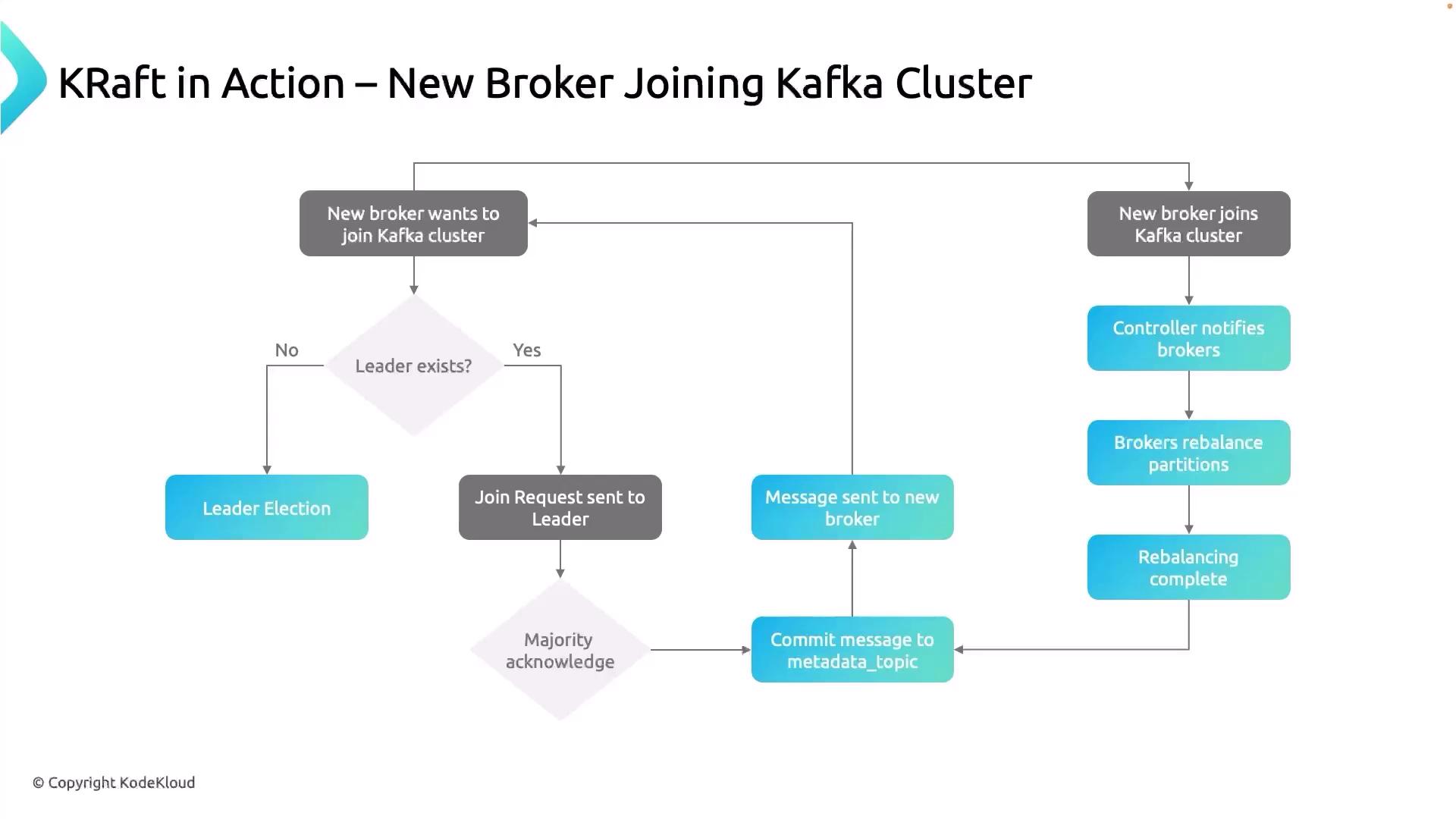
Cluster Join Workflow
Below is a high-level overview of each step in the broker-join process:| Step | Description | Component |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Broker startup and leader check | New Broker & Controllers |
| 2 | Submit BrokerRegistration request | Broker → Controller |
| 3 | Quorum consensus on registration | Controller Quorum |
| 4 | Update _cluster_metadata and acknowledge | Controller |
| 5 | Notify all brokers of the new member | Controller → Brokers |
| 6 | Rebalance partitions across the cluster | Partition Reassigner |
| 7 | Commit final partition assignments to metadata | Metadata Topic |
1. Broker Startup and Leader Election
- The new broker process launches and attempts to join the cluster.
- It checks if a controller (leader) exists:
- No controller: KRaft controllers trigger a leader election.
- Controller present: Broker proceeds to send its join request.
2. Sending the BrokerRegistration Request
The broker sends a BrokerRegistration RPC to the elected controller to initiate the join.
Before accepting the request, the controller validates broker settings—unique
broker.id, version compatibility, listener configurations, and any security protocols.3. Achieving Quorum Consensus
- The controller broadcasts the registration to the controller quorum.
- A majority of controllers must acknowledge to confirm the new broker can join.
4. Metadata Topic Update and Acknowledgment
Once consensus is reached:- The controller appends the new broker’s entry to the
_cluster_metadatatopic. - An acknowledgment is sent back to the joining broker, marking it as active.
5. Cluster-wide Notification
- All existing brokers receive a notification about the new member.
- This event is also recorded in the metadata topic to ensure durability.
6. Partition Rebalancing
After onboarding:- The cluster evaluates current partition assignments.
- Partitions are redistributed to include the new broker, balancing load.
Partition rebalancing can temporarily increase network and disk I/O. Schedule rebalances during off-peak hours or monitor metrics closely.
7. Finalizing the Integration
- Updated partition assignments are committed to the
_cluster_metadatatopic. - The cluster is now fully operational with the new broker integrated.
By leveraging KRaft’s built-in controller quorum and metadata topics, Kafka ensures high availability, strong consistency, and seamless scaling—eliminating the need for an external ZooKeeper service.