
Honeypots
Honeypots are decoy systems that mimic real servers, workstations, or network services. Their primary function is to attract attackers, enabling security teams to detect, analyze, and understand malicious activity. By deploying honeypots, organizations gain valuable insights into cyber threats and can reinforce their overall security posture.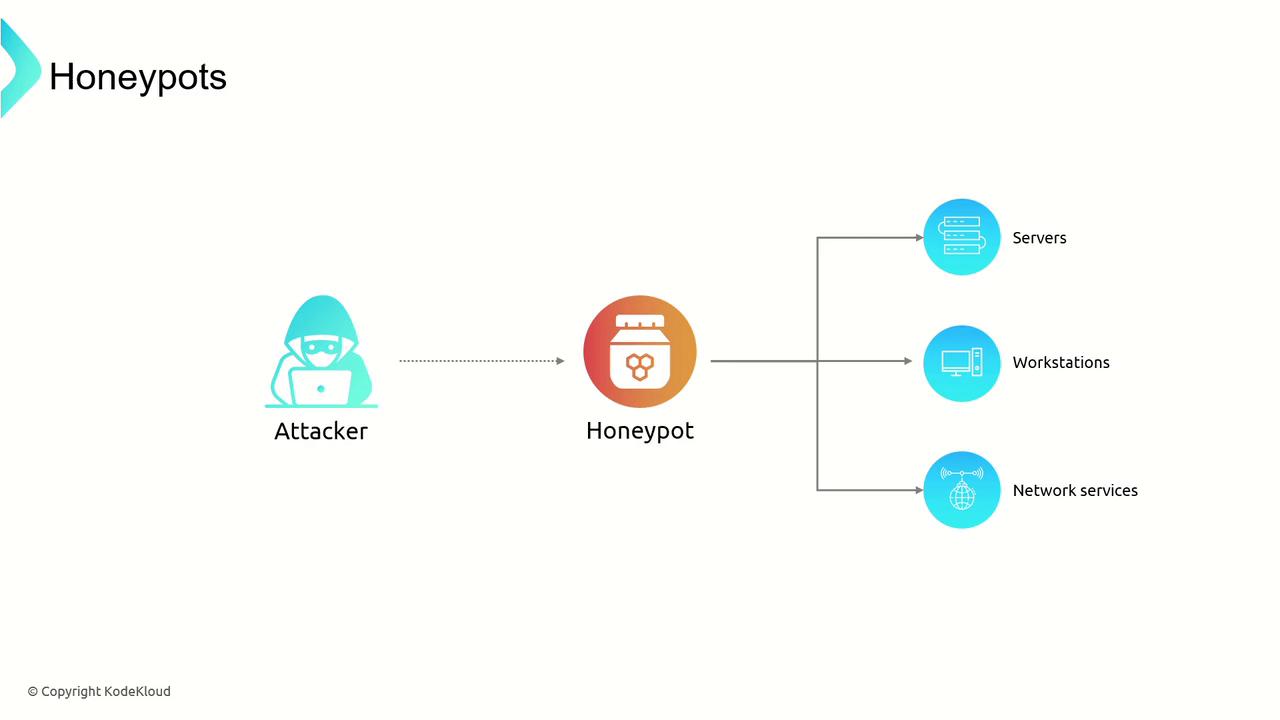
Honeynets
A honeynet takes the concept of a honeypot a step further by simulating an entire network environment. This realistic setup provides a holistic view of attacker behavior as they interact with multiple simulated systems, making it easier to observe complex attacks and trace intruder tactics.How Honeynets Work
Honeynets are configured to replicate operational networks with a mix of devices, servers, and services. Every interaction—from network traffic and system commands to application-level events—is meticulously monitored and logged. This comprehensive data collection helps analysts decode attacker techniques, tactics, and procedures (TTPs), fueling the development of robust cybersecurity defenses.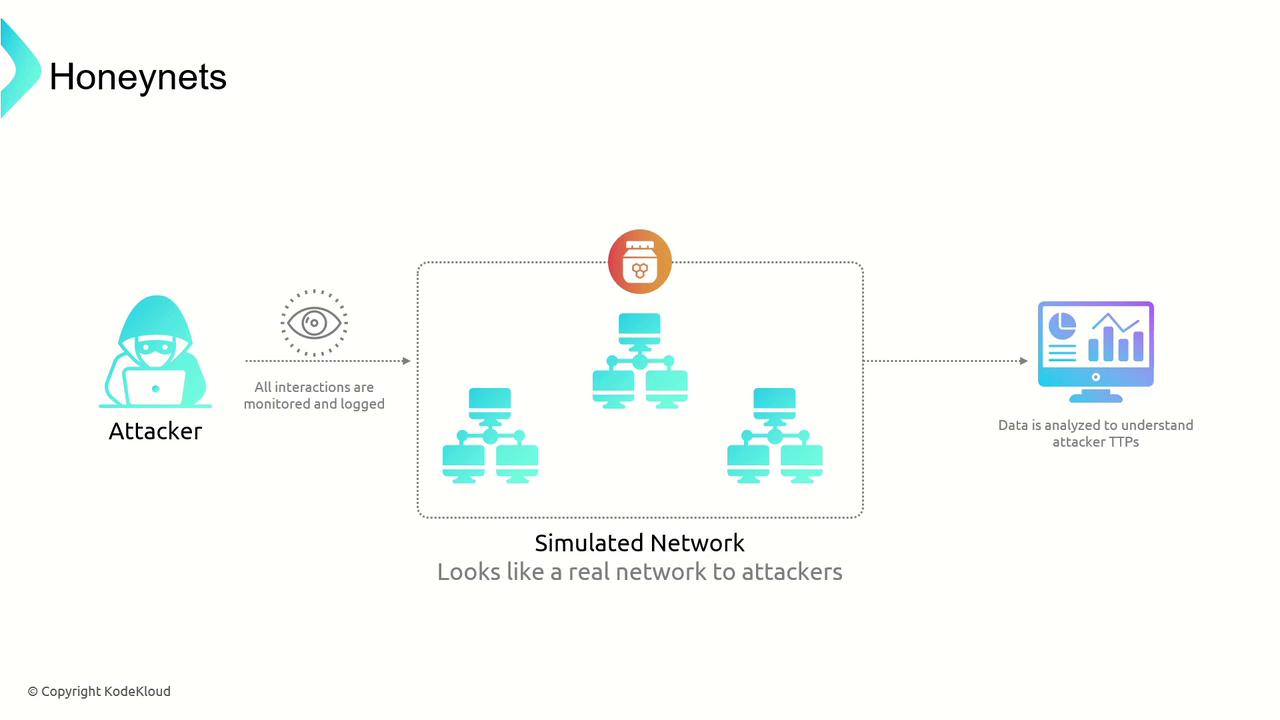
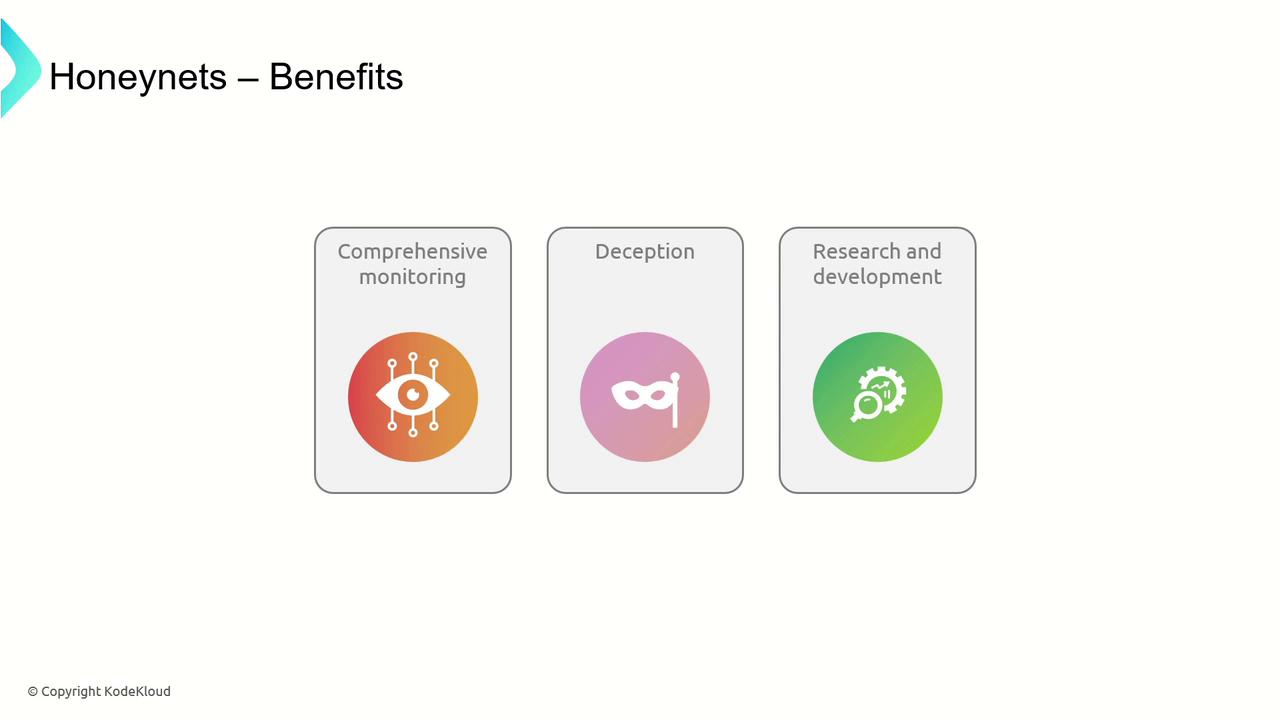
- Comprehensive monitoring of network activities.
- Enhanced deception using realistic decoy systems.
- Valuable research opportunities for developing new defense strategies.
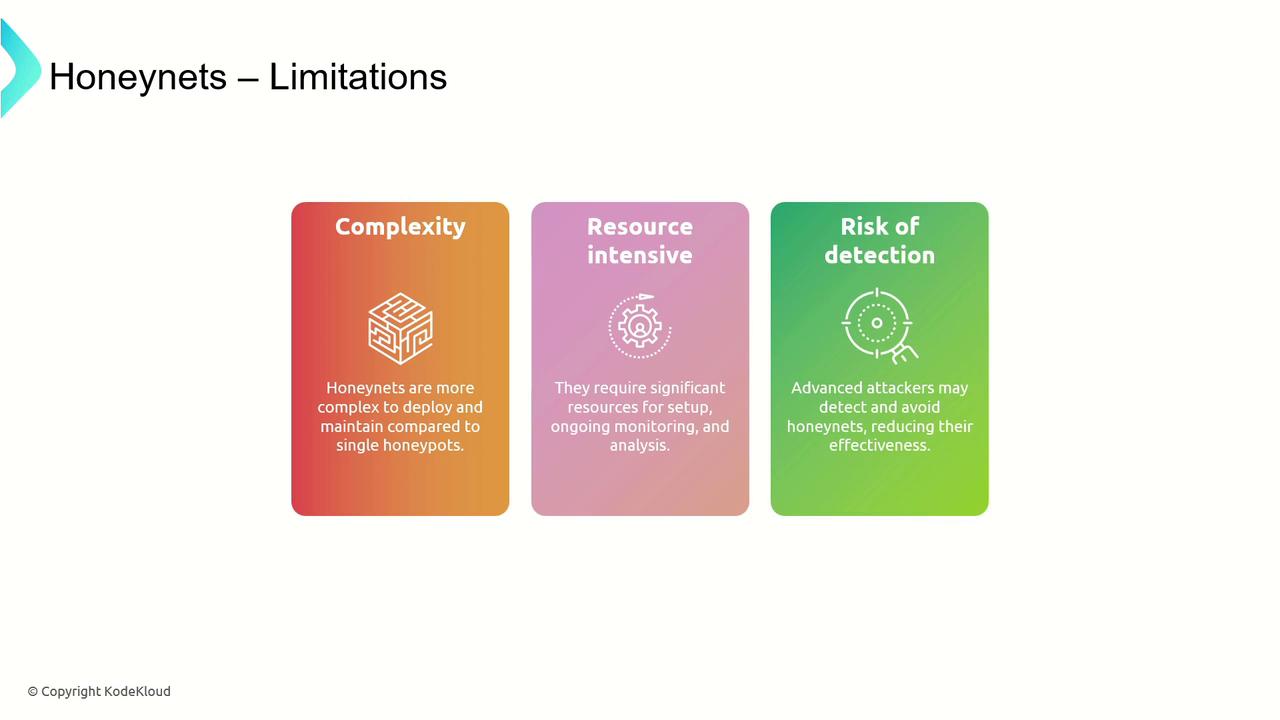
Keep in mind that honeynets require significant management due to their complexity and resource needs. They must be carefully maintained to avoid detection by advanced attackers.
Honeyfiles
Honeyfiles are decoy files strategically placed within a file system to attract attackers by simulating valuable data. Any attempt to access, copy, or modify these files triggers alerts, helping security teams to identify and analyze unauthorized activities.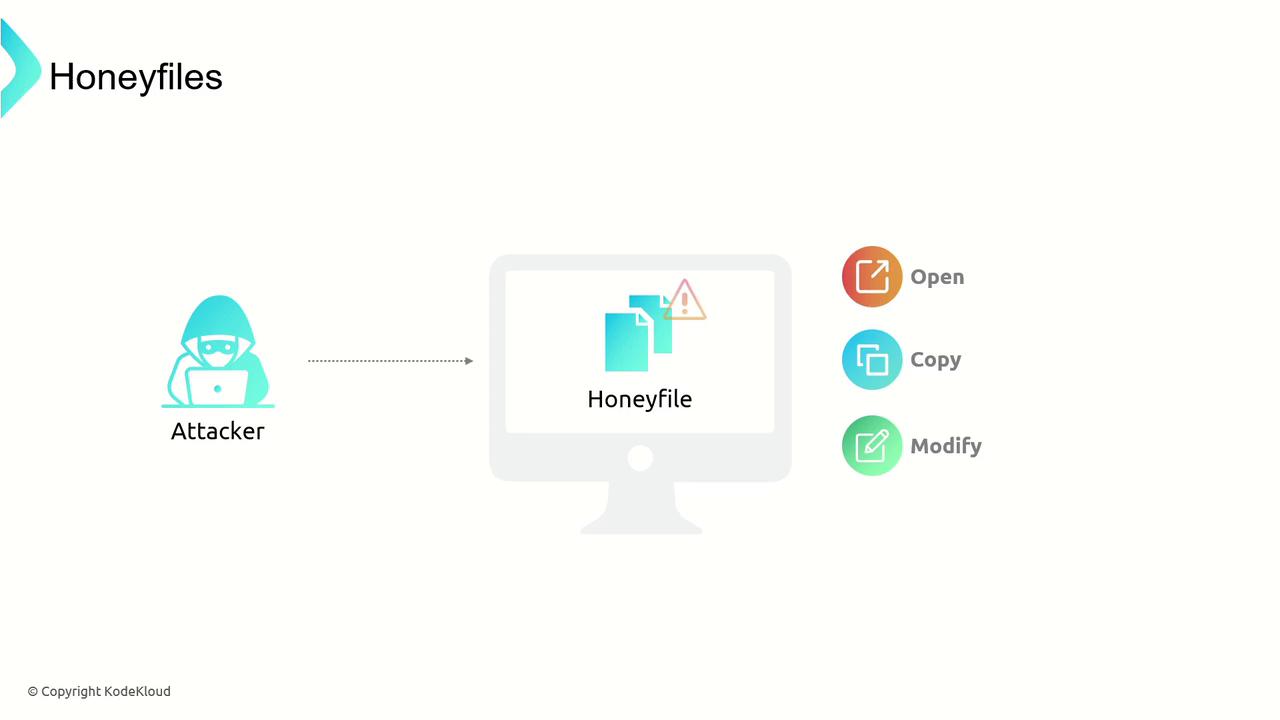

Honeytokens
Honeytokens are small decoy data elements—such as fake usernames, credentials, or records—integrated into databases or applications. Unlike complete files, these tokens offer granular interaction points that, when accessed or manipulated, raise immediate alerts. This helps determine both the attack vector and the attacker’s intent.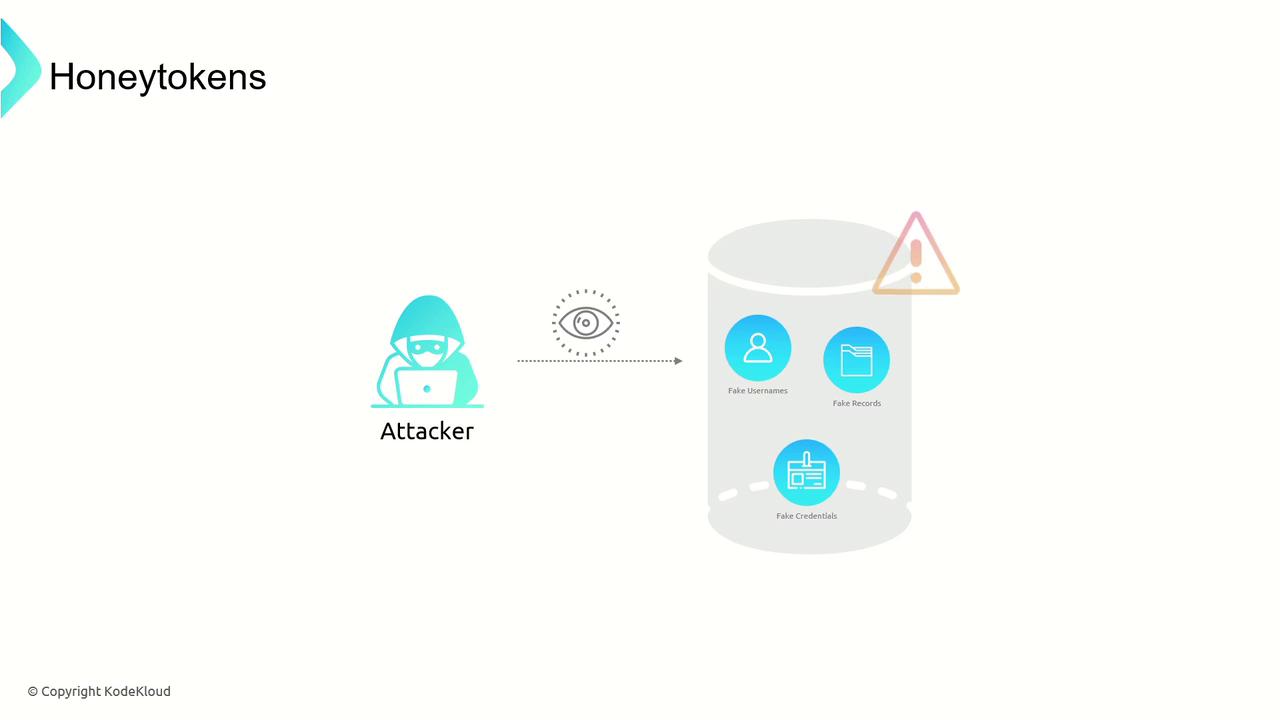
- Versatility in deployment across various data stores.
- Effective detection of unauthorized activities with minimal performance impact.
- Ease of integration within existing systems.

Conclusion
Honeypots, honeynets, honeyfiles, and honeytokens are essential components in a layered cybersecurity strategy. They provide early threat detection, deep insights into attacker behaviors, and contribute significantly to strengthening an organization’s security defenses. While not a complete solution on their own, these decoy technologies are valuable for proactive threat intelligence and risk mitigation.