Fundamentals of MLOps
Data Security and Governance
Data Access Management
Welcome to this lesson on Data Access Management (DAM). In today's digital landscape, ensuring secure and efficient data access is critical. DAM enables organizations to deliver the right resources to the right users while upholding strict security standards.
Pillars of Data Access Management
Data Access Management relies on several core components to secure and streamline access:
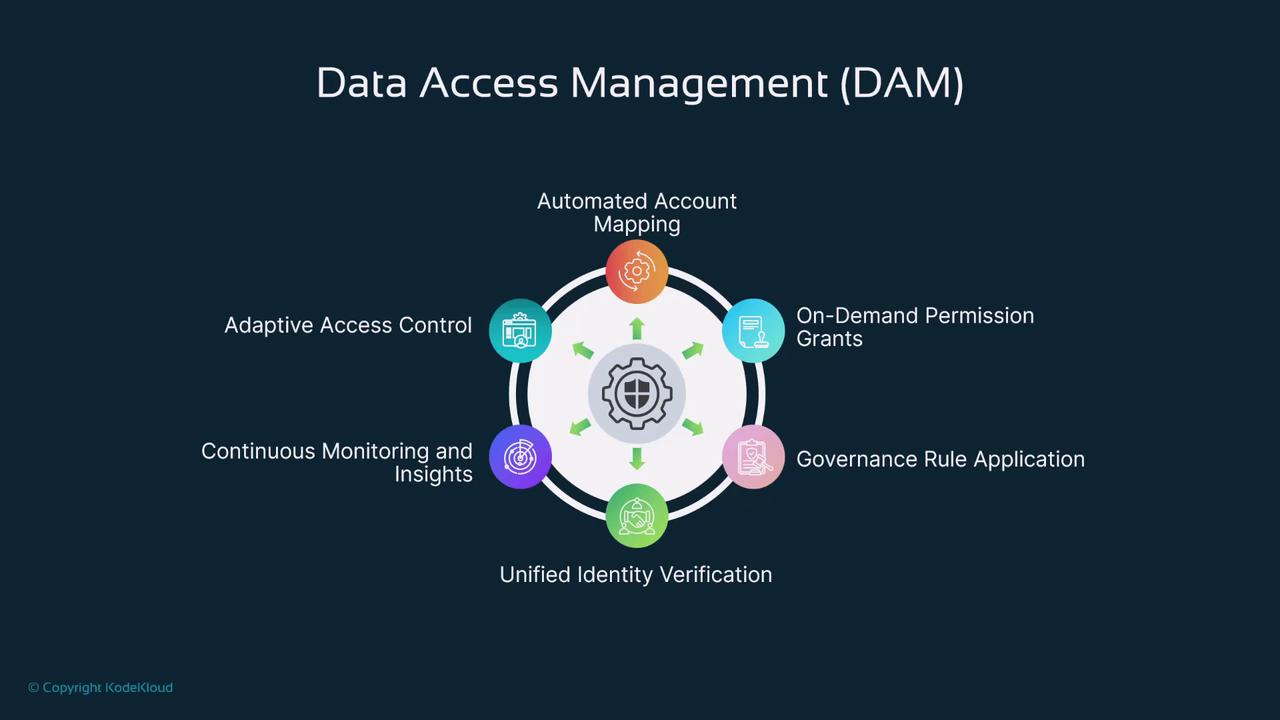
Automated Account Mapping
This process simplifies user onboarding by linking employee accounts automatically to the tools and platforms needed for their roles. For example, when a new employee joins, the system assigns the necessary resource permissions automatically.On-Demand Permission Grants
Users can request temporary access to specific resources as situations arise. For instance, a developer may request temporary access to a production database for troubleshooting, with the permission automatically revoked after a defined period.Governance Rule Application
Governance ensures that access policies adhere to regulatory and compliance standards. A financial institution, for example, might enforce strict data access rules to protect sensitive information in line with GDPR or PCI guidelines.Unified Identity Verification
This component consolidates multiple authentication factors—such as passwords, biometrics, and device recognition—to verify user identities reliably in a single streamlined process.Continuous Monitoring and Insights
Real-time monitoring offers visibility into data access activities. Security teams can promptly address unauthorized access attempts with timely alerts.Adaptive Access Control
Access permissions are dynamically tailored based on context such as location or device. For example, if a user logs in from an unfamiliar country, additional verification steps may be triggered.
Below is a diagram illustrating the six components of data access management:
Key Technical Components
To build an effective DAM system, several technical elements come into play:
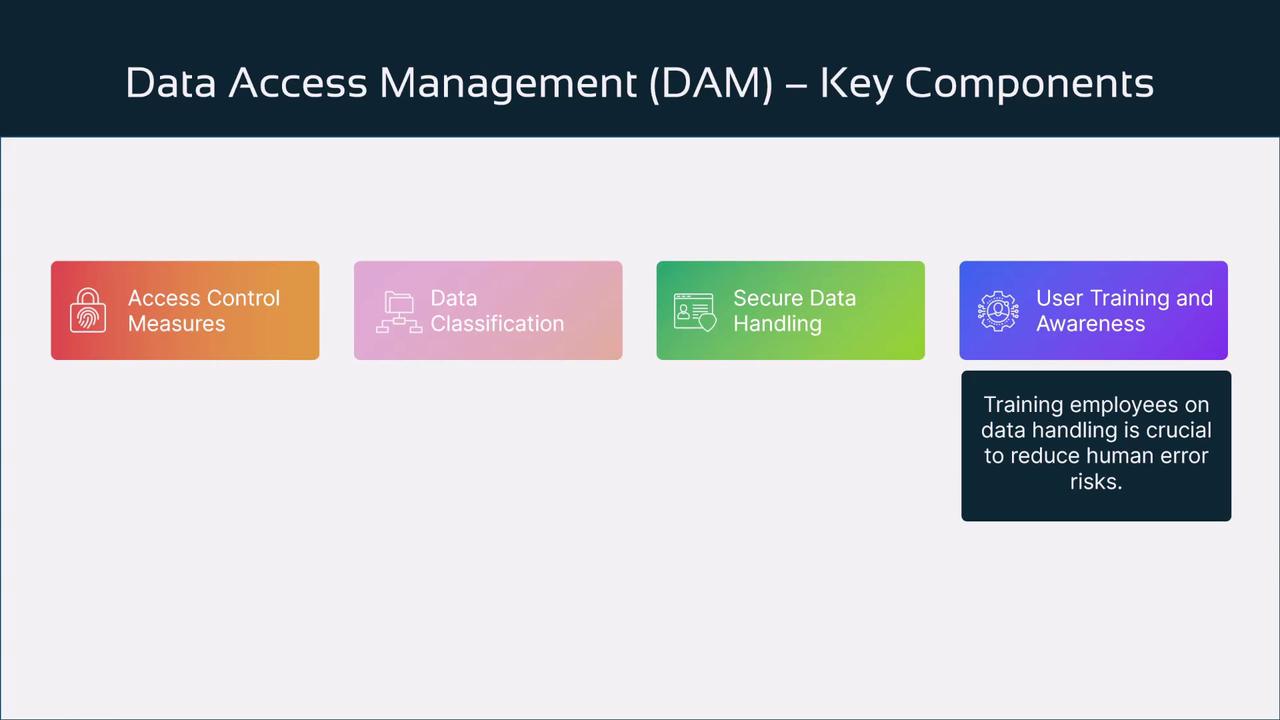
Access Control Measures
Technologies like multi-factor authentication and biometric verification provide robust security. For example, many companies require both a password and a fingerprint scan for system access.
Data Classification
Categorizing data by sensitivity (e.g., public, confidential, or restricted) ensures that appropriate controls are in place. In a hospital, patient medical records might be classified as confidential, while general announcements remain public.
Secure Data Handling
Encryption is critical for protecting data both at rest and in transit. Financial institutions, for instance, encrypt databases and secure online transaction data to prevent unauthorized interception.
User Training and Awareness
Regular training sessions empower employees to recognize phishing attempts and manage data responsibly. Educated users are less likely to inadvertently compromise sensitive information.
The diagram below outlines these key components:
Implementing Data Access Management
Organizations can implement effective DAM strategies by adopting several foundational practices:
Robust Policies
Clear guidelines should specify who can access what resources and under which conditions. For example, an HR policy might dictate that only payroll staff can view salary information.Access Control Models
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Access is granted based on job responsibilities.
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC): Resource owners determine access permissions. For instance, a project manager might control editing rights for shared documents.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Strict access is enforced based on clearance levels, commonly used in military and highly secure environments.
Automated Identity Management
Leveraging automation reduces manual errors, such as ensuring that employee access is automatically removed when they leave the organization.Regular Audits and Monitoring
Routine audits help identify unauthorized access attempts. When discrepancies occur—such as a user accessing a system without permission—prompt corrective action can be taken.
Note
Regular auditing and continuous monitoring not only ensure compliance but also help in early detection of potential security breaches.
Best Practices for Data Access Management
Consider the following practices to maintain a secure data environment:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users only the access necessary to complete their tasks. For example, a marketing intern does not need access to financial records.
- Regular Permission Reviews: Continuously verify and update access rights as roles change; for instance, when an employee transfers between departments.
- Comprehensive Logging: Maintain detailed logs of data access events to support audits and investigations in case of security incidents.
- Ongoing Employee Education: Consistent training on emerging security threats and best practices reinforces the protection of sensitive data.
The diagram below visually summarizes these best practices:

Warning
Failure to regularly update and monitor access privileges can result in security vulnerabilities and increased risk of data breaches.
Conclusion
Data Access Management is essential not only for protecting sensitive information but also for ensuring that organizations operate securely and efficiently. By automating processes, enforcing strict controls, continuously monitoring access, and investing in employee education, organizations can create a secure, compliant, and well-managed data environment.
For more in-depth information, consider exploring additional resources such as Kubernetes Documentation or Docker Hub.
Watch Video
Watch video content