Understanding Kubernetes Volumes
In Kubernetes, volumes are typically provisioned through Persistent Volumes (PVs) using Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs). One common cause of access errors is a misconfiguration of access modes, which control how many pods can use a volume concurrently. Consider the diagram below, which illustrates two pods accessing volumes through PVCs: On the right side of the diagram, Pod 1 and Pod 2 are shown. Pod 1 is attached to two volumes via PVCs. The first volume is configured with the “ReadWriteOnce” access mode, meaning it supports mounting to only one pod at a time. The second volume has a “ReadWriteMany” access mode, allowing it to be mounted by multiple pods simultaneously.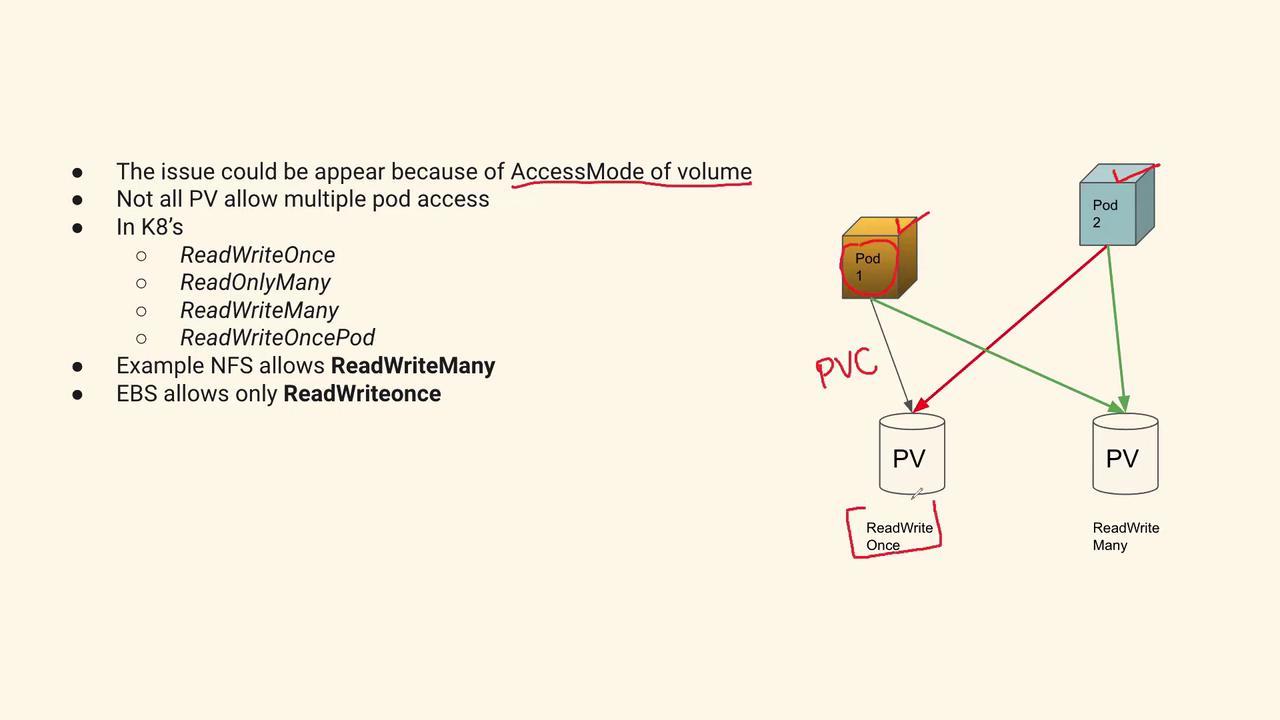
Ensure that the PVC for volumes with “ReadWriteMany” is successful when shared among pods, whereas volumes configured with “ReadWriteOnce” will fail if accessed by more than one pod.
Key Points on Kubernetes Volume Access Modes
When working with Kubernetes volumes, it is important to understand the following access mode options:- ReadWriteOnce (RWO): The volume can be mounted as read-write by a single pod or node.
- ReadWriteMany (RWX): The volume can be mounted as read-write by multiple pods or nodes.
- ReadOnlyMany (ROX): The volume can be mounted as read-only by multiple pods or nodes.
- An NFS (Network File System) volume typically uses the ReadWriteMany access mode.
- An AWS EBS (Elastic Block Store) volume leverages the ReadWriteOnce access mode.
Diagnosing and Resolving Volume Access Issues
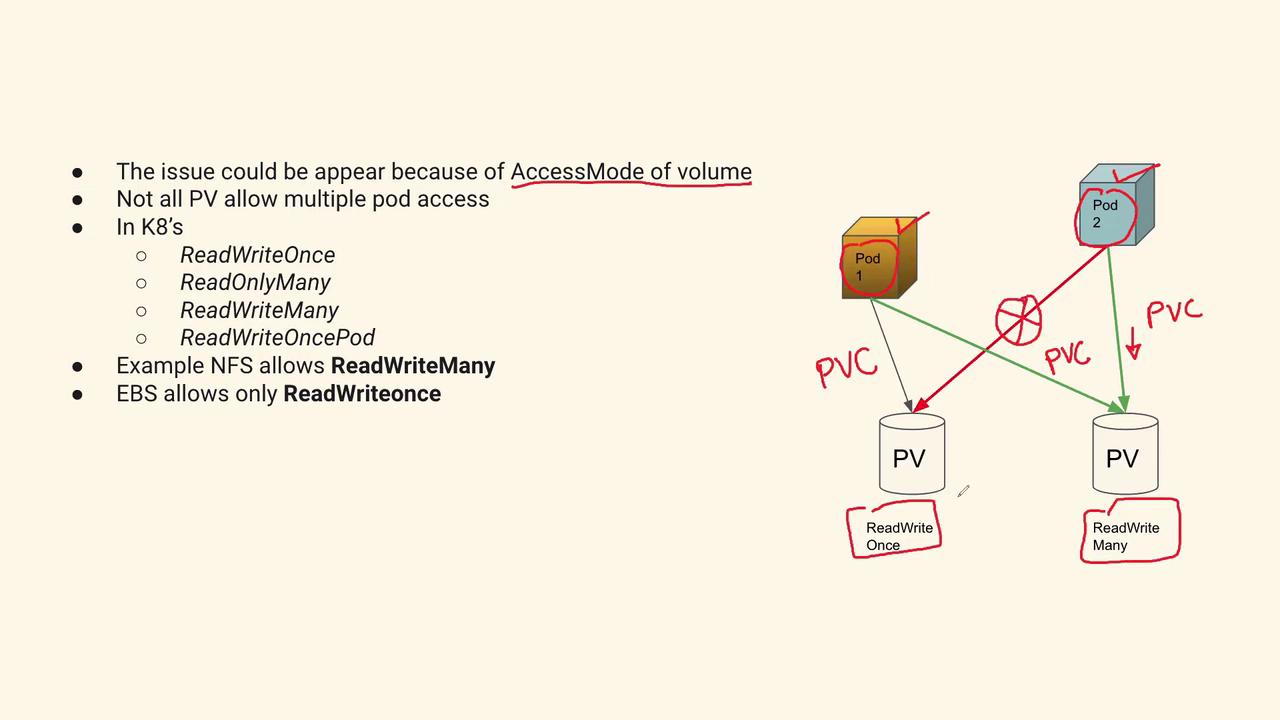
The volume access error occurs because a pod tries to attach to a volume that only supports the ReadWriteOnce access mode, which restricts simultaneous mounting by multiple pods. Here are two strategies to resolve this issue:- Adjust the PV and PVC Configurations:
- Update the PersistentVolume (PV) and PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) definitions to use the ReadWriteMany access mode if the volume needs to be shared among multiple pods.
- Assign Dedicated Volumes for Each Pod:
- Create separate volumes with the appropriate access mode and configure each pod to use its own dedicated volume.
When choosing an access mode, consider the workload and sharing requirements. For example, use an NFS volume for shared access scenarios and an AWS EBS volume for isolated, single-pod access.