- User provisioning
- Resource provisioning
- Guardrails
- Security groups
- Ticket creation and escalation
- Enabling/disabling services and access
- Continuous integration and testing
- API integrations

User Provisioning
User provisioning involves automating the creation, management, and maintenance of user accounts and access rights within IT systems. This process ensures that new employees obtain the appropriate access swiftly and efficiently. For example, automated scripts can:- Create new user accounts in Active Directory
- Assign roles and permissions
- Configure email and other critical services
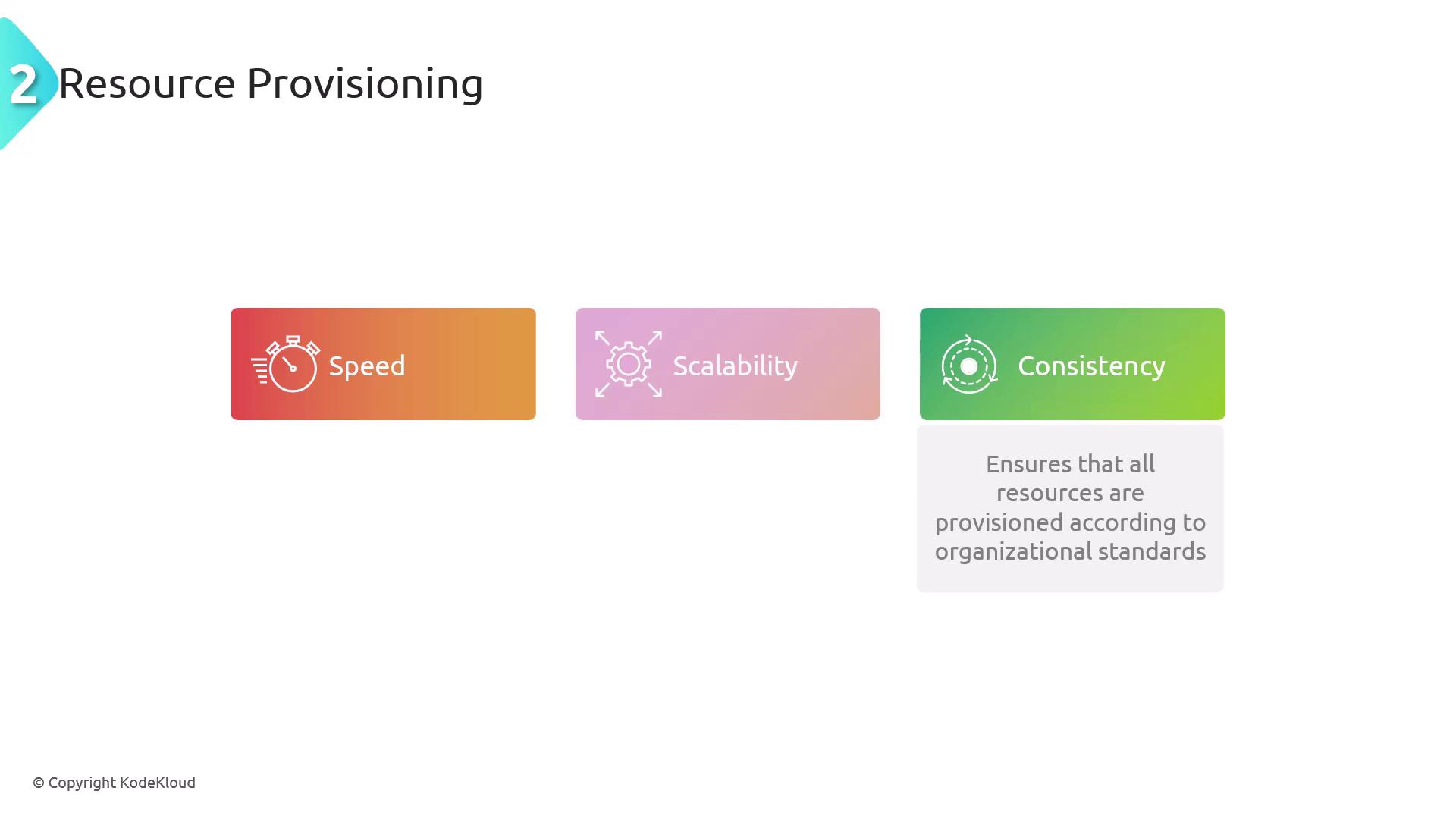
Resource Provisioning
Resource provisioning focuses on automating the allocation and management of IT resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and network components. Automation streamlines the deployment and configuration of resources, especially in cloud environments. An example includes a script that deploys a virtual machine on AWS or Azure using predefined settings. Key benefits of automating resource provisioning include:| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed | Rapid deployment of resources |
| Scalability | Dynamic scaling based on demand |
| Consistency | Standardized configurations across environments |
Guardrails
Guardrails are automated policies and controls designed to enforce security and operational compliance. When guardrails are automated, resources consistently adhere to organizational security policies. For example, a script can enforce tagging policies on cloud resources, which aids in proper categorization and cost management.Automated guardrails enhance compliance and reduce risk by minimizing security breaches and non-compliant behavior.

Security Groups
Security groups define and automate network access controls similar to firewall rules or ACLs. Automating the management of security groups ensures that network access policies are applied uniformly across the infrastructure. For example, a script can automatically create and configure security groups in a cloud environment to regulate incoming and outgoing traffic.
Ticket Creation and Escalation
Ticket Creation
Automating ticket creation is crucial for prompt and accurate logging of IT issues and support requests. For instance, when a system alert is triggered, an automated script can generate a ticket in the help desk system. This practice ensures that incidents are captured efficiently, improving overall issue management.
Escalation
Escalation automates the process of increasing issue priority, ensuring that critical incidents receive the necessary attention and are resolved promptly. For example, if a ticket remains unresolved beyond a set threshold, an automated process can trigger an escalation to a higher-level support team.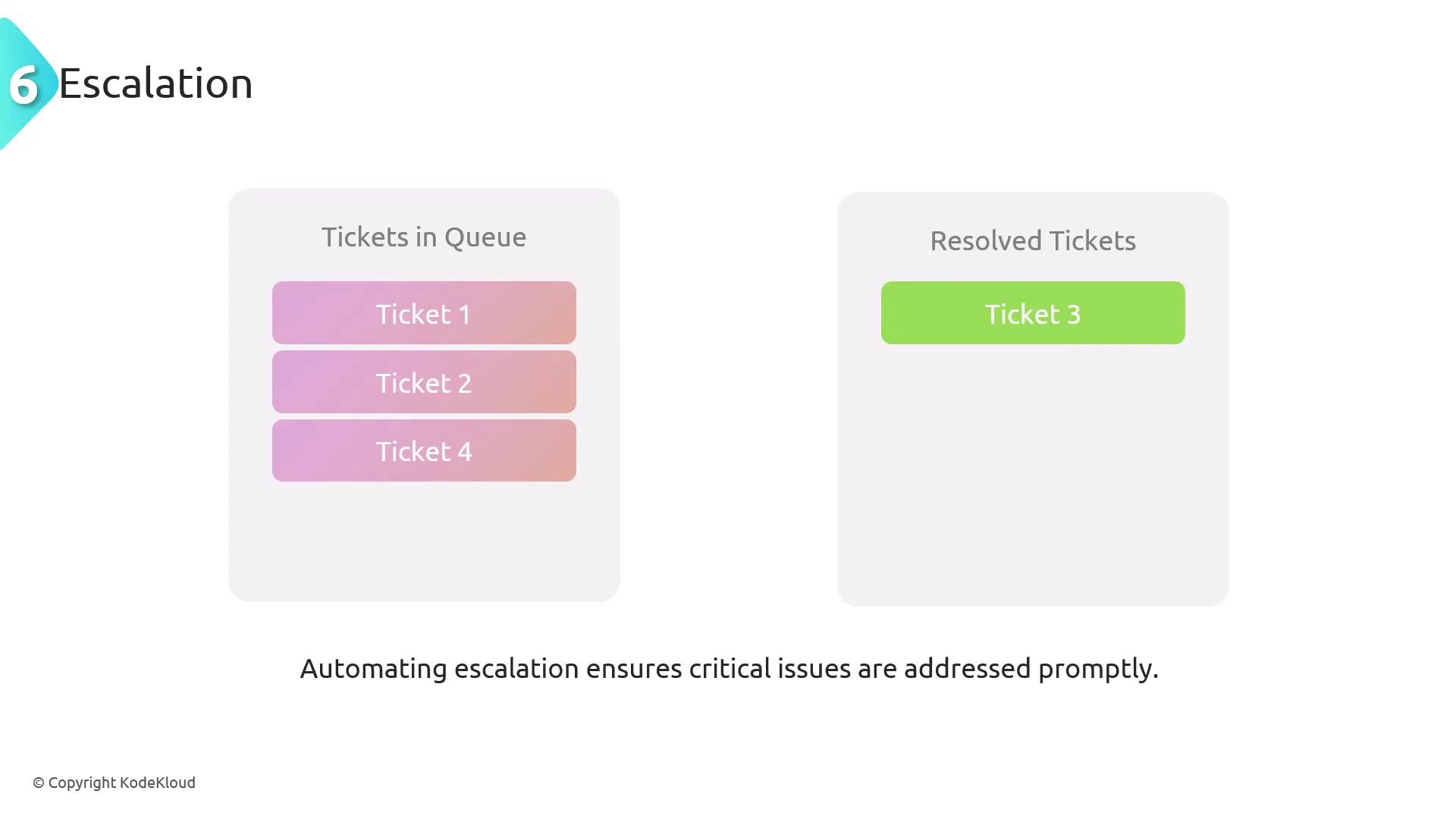
Enabling and Disabling Services and Access
Managing the availability of IT services and user access can also be automated. Conditions such as time-of-day or security alerts can trigger automated scripts to enable or disable services or access rights accordingly. For example, a system might automatically disable user access after business hours and re-enable it during working hours, aligning with organizational policies.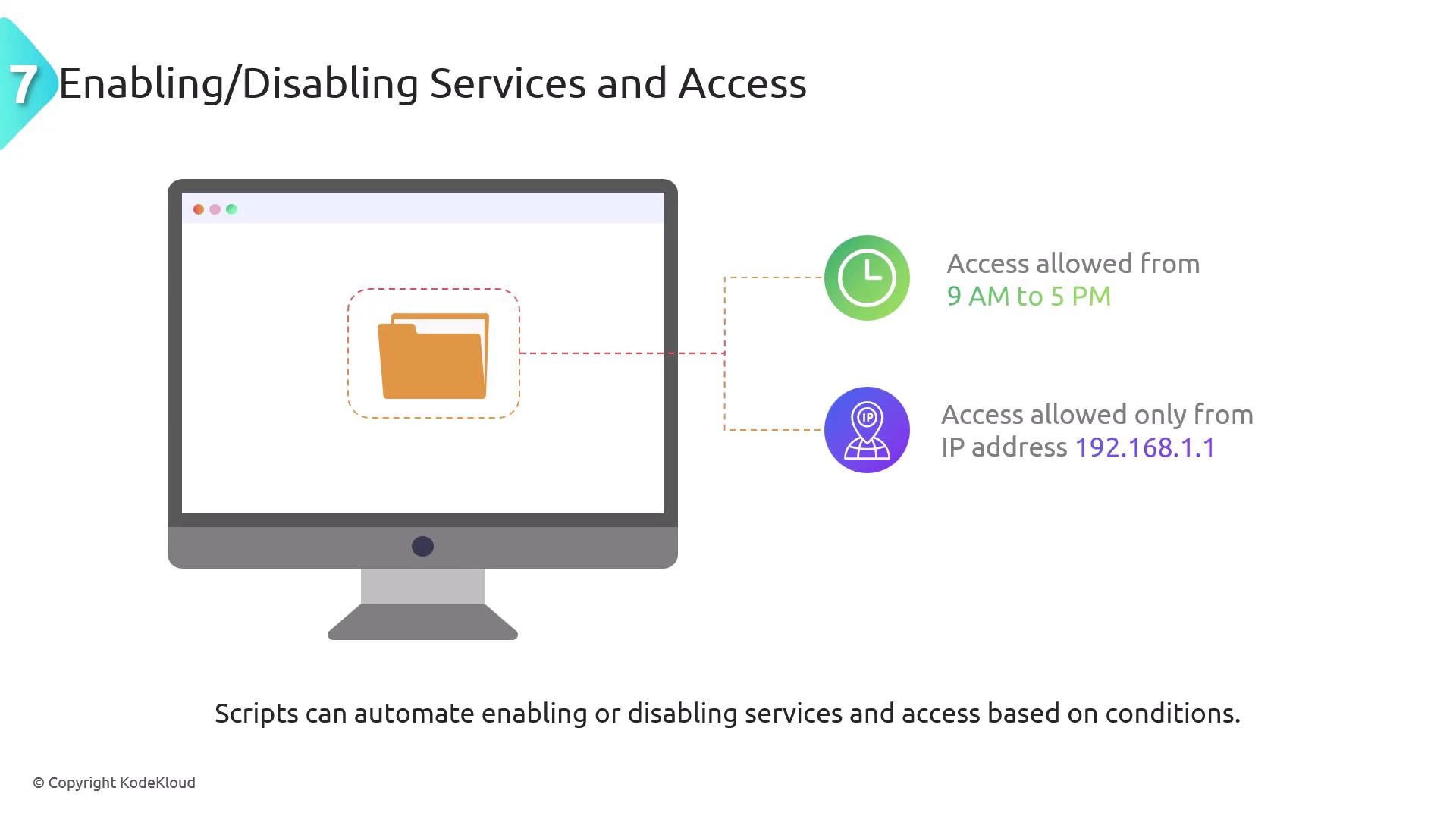
Continuous Integration and Testing
Continuous integration and testing (CI/CD) pipelines benefit greatly from automation. Integrating code changes and running tests automatically upon each push ensures consistent quality and prompt detection of issues. This process is key to maintaining high software quality standards.
API Integrations
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) facilitate communication between diverse software systems, enabling the automation of complex workflows. For instance, automation can integrate a monitoring system with a ticketing platform, ensuring alerts automatically generate support tickets, which streamlines incident response.