Non-Repudiation
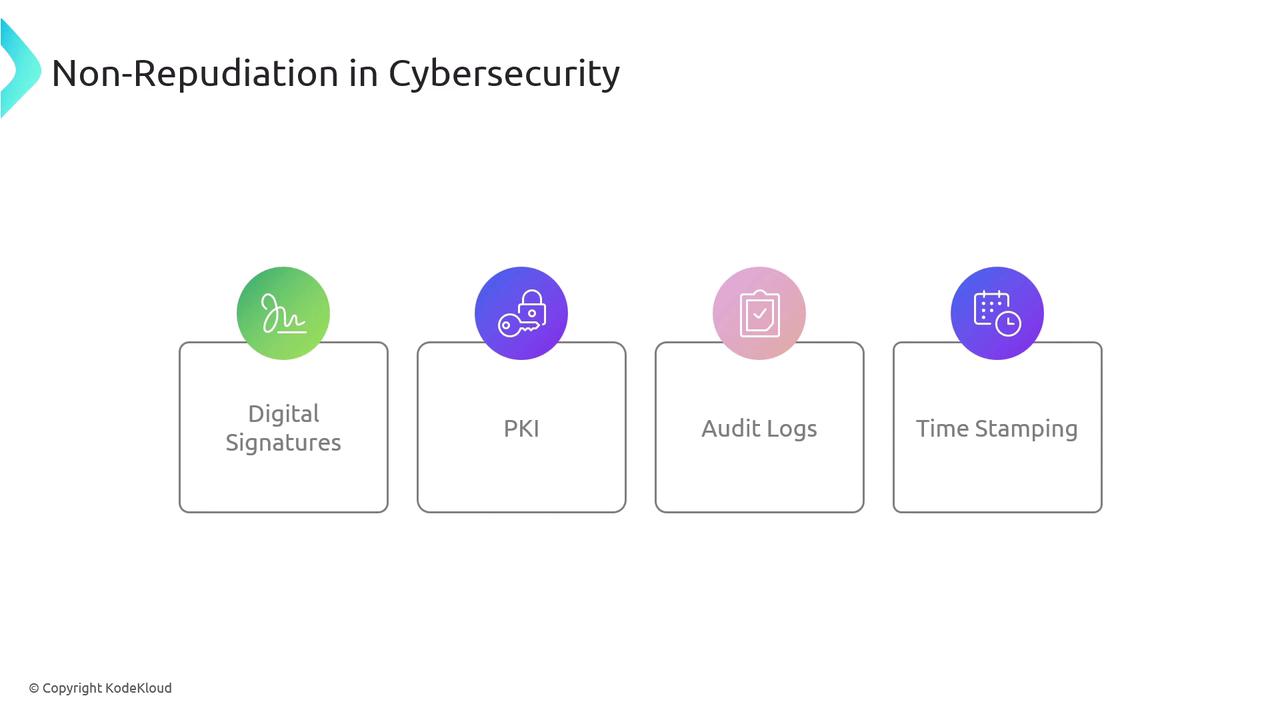
Non-repudiation is a security measure that guarantees a message or action can be incontrovertibly attributed to its sender. By providing undeniable evidence of origin, it prevents any party from later denying their participation. This concept is essential in environments where accountability and trust are critical, such as financial transactions, healthcare data management, and e-commerce operations. For instance, if an individual sends an email or initiates a transaction, non-repudiation ensures they cannot later claim non-involvement. Techniques such as digital signatures, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), audit logs, and timestamping establish a verifiable record of a message’s origin and its integrity.
The AAA Framework
After establishing the importance of non-repudiation, let’s turn our attention to the AAA framework. This framework is fundamental in securing access to resources, managing permissions, and tracking user activities to ensure a strong security posture.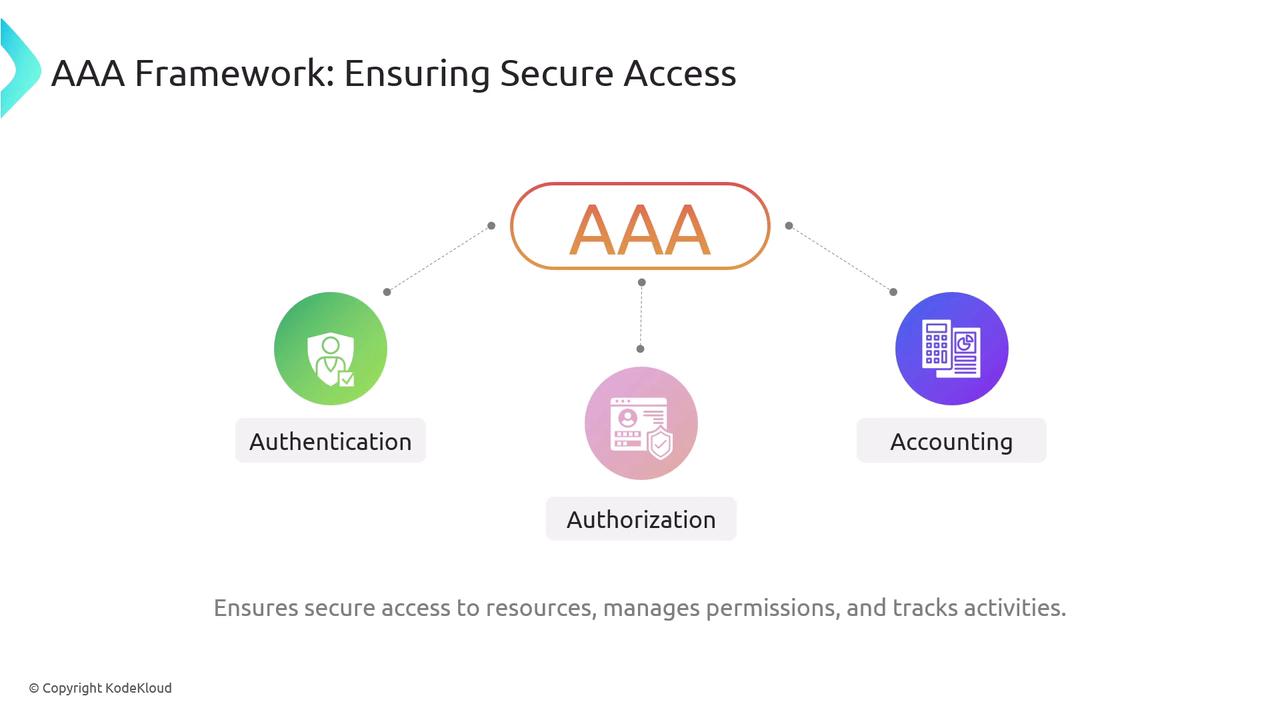
Authentication
Authentication verifies the identity of a user, device, or system, confirming that the entity requesting access is legitimate. This process is pivotal in preventing unauthorized access to systems and sensitive information. Common authentication methods include passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and biometrics.For enhanced security, consider combining multiple authentication factors to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Authorization
Following authentication, authorization determines what resources an authenticated user is permitted to access and what actions they can perform. This process is implemented via various access control mechanisms, including:- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Grants permissions based on assigned roles (e.g., employee, manager, administrator).
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Grants access based on attributes related to the user, resource, or environment (e.g., department, job title, time of day).
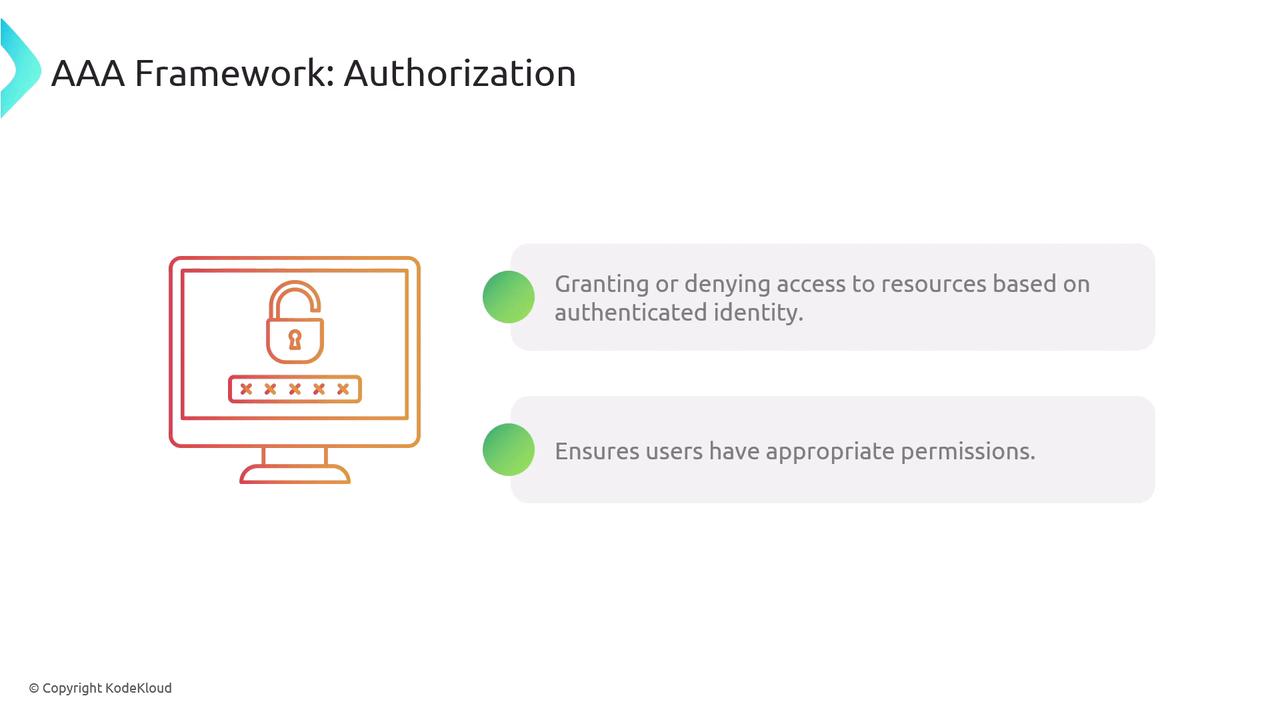
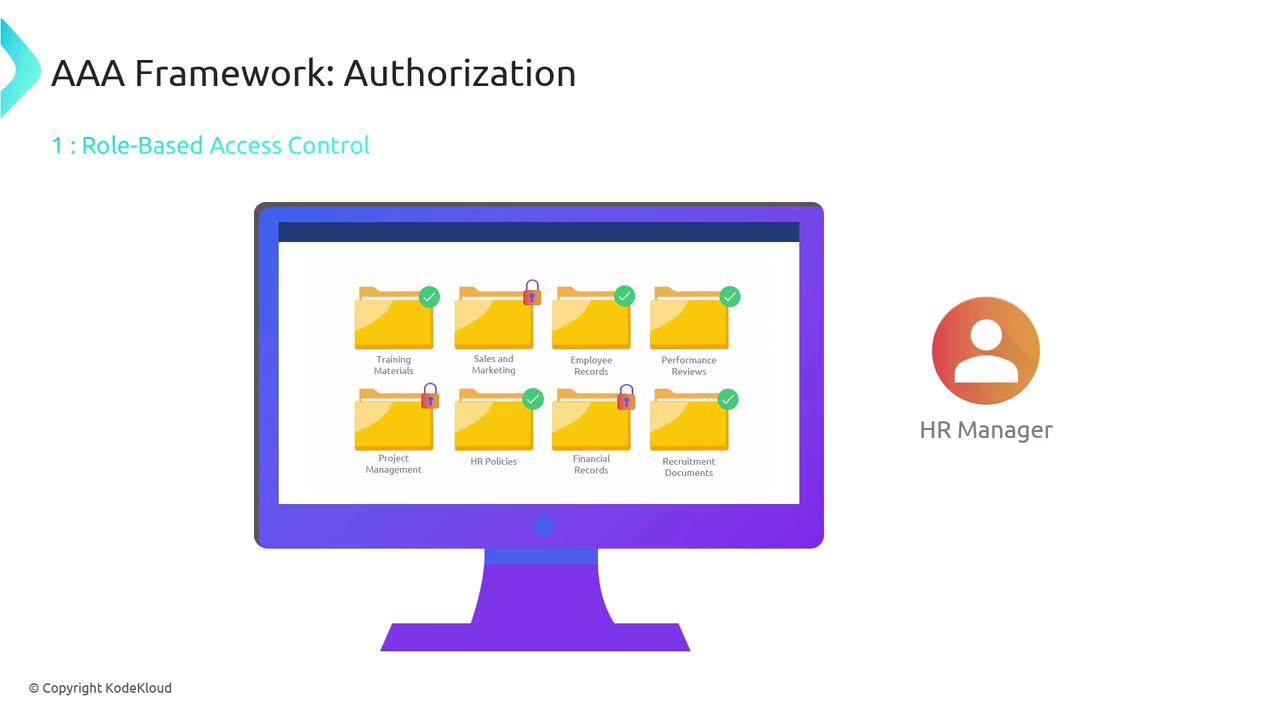

Implement clear access control policies to ensure that authorization is consistently enforced and regularly audited.
Accounting
The final component, Accounting, is focused on logging and monitoring user activities and resource usage. Also known as Auditing, this process establishes records that reinforce non-repudiation and support forensic analysis, system auditing, and accountability. Detailed audit trails play a crucial role in detecting security breaches and ensuring that actions can be traced back to the responsible party.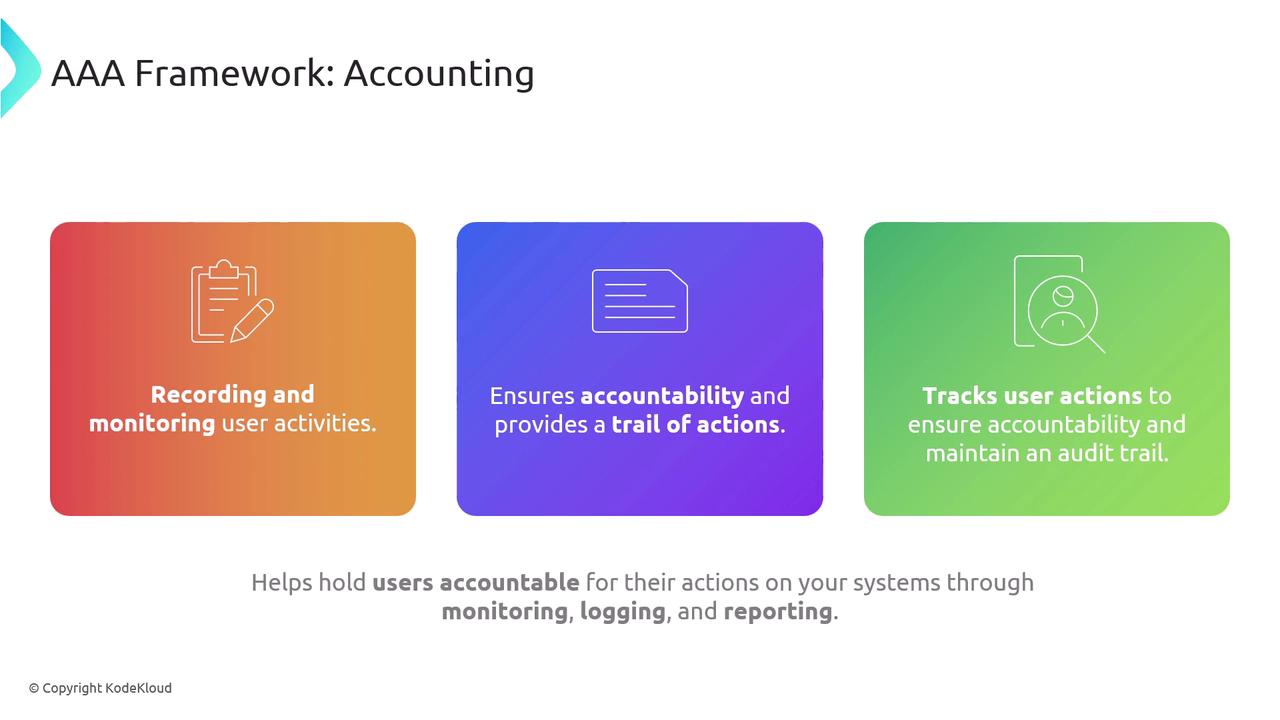
Ensure audit logs are securely stored and regularly reviewed to rapidly identify and respond to potential security incidents.
Conclusion
In summary, the AAA framework—comprising Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting—is integral to effective access control, permission management, and user activity tracking within any organization. When paired with robust non-repudiation measures, these elements build a comprehensive security strategy that not only protects sensitive data but also fosters trust and complies with regulatory standards.