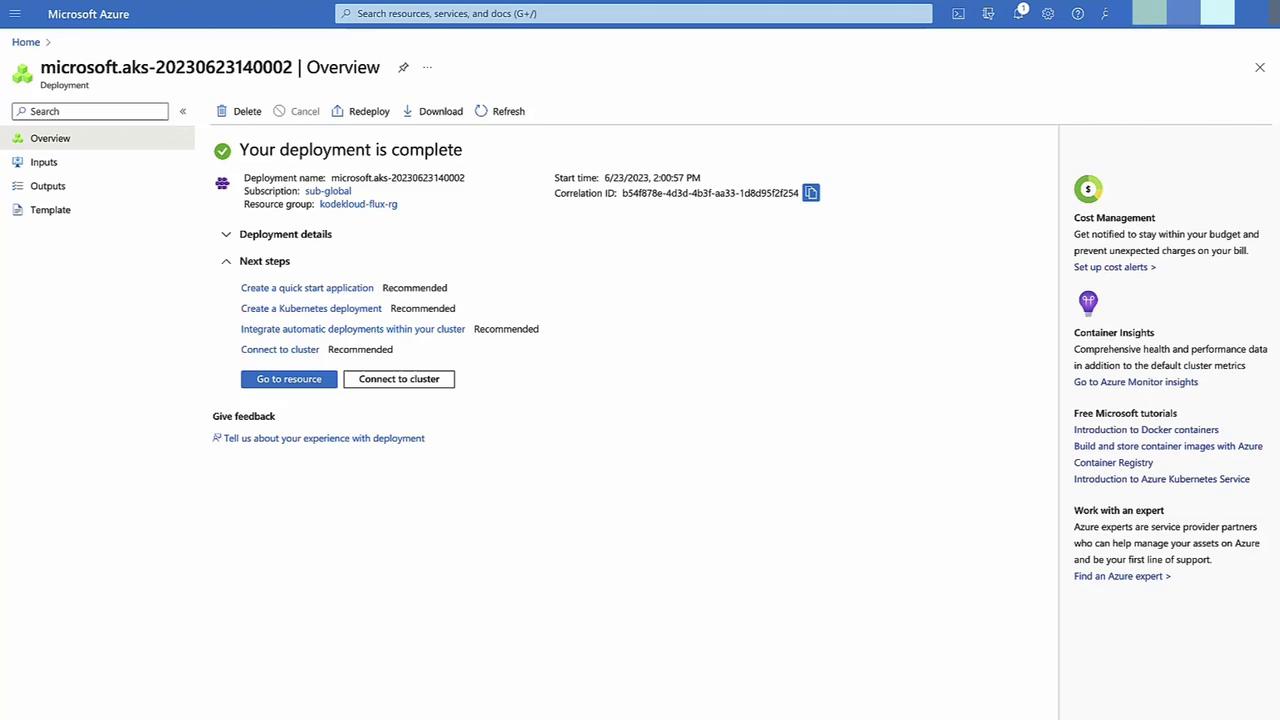
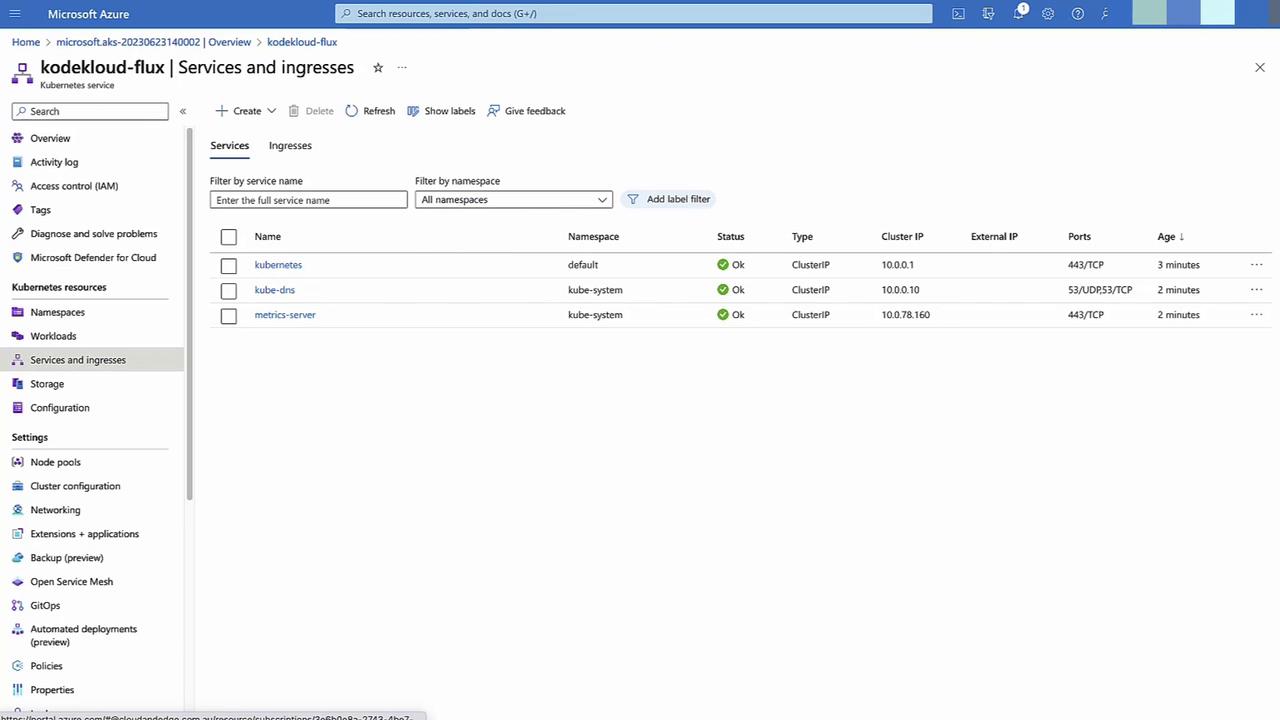
Inspect Default Namespaces & Services
In Namespace and services, view the default AKS resources.Configure GitOps in Azure Portal
Go to GitOps → + Configuration.- Name:
cluster-config - Scope: Cluster
- Namespace:
cluster-config
→ Next
Enter your public Git repo URL, branch
main, no auth required.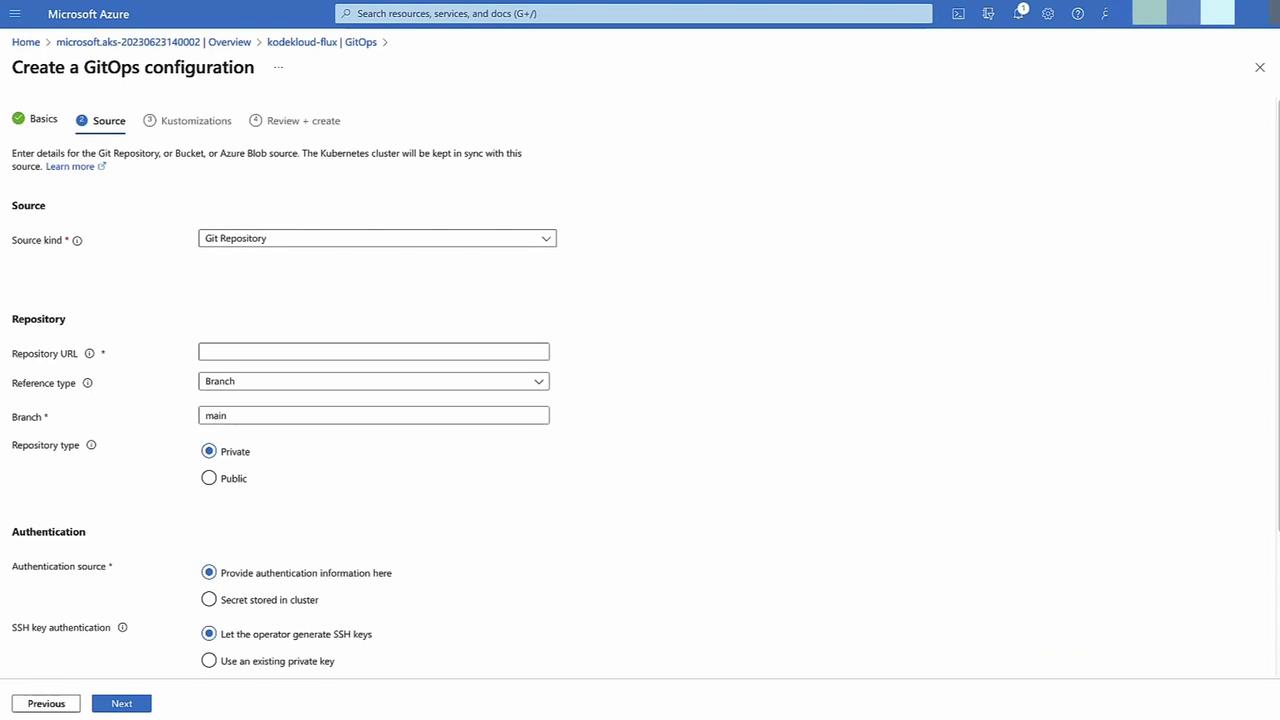
- Name:
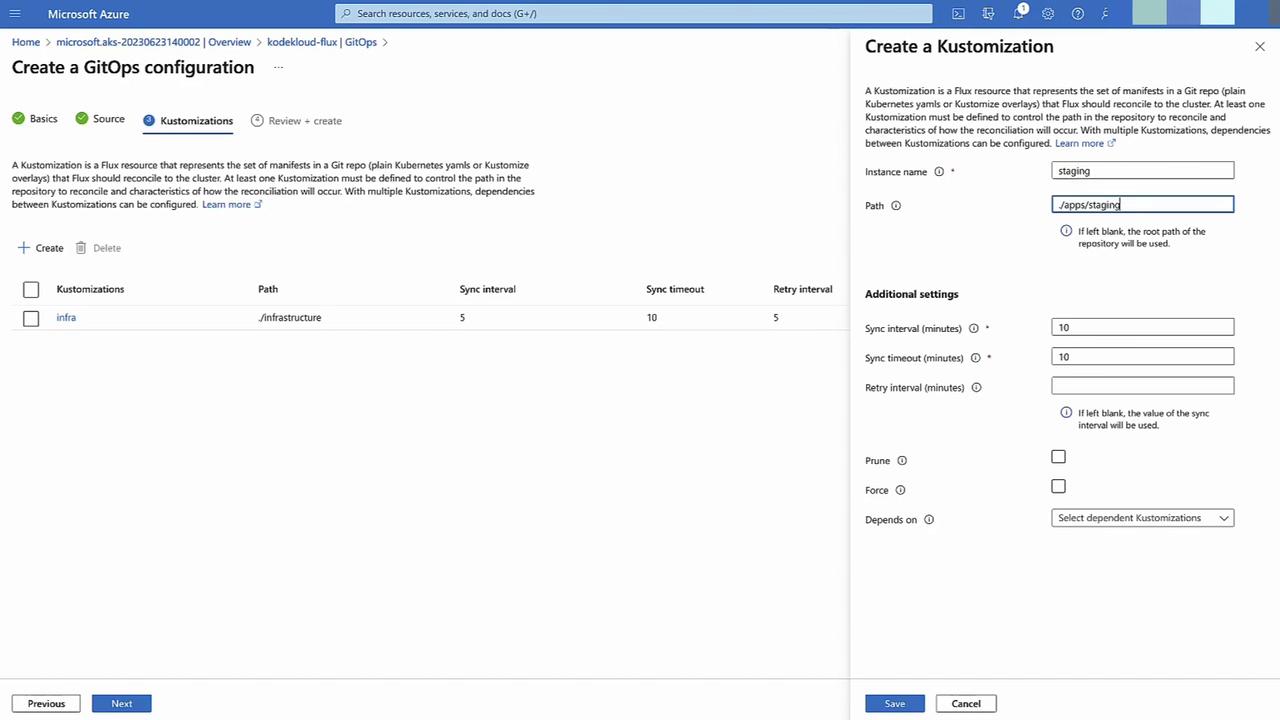
Define Kustomizations
- Sync interval: 5 minutes
- Infrastructure: path
infrastructure - Staging: path
apps/staging, depends oninfrastructure
Apply and Monitor
Click Create. Flux begins syncing—infrastructurewill reconcile first, thenstaging. Monitor compliance status in the GitOps pane.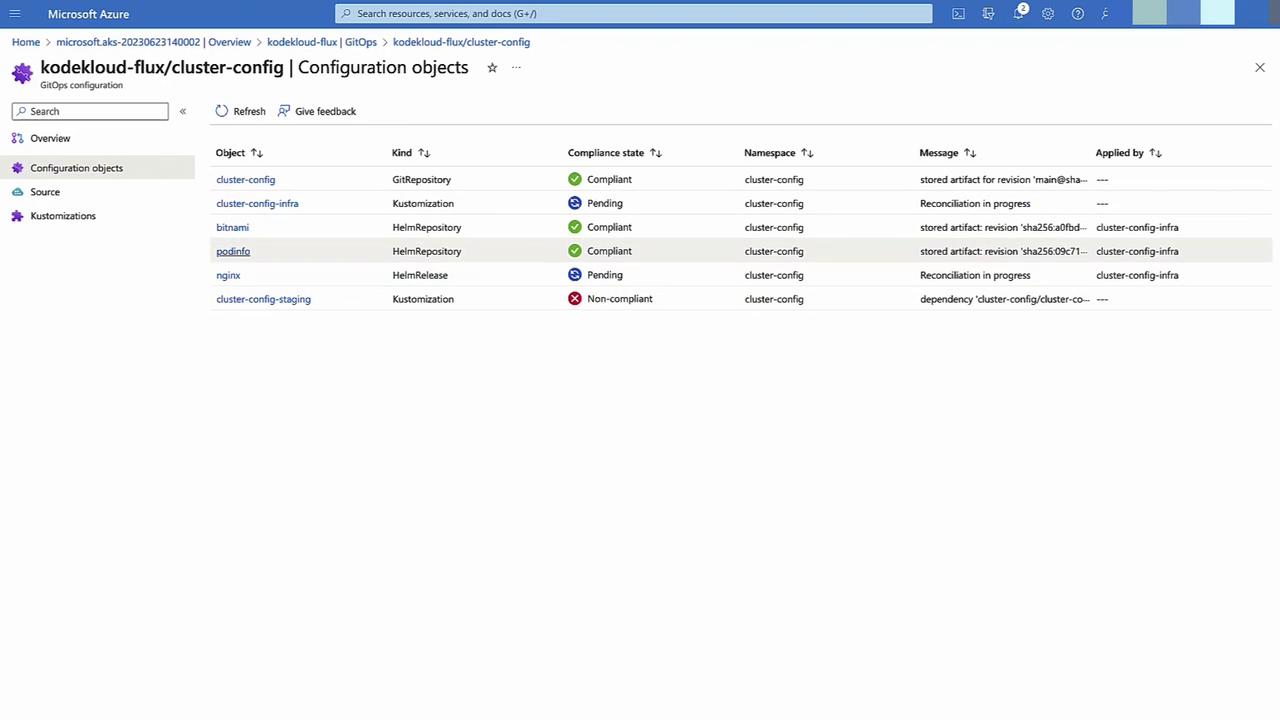
Validate Deployment
Return to Namespaces and Services to confirmnginx(and its namespace) is running.Demonstrate Drift Correction
In your repo, updateinfrastructure/kustomization.yaml:resources: - sources - nginx - redisCommit and push. Within 5 minutes, Flux deploys the Redis namespace and service.
With GitOps on AKS, you gain declarative, version-controlled deployments, self-healing infrastructure, and clear audit trails for every change.
Watch Video
Watch video content