
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
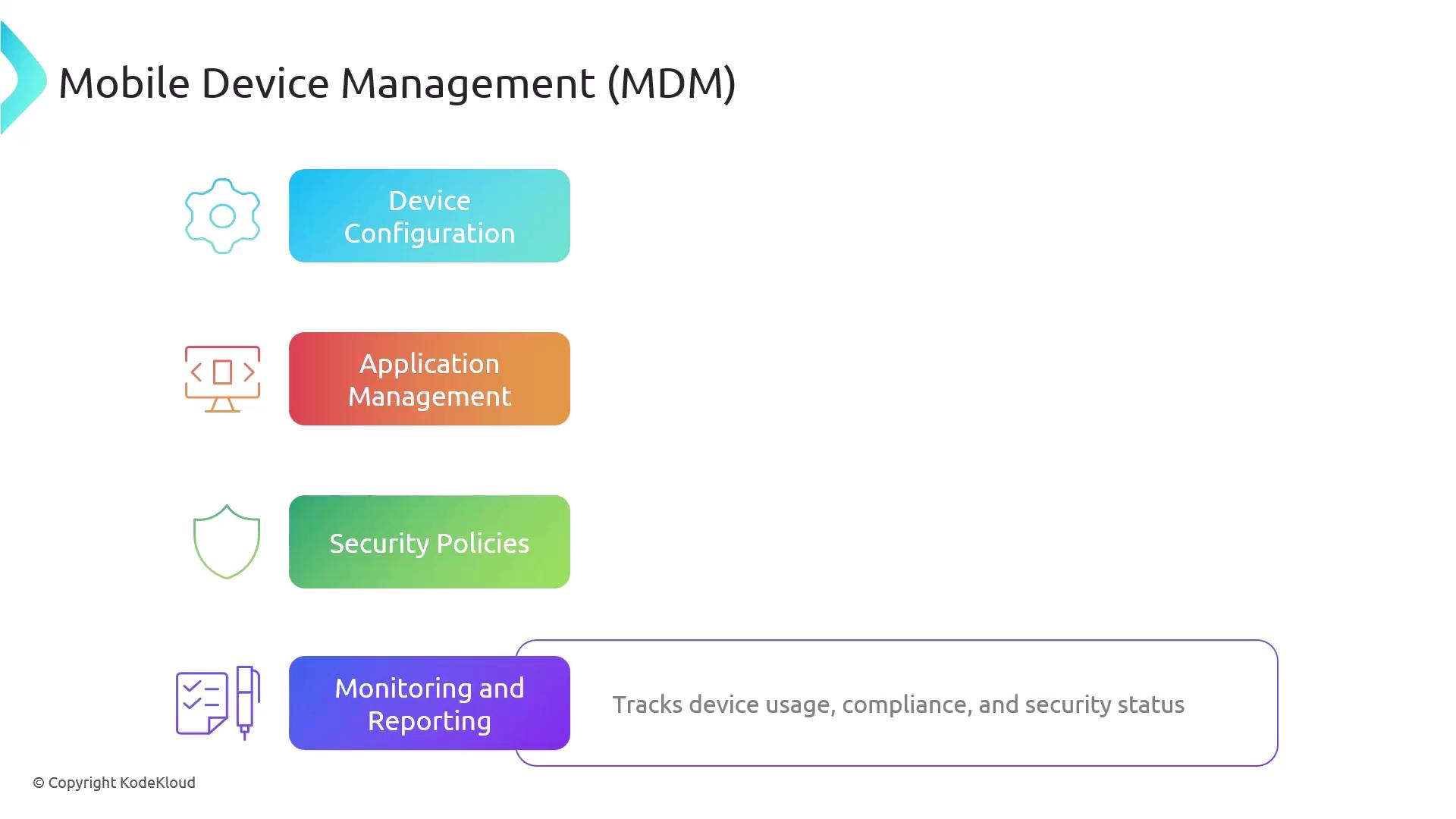
Mobile Device Management (MDM) is a powerful solution that allows organizations to manage, monitor, and secure mobile devices used by employees. Using MDM, IT departments can enforce security policies, control device configurations, and deploy applications efficiently. Key capabilities of MDM include:- Device Configuration: Enforce critical security settings such as passcodes, encryption, and VPN configurations.
- Application Management: Oversee the installation, updating, and removal of apps.
- Security Policies: Remotely wipe, lock devices, and enforce data encryption to safeguard sensitive information.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Track device usage, compliance, and security status with detailed reports.
Mobile Deployment Models
Understanding mobile deployment models is crucial for balancing employee flexibility with organizational security. The following models offer different levels of control and convenience.Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
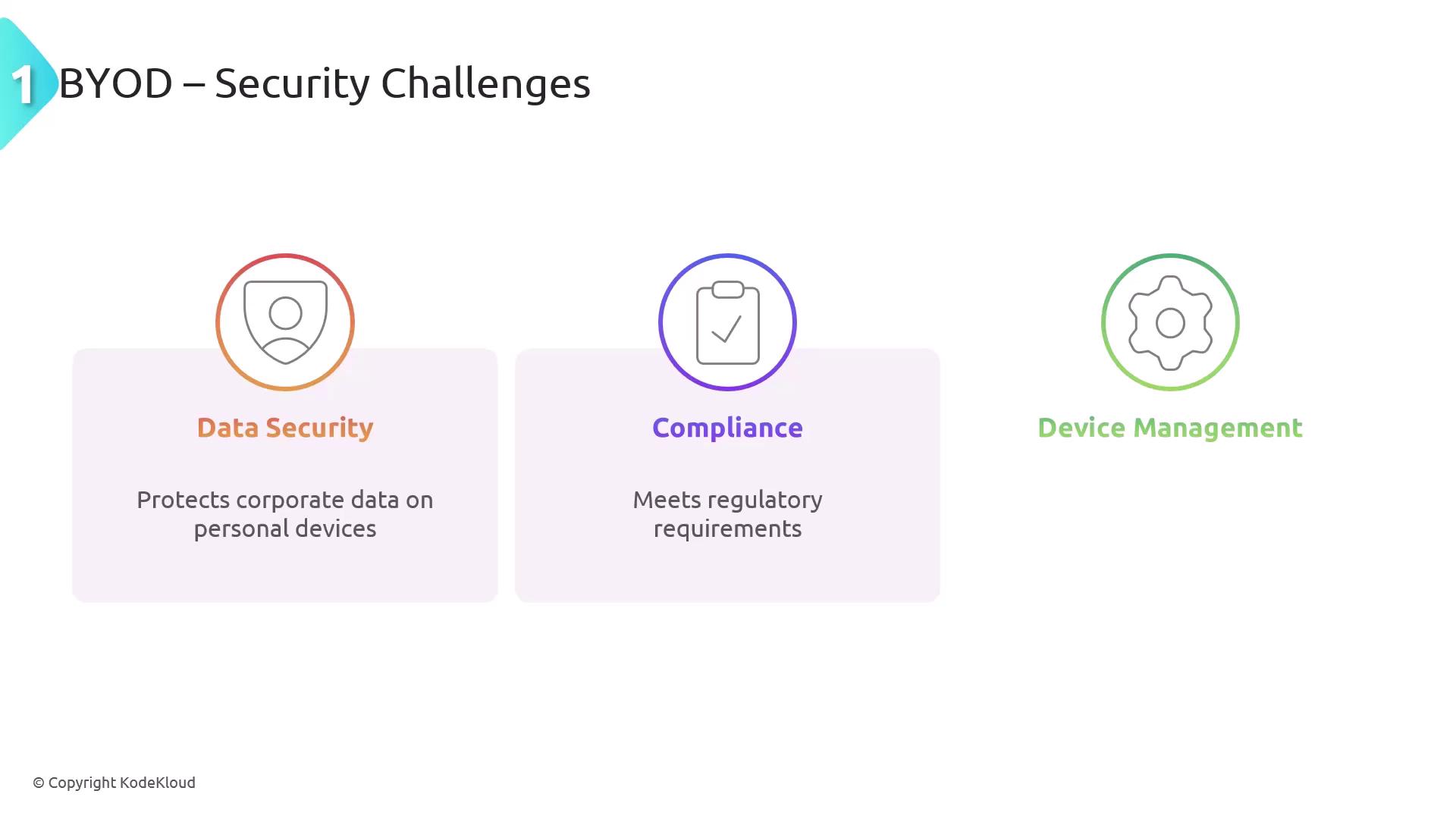
BYOD enables employees to use their personal devices for work, offering flexibility and cost savings while leveraging familiar technology. However, it introduces various security challenges:- Data Security: Protect corporate data stored on personal devices.
- Compliance: Ensure regulatory and compliance requirements are met when personal devices are used for work.
- Device Management: Secure a wide range of devices and operating systems.

Corporate Owned Personally Enabled (COPE)
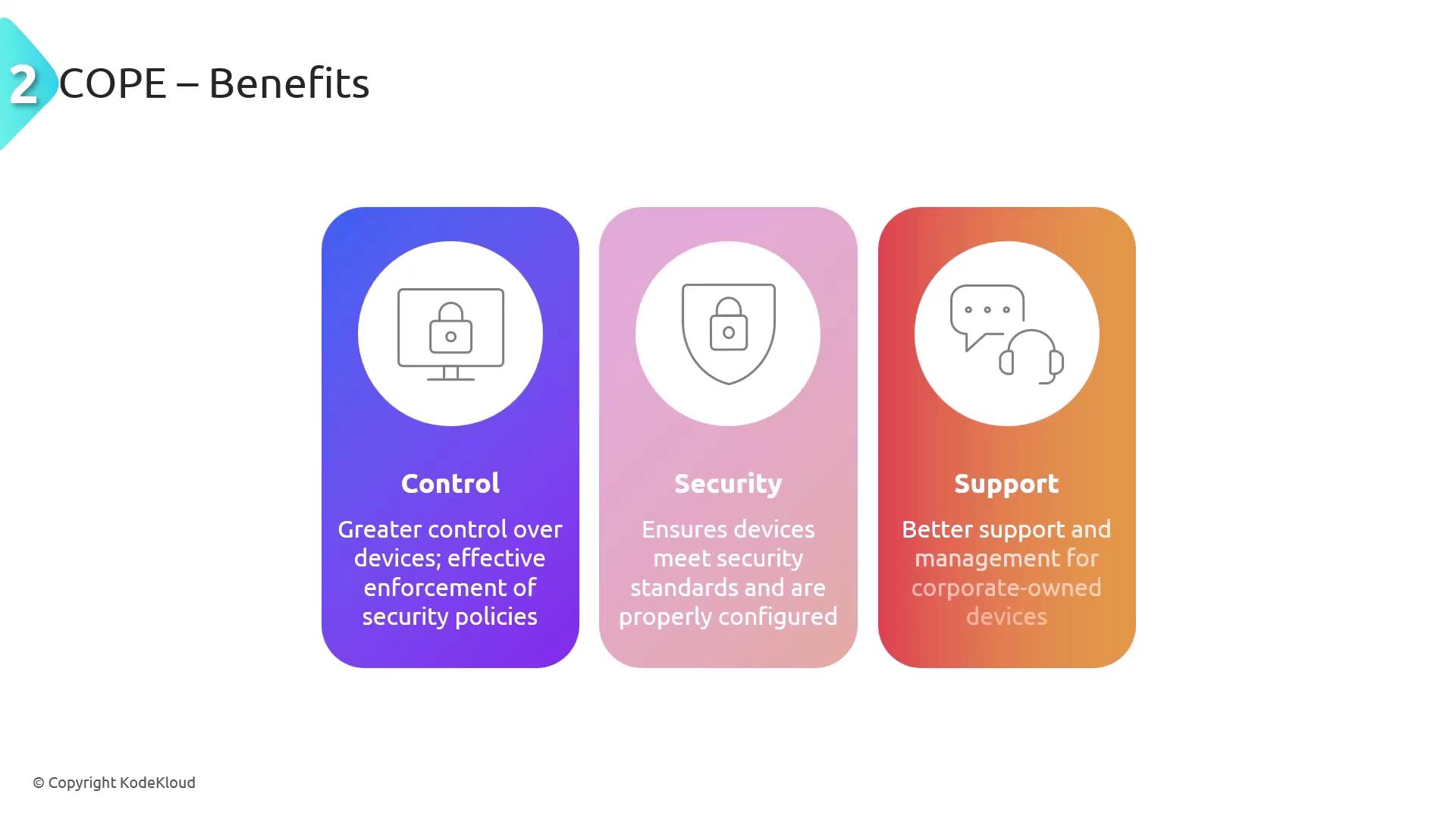
COPE is a model in which organizations provide devices that can be used for both work and limited personal use. This approach offers enhanced control, improved security, and better IT support compared to BYOD. With COPE, organizations can:- Enforce robust security policies due to full control over the devices.
- Configure devices uniformly to meet strict security standards.
- Provide dedicated support for corporate-owned technology.
Choose Your Own Device (CYOD)
CYOD offers a balanced approach where employees choose from a range of approved devices provided by the organization. This model ensures that all selected devices comply with security and compatibility requirements while giving users a degree of flexibility. Similar to COPE, CYOD relies on robust MDM solutions and clear usage policies to maintain device security.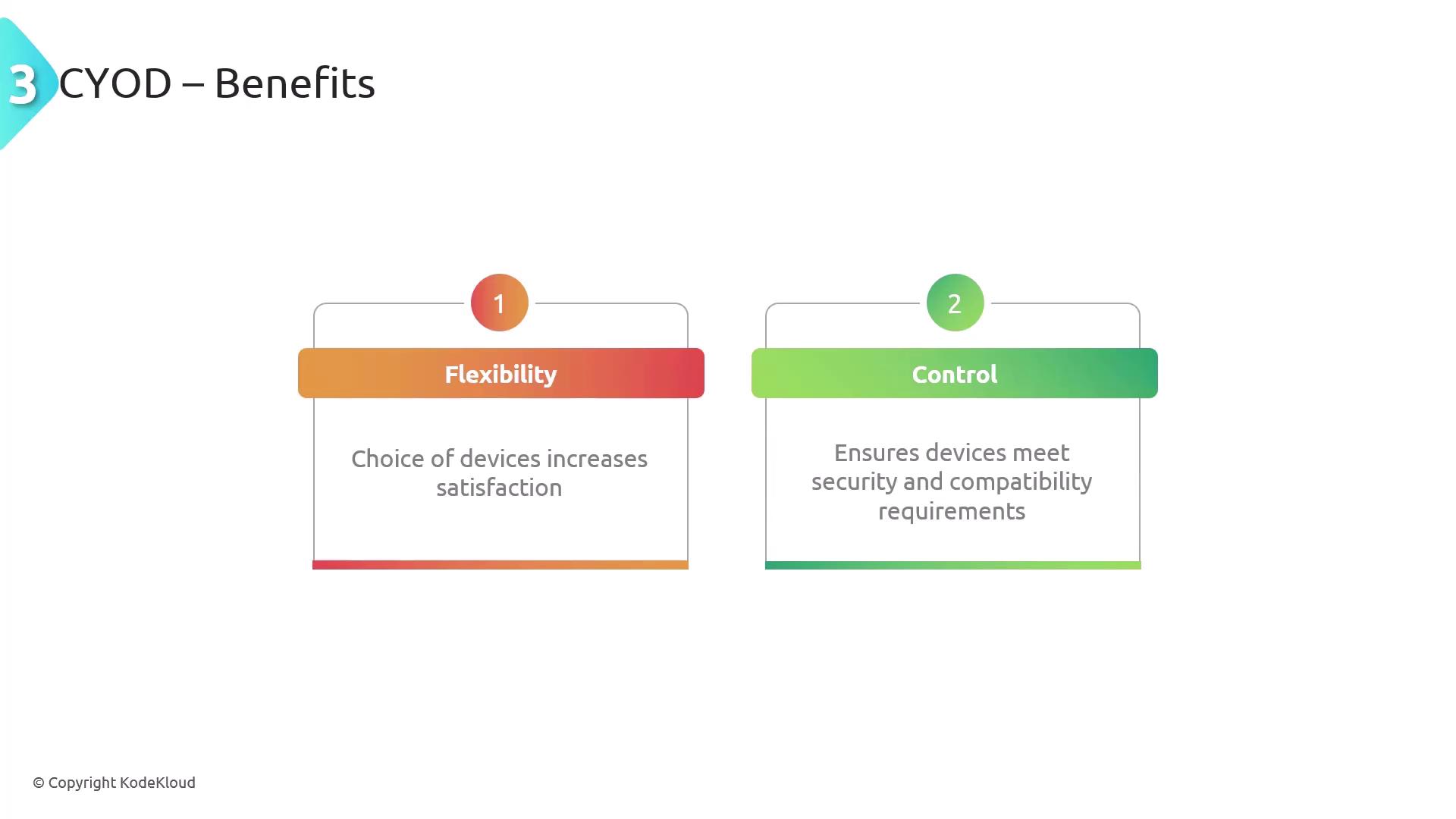
Mobile Device Connection Methods
Securing the connection methods used by mobile devices is vital for protecting data in transit. Here we examine two common connection methods:Cellular
Cellular connections use mobile networks (such as 4G and 5G) to enable internet access and communication services. To secure cellular data transmission, ensure that:- All data is encrypted during transmission.
- VPN solutions are in place to safeguard communication against interception.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology used for exchanging data between devices. To enhance Bluetooth security, consider the following:- Secure Pairing: Always use secure pairing methods and change default PINs to prevent unauthorized connections.
- Device Visibility: Keep Bluetooth devices in non-discoverable mode when not actively in use.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly update firmware to address and fix security vulnerabilities.
Ensure that both connection methods are part of your overall mobile security strategy, as vulnerabilities in either can jeopardize sensitive data.
Conclusion
Securing mobile devices and their connections is imperative for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring reliable communication. By deploying robust mobile solutions such as MDM, selecting the appropriate deployment model (BYOD, COPE, or CYOD), and securing connection methods with encryption, VPNs, and regular updates, organizations can effectively protect their mobile environments.