CompTIA Security+ Certification
Threats Vulnerabilities and Mitigations
Cloud and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
In this article, we explore how cloud computing offers numerous benefits to organizations while introducing new security challenges. Understanding these risks is critical to securing both your cloud infrastructure and your supply chain.
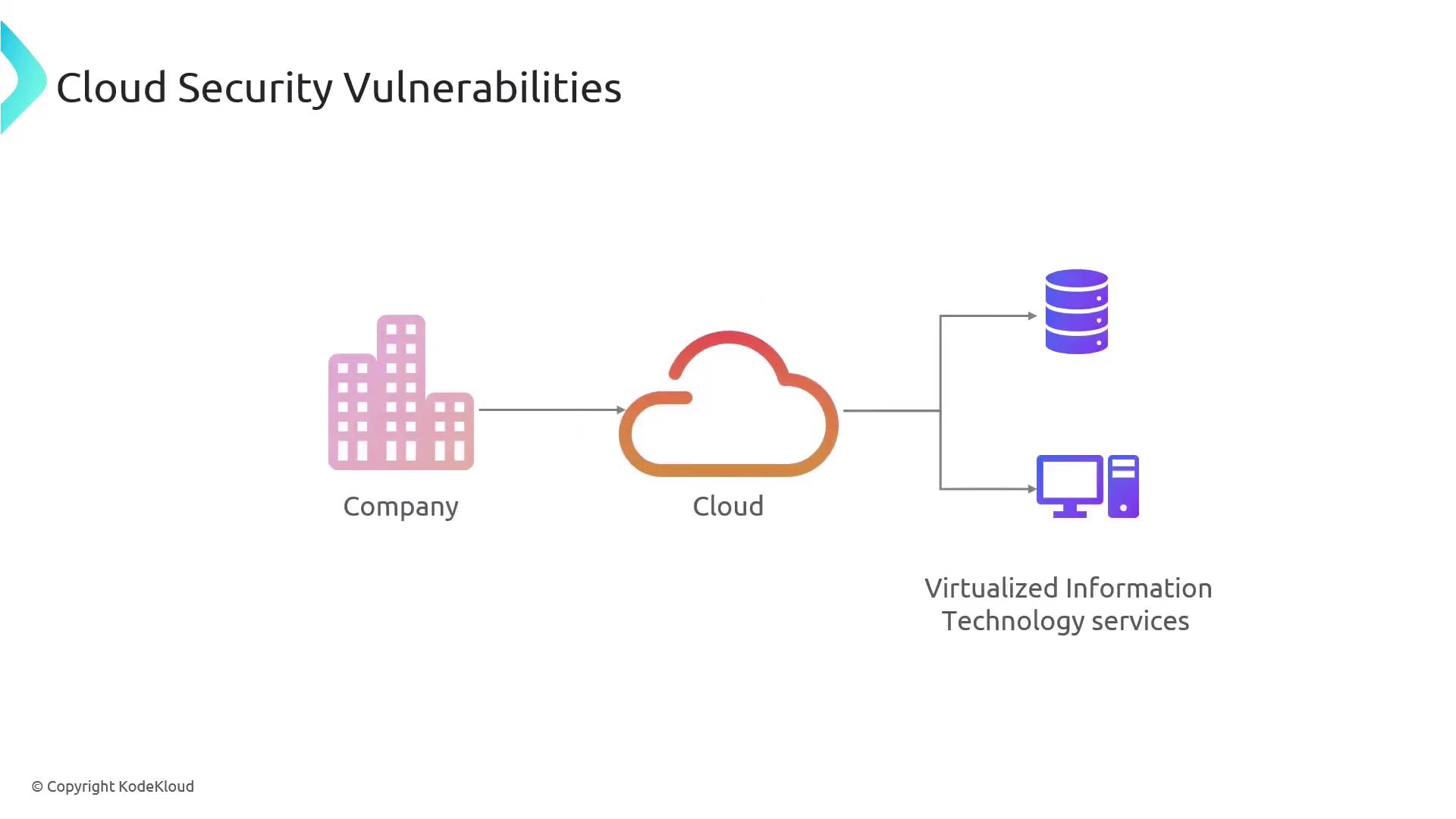
Cloud computing reduces operational costs by allowing companies to access virtualized IT services over the Internet instead of investing in on-premises infrastructure. However, these services can also introduce potential attack vectors if not properly secured.
Note
Before diving into vulnerabilities, it is crucial to have a solid grasp of core cloud concepts, as these form the foundation for identifying and mitigating risks.
Core Cloud Concepts
Cloud platforms deliver virtualized IT services that companies can rent, significantly lowering costs and management overhead compared to maintaining internal infrastructure.
Cloud Service Models
Cloud services typically follow one of these models:
| Service Model | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Software as a Service (SaaS) | Provides fully functional software on a pay-as-you-go basis. Users access applications directly over the Internet without local installation. | Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce |
| Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) | Offers virtualized IT components such as networks, servers, and storage. Allows organizations to configure and manage their own infrastructure. | Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure VM |
| Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Provides a developer-friendly environment for building and deploying applications in the cloud without managing the underlying infrastructure. | Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk |
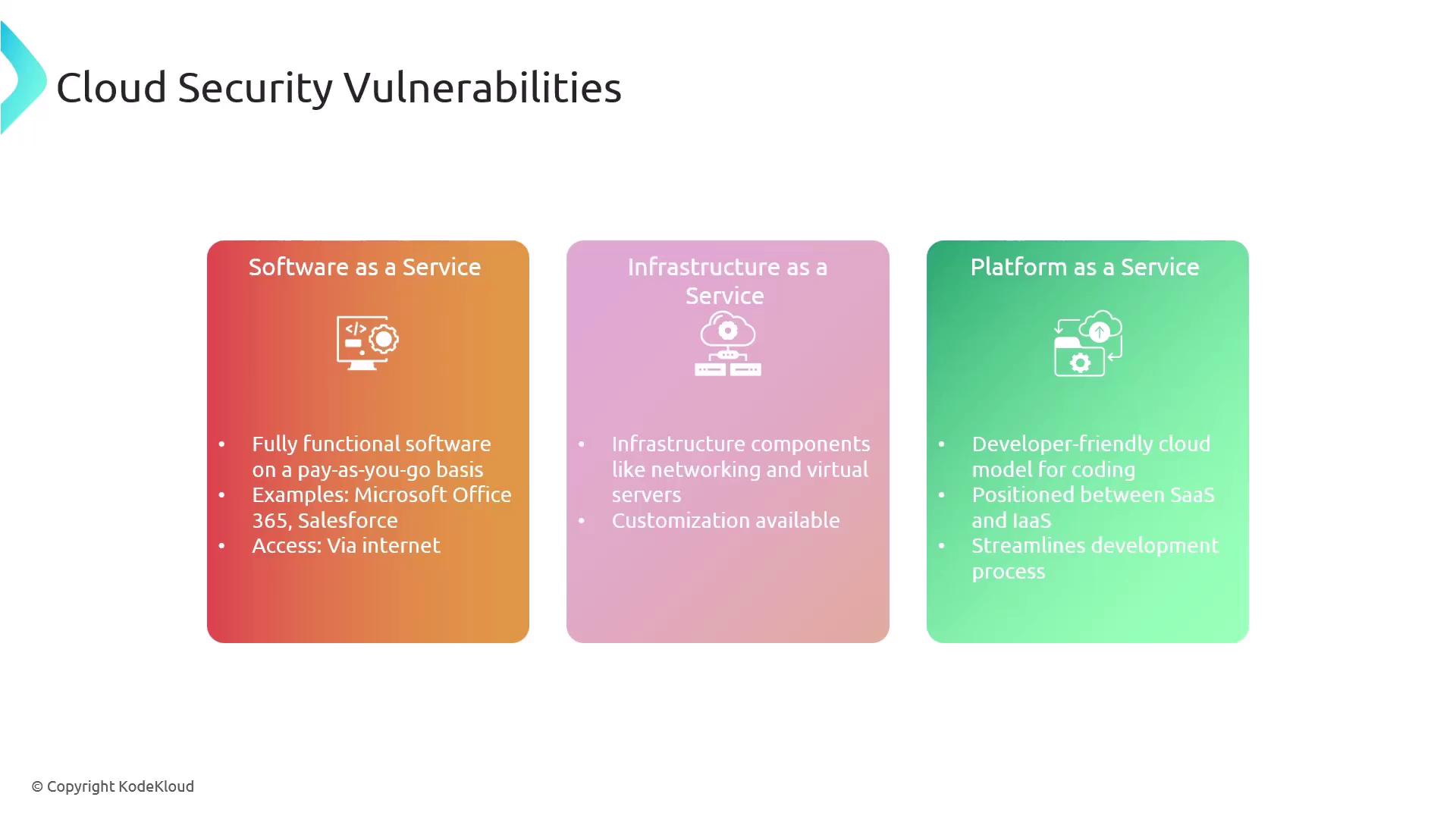
When addressing cloud security, remember that the customer is responsible for securing the components they configure. This shared responsibility applies particularly to IaaS and PaaS elements, while the cloud provider secures the underlying cloud infrastructure.
Supply Chain Dependencies
Many organizations depend on external suppliers, vendors, and business partners to support manufacturing and distribution processes. These relationships often require external entities to have connectivity to your systems, expanding your security perimeter.
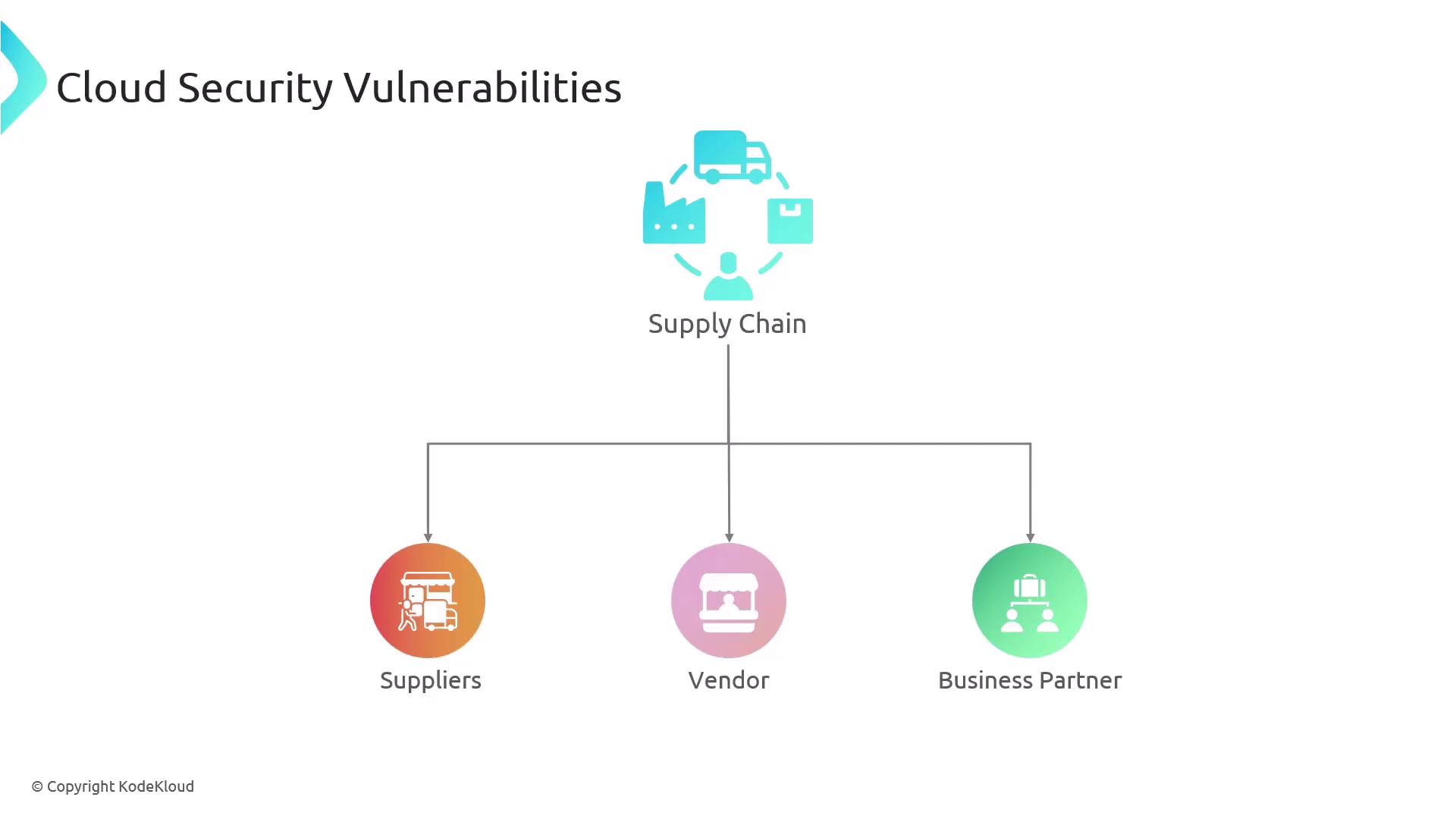
Even if your internal systems are secure, threat actors might target a less-secure external partner to gain indirect access to your primary infrastructure. In cloud environments, reliance on third-party providers further underscores the significance of maintaining robust security practices across all connections.
Warning
In a SaaS model, your security is tied to the provider’s practices. If they fail to adhere to the Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA) principles or employ weak security measures, both your organization and the provider may be at increased risk.
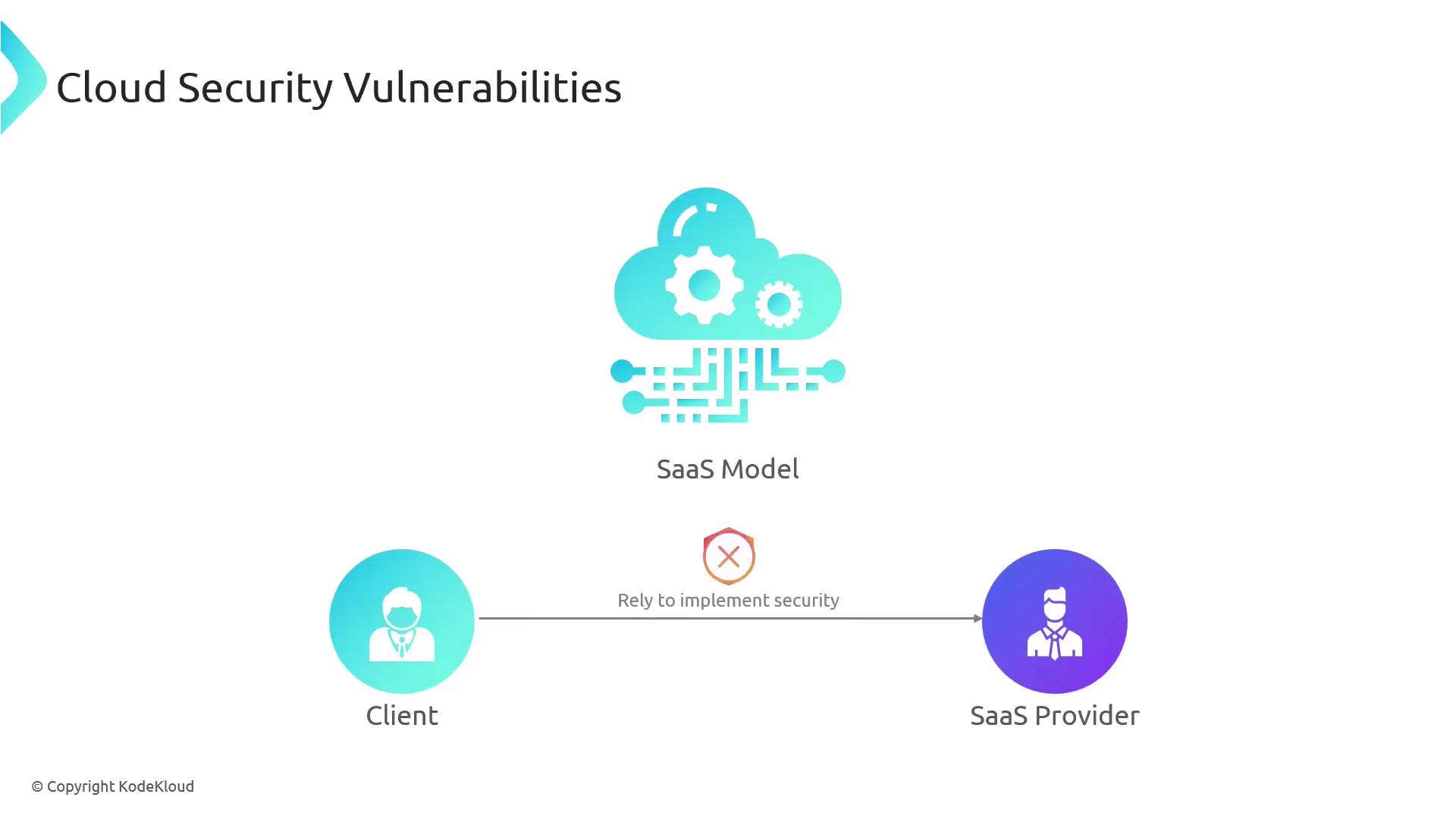
Conclusion
Understanding both the cloud service models and the dependencies in your supply chain is essential for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities. Securing your organization requires diligent internal configuration and ensuring that external partners adhere to strong security practices. For more information on cloud security best practices, consider exploring additional cloud security documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content