- Regulated Data
- Trade Secrets
- Legal Data
- Financial Data
- Human-Readable Data
- Non-Human-Readable Data
Classifying data correctly helps organizations apply the most appropriate controls to protect each category of information.
Regulated Data
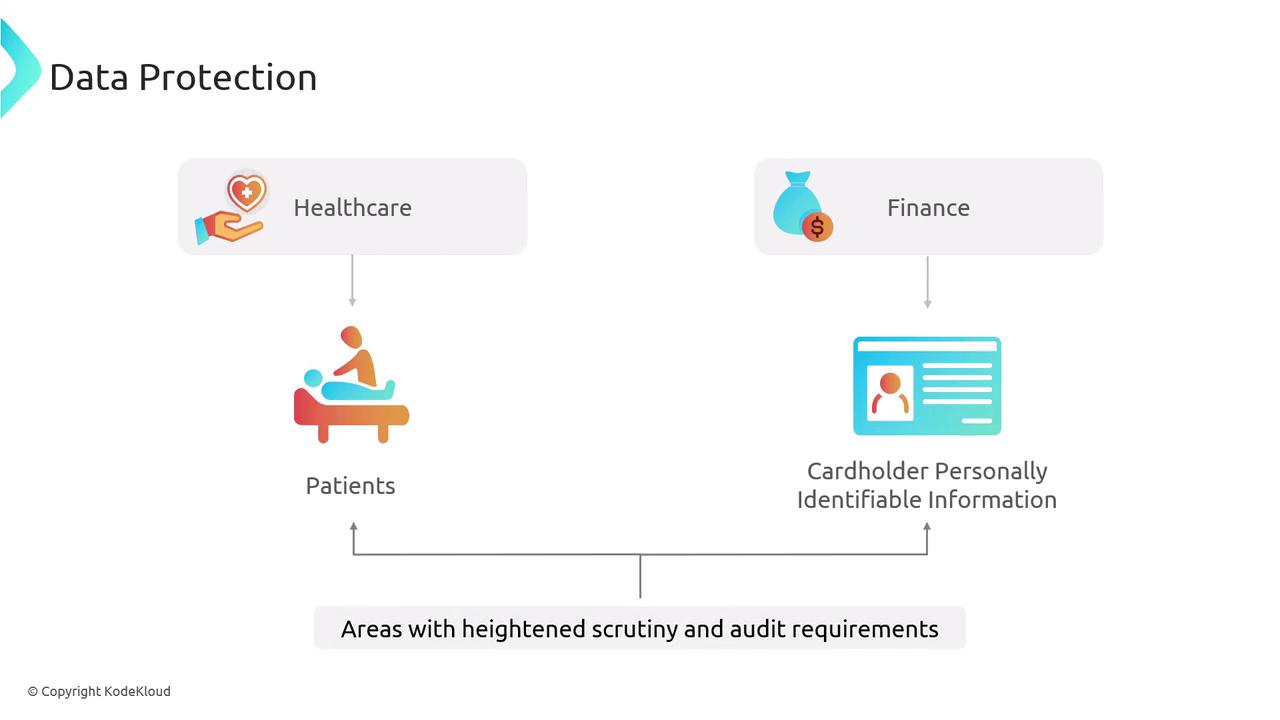
Regulated data comprises information that must adhere to specific legal and regulatory mandates regarding its handling, protection, and storage. These provisions are designed to ensure the privacy, security, and proper usage of highly sensitive details such as personally identifiable information (PII).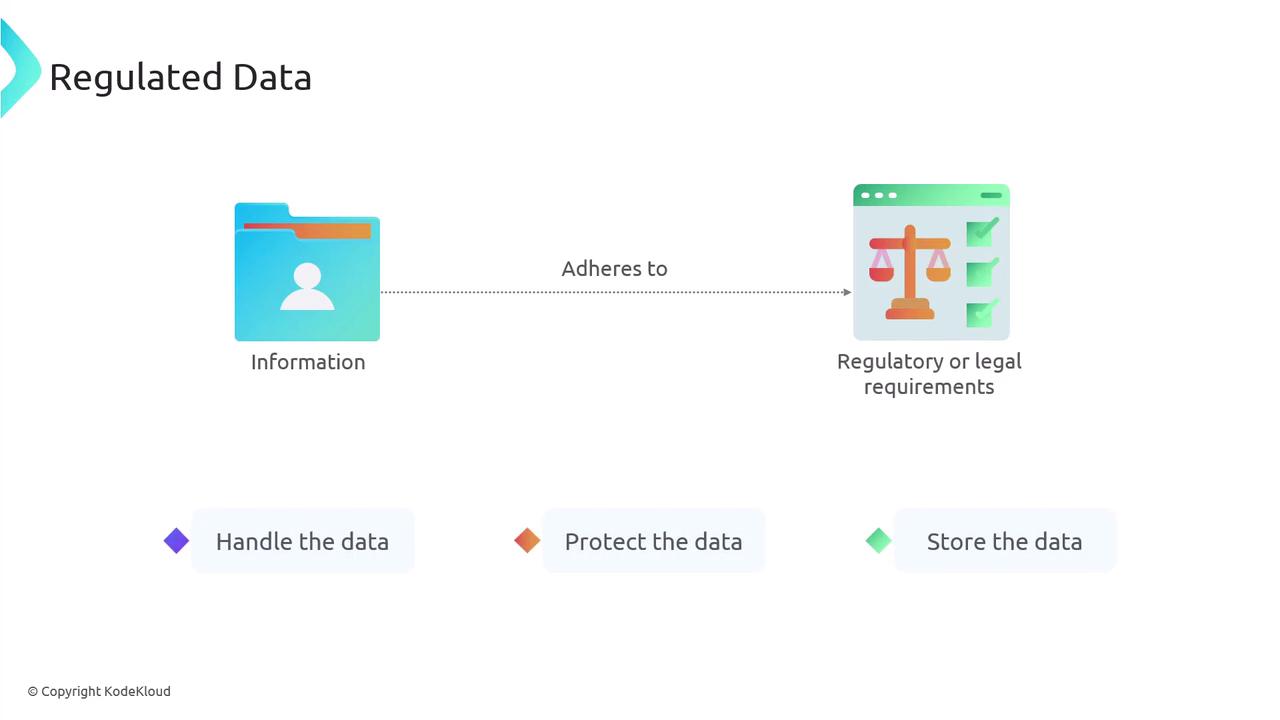
- Healthcare records
- Financial information
- Social security numbers
- Birth dates
- Credit card details
Trade Secrets
Trade secrets are non-public, proprietary information that gives a business its competitive edge. This category includes confidential data such as customer lists, marketing strategies, formulas, and other critical business insights that, if disclosed, could benefit competitors.Legal Data
Legal data covers documents such as contracts, court filings, and legal agreements. This information is crucial for corporate governance and ensuring that organizations comply with all applicable laws and regulations.Financial Data
Financial data pertains to a company’s financial activities, performance, and transactions. This sensitive information includes accounting ledgers, transactional records, and other data directly related to financial operations.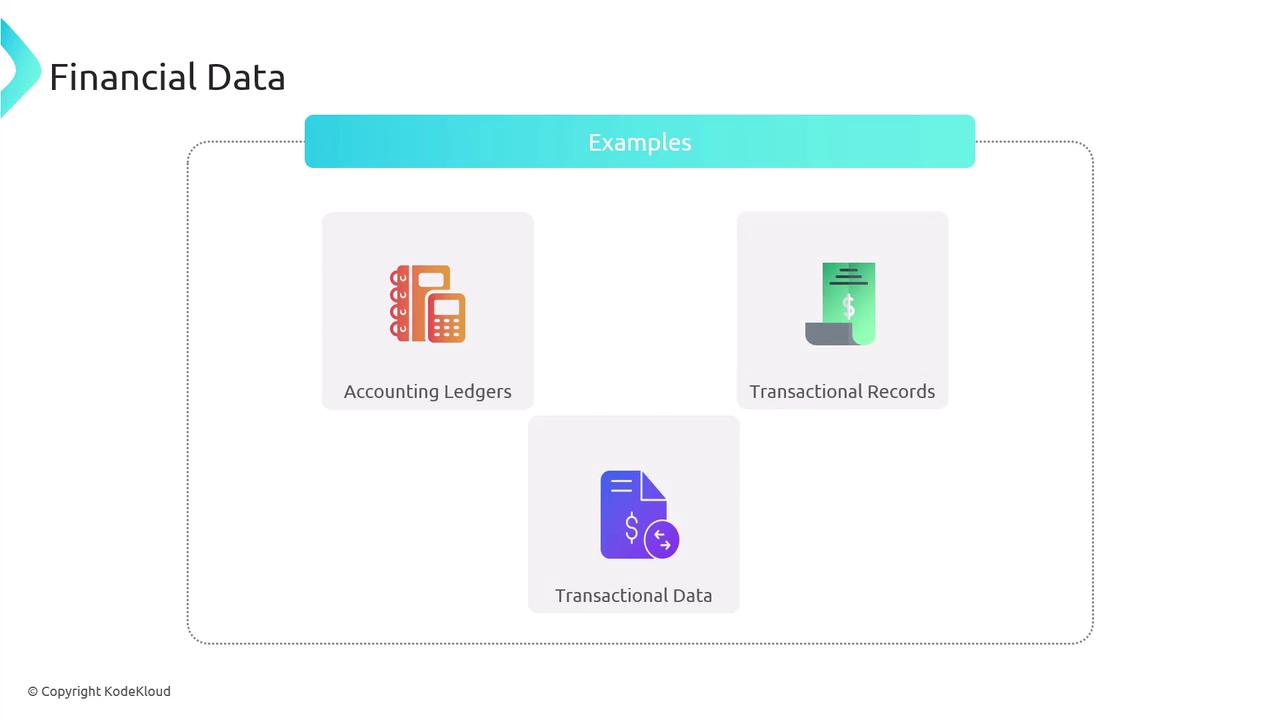
Data Classification by Readability
Data can also be classified based on its readability:- Human-Readable Data: This includes documents, emails, presentations, and other content that can be easily interpreted by people.
- Non-Human-Readable Data: This category consists of binary files, source code, or encrypted information that requires specialized tools or processing to be understood.
By accurately classifying data, organizations can tailor their security strategies to ensure robust protection across all data types.