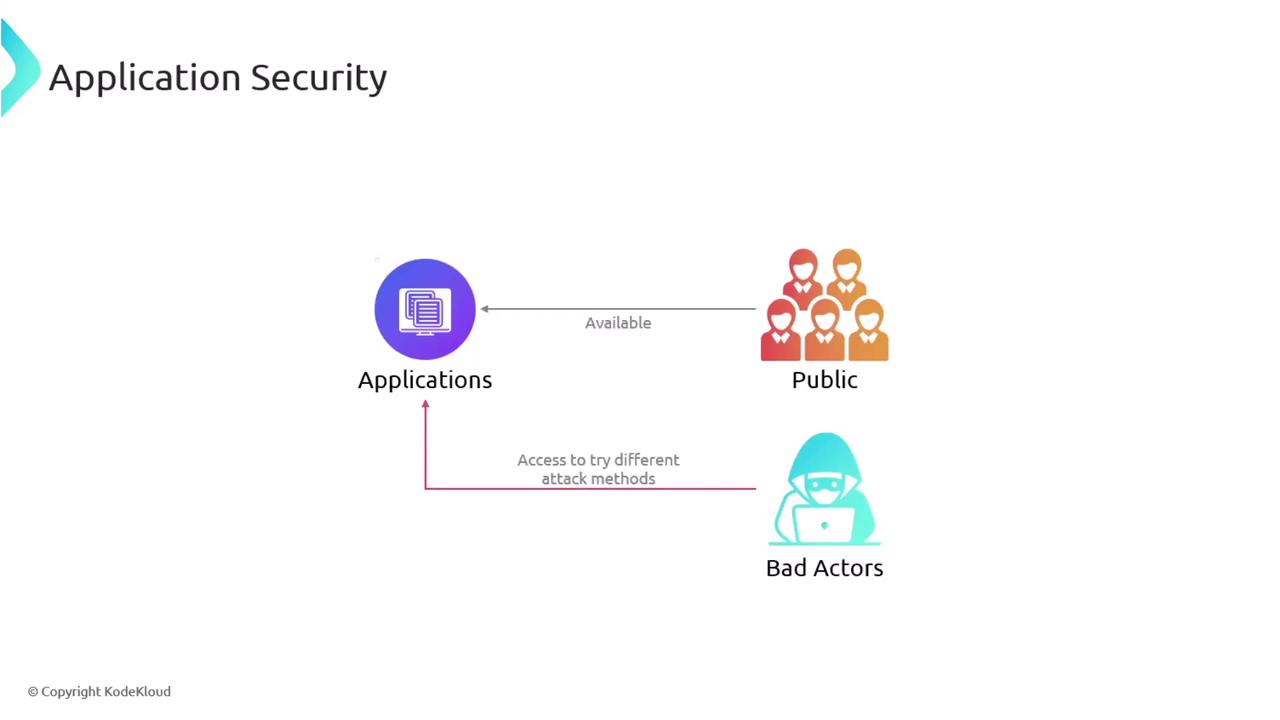
Implementing a comprehensive security strategy helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Prioritize these measures early in the development lifecycle to reduce risk.
Input Validation
Input validation plays a pivotal role in defending against injection attacks. By verifying and sanitizing user inputs, you limit the ability of threat actors to submit malicious data. Failure to validate inputs properly may enable attackers to exploit vulnerabilities through SQL injection, code injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other methods.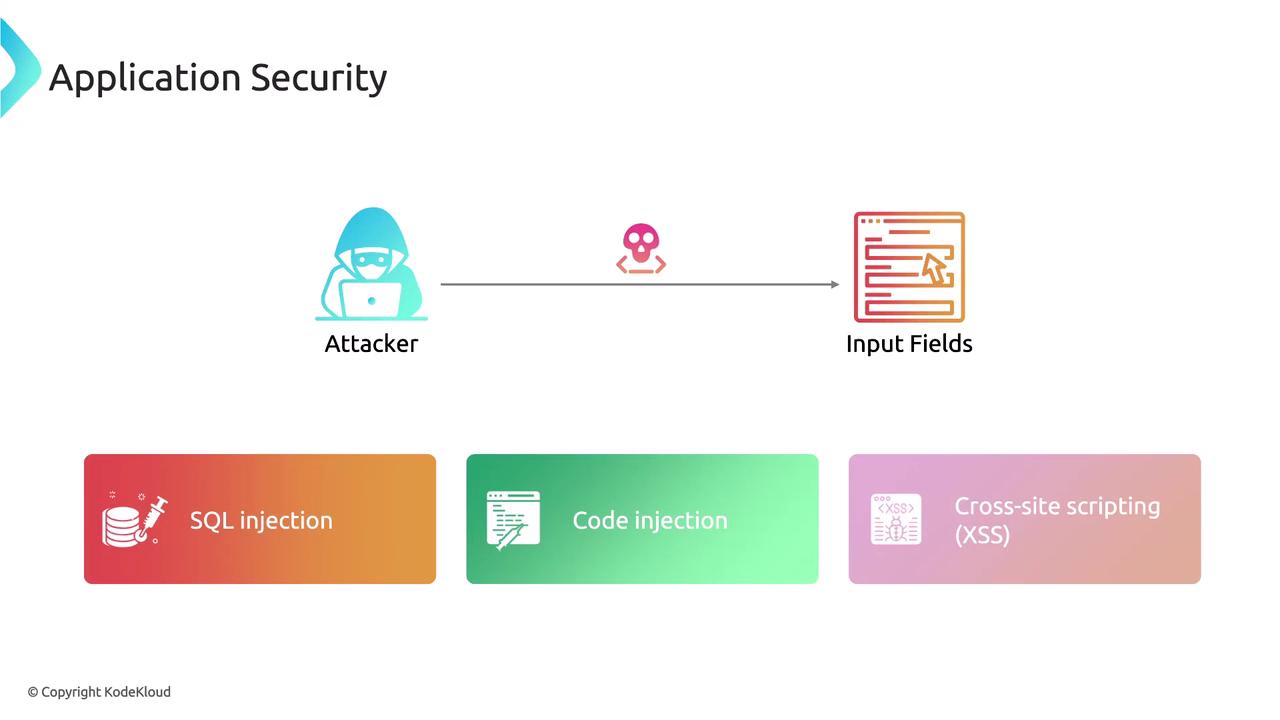
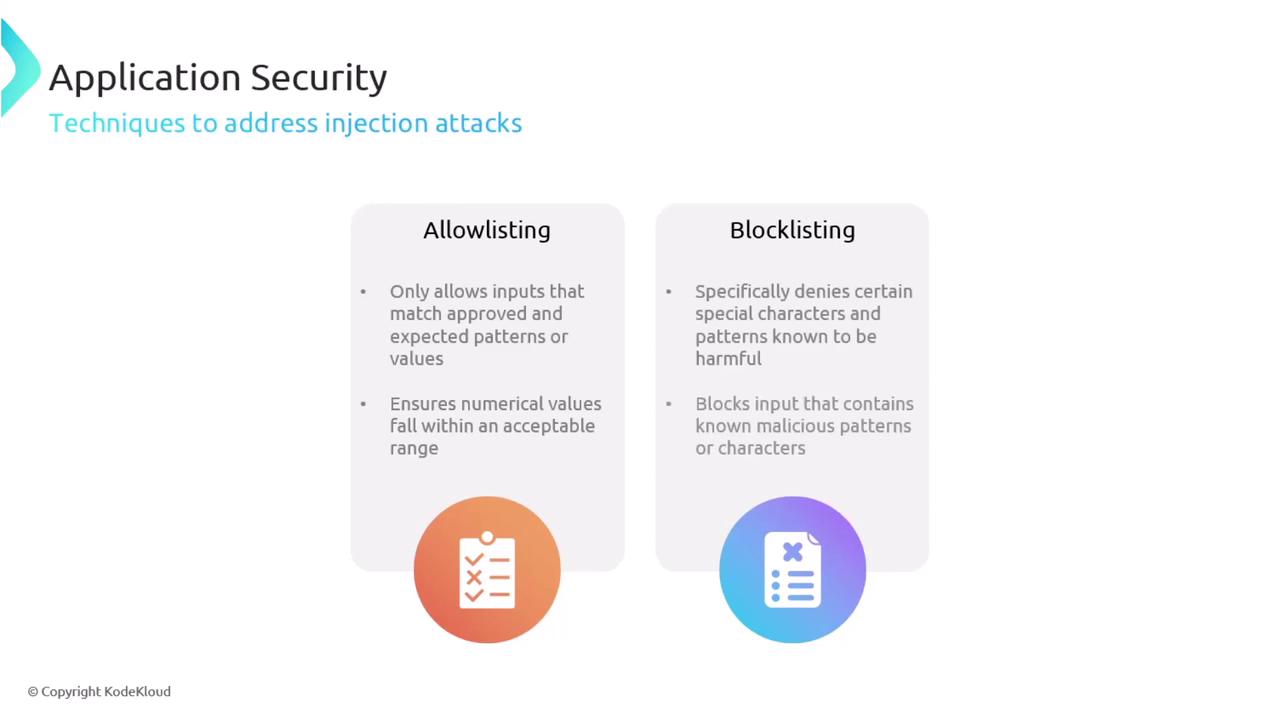
- Allow Listing: Define approved patterns or values, ensuring that inputs match expected criteria.
- Block Listing: Identify and deny inputs containing harmful characters or patterns, such as ensuring numerical ranges are within acceptable limits.
Static Code Analysis
Static code analysis is an integral part of the secure software development process. By examining source code without executing it, potential vulnerabilities and errors can be identified early. This proactive approach ensures that issues are addressed before software deployment, enhancing overall reliability and security.Code Signing
Code signing uses digital signatures to verify both the authenticity and integrity of software. This process confirms that the software originates from a trusted source and remains unaltered post-release. Code signing is crucial for maintaining user confidence and preventing distribution of tampered code.Cookie Security
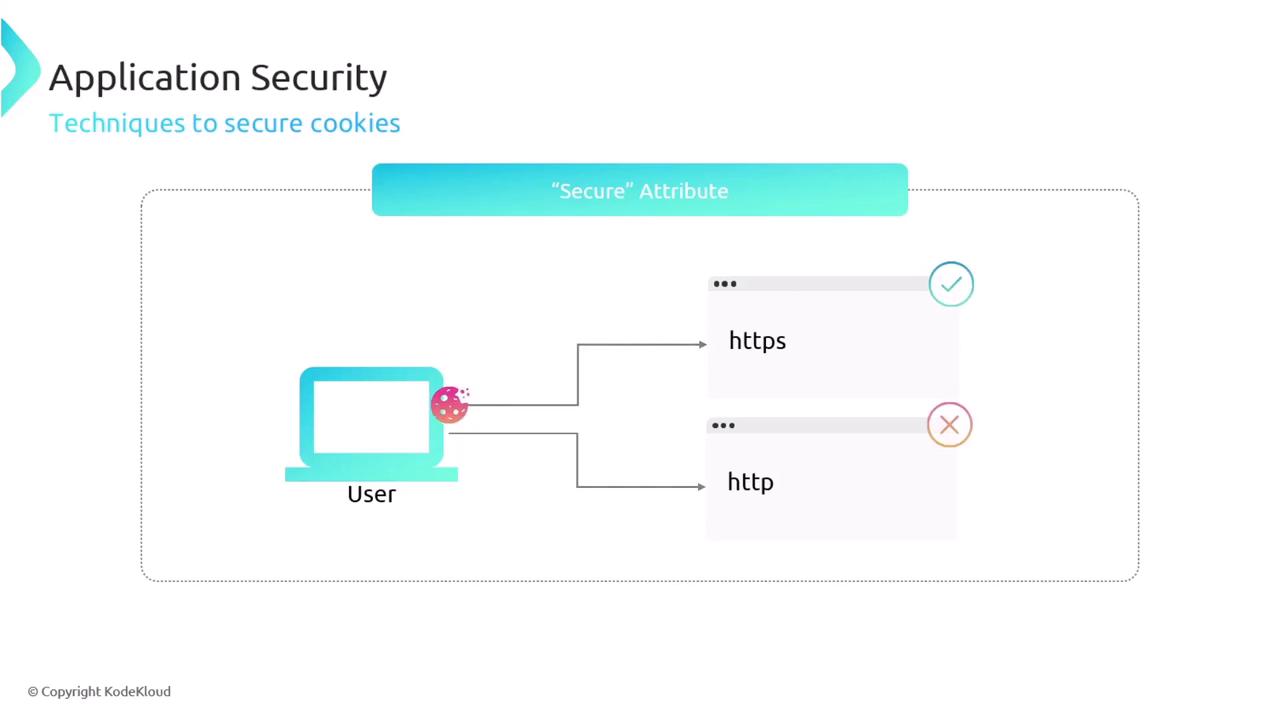
Cookies are small data files stored by browsers to retain user settings, session states, and preferences. However, if not properly secured, cookies can be exploited through attacks such as cross-site scripting (XSS) or session hijacking. Implementing secure cookie practices is essential for protecting user data. Key security techniques for cookies include:- Using the Secure Attribute: This ensures cookies are transmitted only over HTTPS connections, providing strong encryption and data integrity protection.
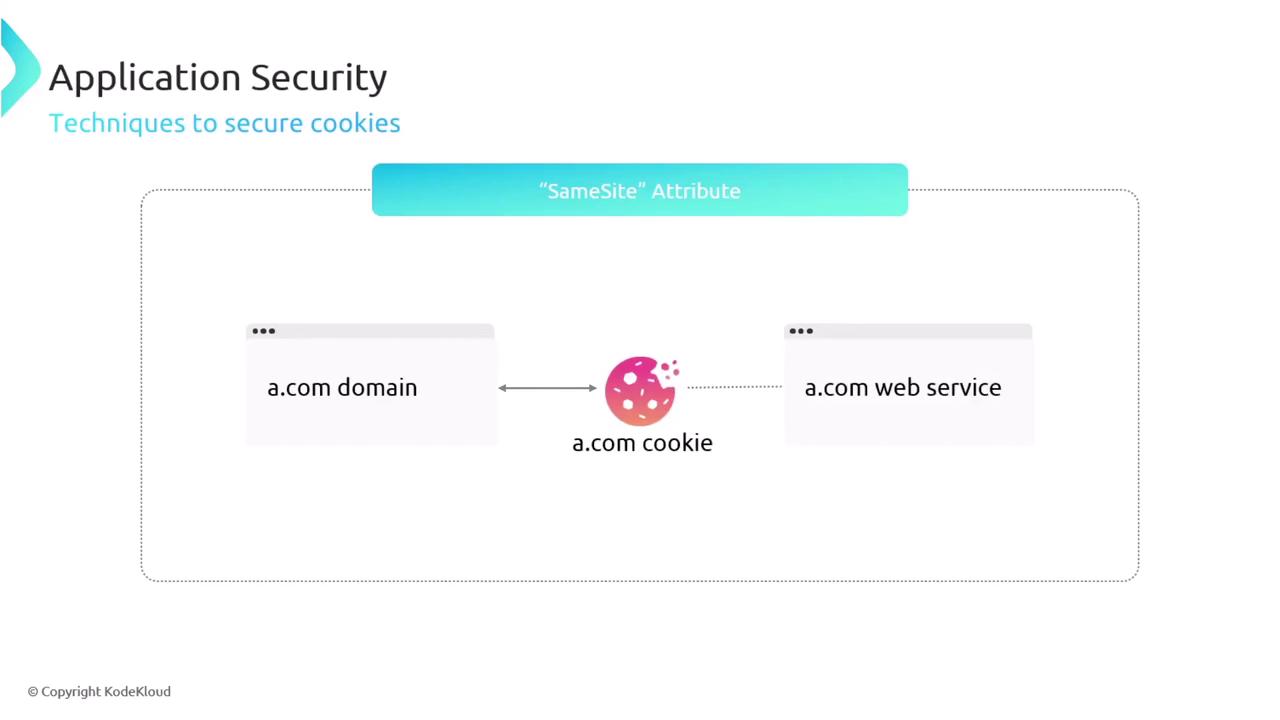
- Using the SameSite Attribute: This attribute prevents cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks by limiting when cookies are sent, thereby protecting against unauthorized data exploitation.
Always ensure that all security practices are consistently applied across your application. Regular audits and updates are essential to adapt to evolving threats.