The in-memory database is intended for development and testing only. All registered components and services are cleared whenever Backstage restarts.
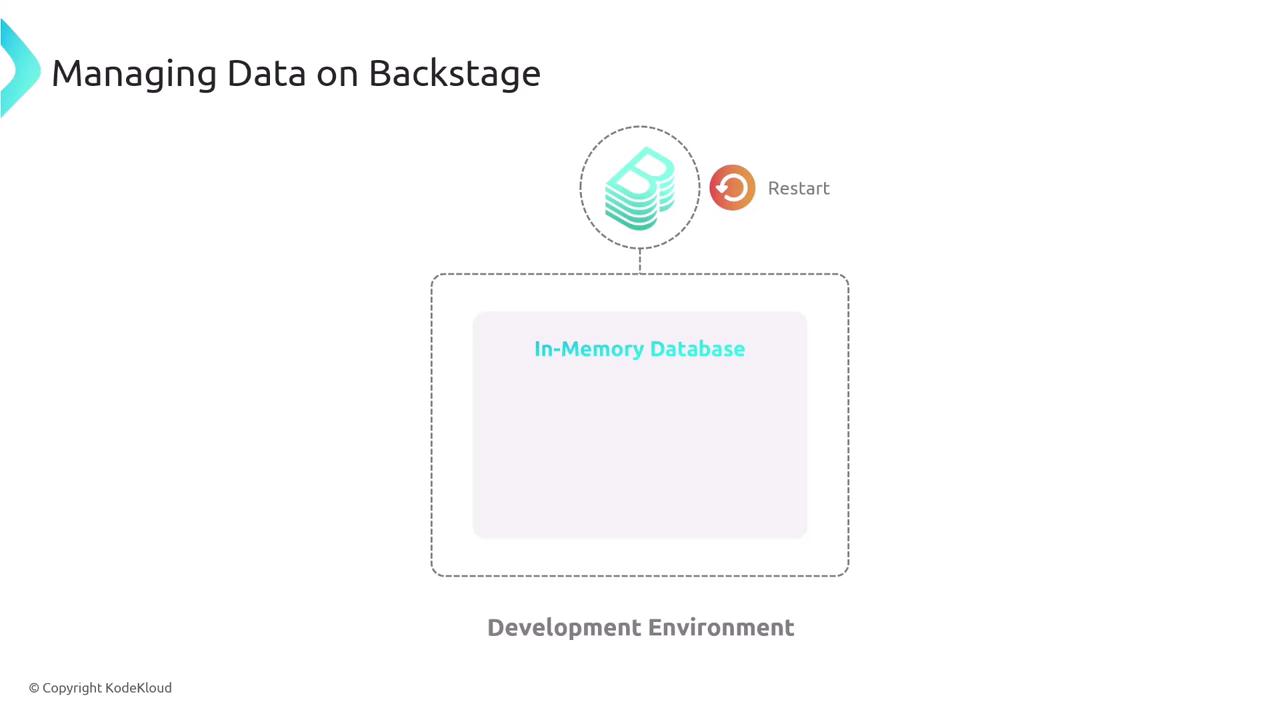
In-Memory Database (Development)
- Quick to set up: No external dependencies required.
- Ideal for prototyping and experimentation.
- Volatile storage: data is lost on every restart.
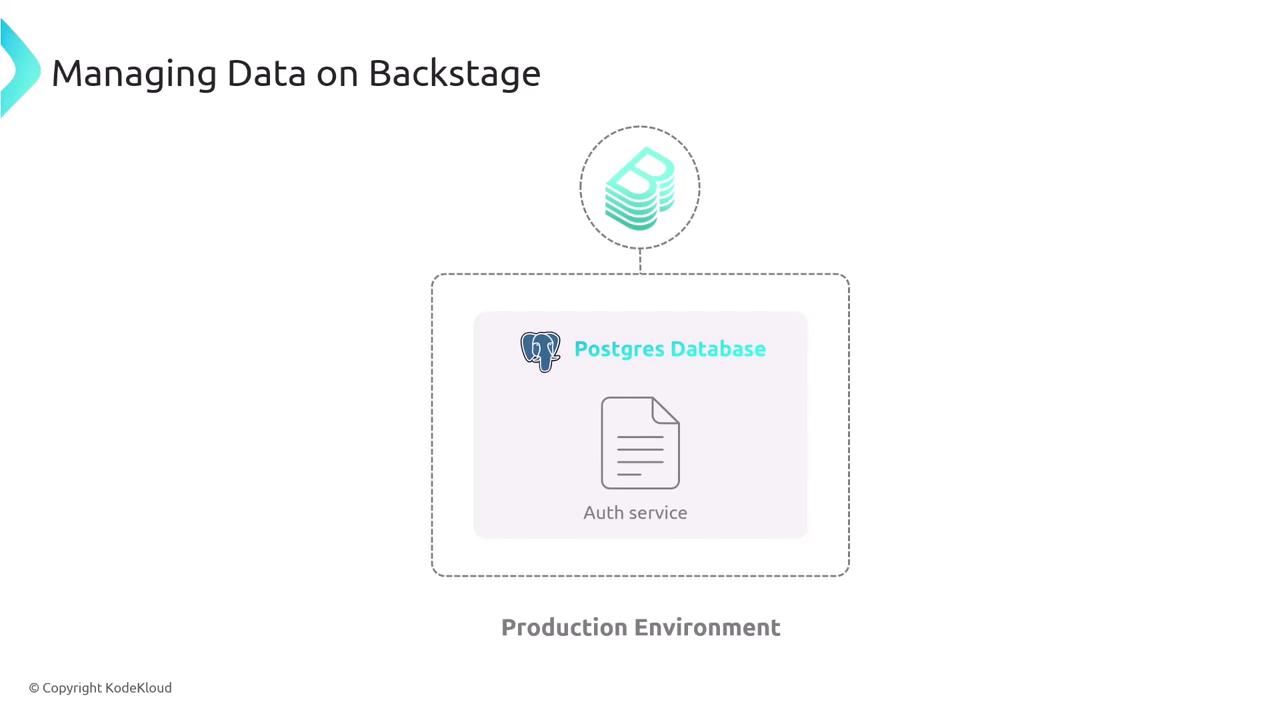
Production Database (PostgreSQL)
| Feature | In-Memory Database | PostgreSQL (Production) |
|---|---|---|
| Persistence | Volatile | Persistent across restarts |
| Setup Complexity | Minimal | Requires external database configuration |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
| Recommended Use | Development/Test | Production |
Later in this lesson, you’ll find step-by-step instructions on integrating PostgreSQL with Backstage, including connection settings and schema migrations.