How Kafka Assigns Partitions
When a producer sends a record, it provides both a key and a value. The Kafka client then:- Fetches Cluster Metadata
The producer connects to a bootstrap server to retrieve metadata (brokers, topics, partitions). - Applies the Partitioner
Using the metadata, the client-side partitioner computes a hash of the key and selects a partition. - Sends to the Leader
The record is routed directly to the leader broker for the chosen partition, avoiding inter-broker forwarding.
Partition Assignment Workflow
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Connect to bootstrap server and fetch metadata |
| 2 | Call the partitioner with the record key |
| 3 | Compute partition_index = hash(key) % num_partitions |
| 4 | Send the record to the leader of partition_index |
| 5 | Leader appends the record to its log and replicates it according to topic settings |
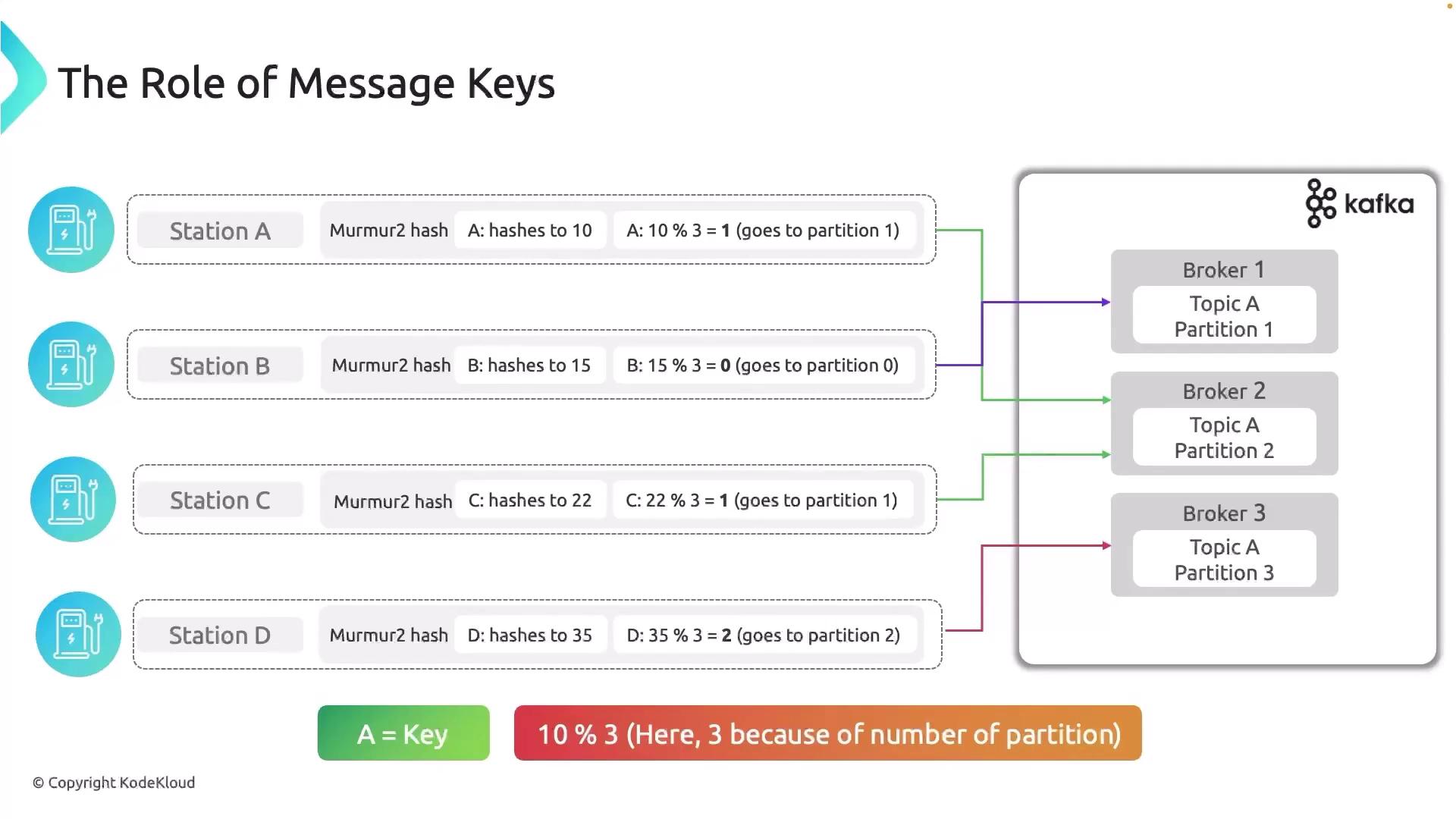
If the record key is
null, the default partitioner falls back to round-robin distribution across available partitions.The Murmur2 Hash Algorithm
Kafka’s default partitioner uses the non-cryptographic MurmurHash2 (Murmur2) function to hash message keys. This choice provides:- Even Distribution: Prevents hotspots by spreading keys across partitions.
- Ordering Guarantees: Ensures messages with the same key always go to the same partition.
- Low Overhead: Fast hashing suitable for high-throughput streaming.
"StationA":
hash = murmur2("StationA") // e.g., 10partition = 10 % 3 = 1- The record always goes to partition 1.
Key Benefits
- Load Balancing: Evenly distributes data to prevent overloaded partitions.
- Parallel Processing: Different partitions can be consumed concurrently.
- Ordering: Guarantees per-key ordering within a partition.
- Client-Side Routing: Reduces broker overhead by computing routes on the producer.