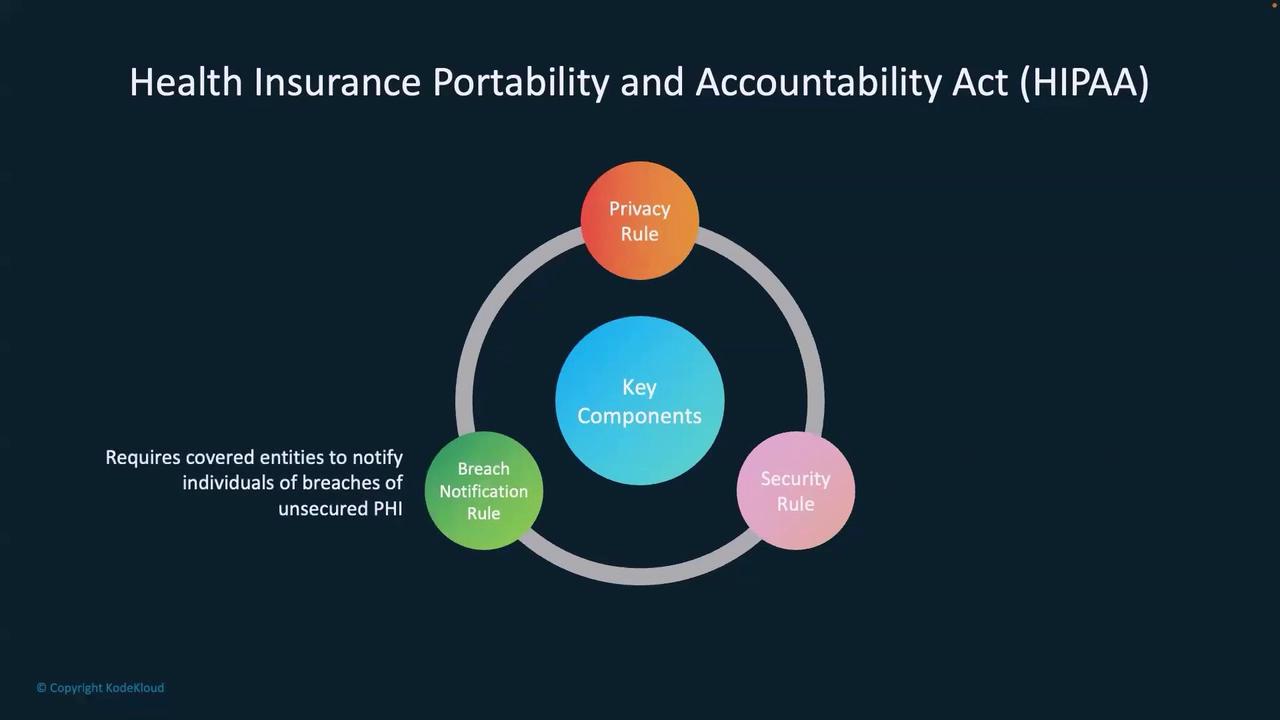
Core Components of HIPAA
HIPAA is built on three fundamental rules:-
Privacy Rule
Establishes national standards for protecting patients’ health records. Under this rule, any medical records maintained at a clinic or hospital are kept strictly confidential. -
Security Rule
Focuses on safeguarding electronic health information. It mandates measures like encryption and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to healthcare systems. -
Breach Notification Rule
Requires prompt notifications to patients if their data is compromised. For example, if a hospital experiences a data breach, it must notify all affected individuals to ensure transparency.
Compliance Requirements
To remain HIPAA-compliant, organizations must implement a variety of safeguards:-
Administrative Safeguards:
Policies and procedures to manage the selection, development, and maintenance of secure systems handling sensitive data. -
Physical Safeguards:
Controls to protect the physical facilities and equipment from unauthorized access. -
Technical Safeguards:
Measures such as secure logins, strict access control, encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
Employee training is critical. Organizations must regularly train staff on privacy policies and security protocols to ensure they handle sensitive data responsibly.

Failure to implement robust HIPAA safeguards can not only lead to legal repercussions but may also damage your organization’s credibility and trust among patients. Always ensure your systems and processes are up to date with HIPAA requirements.