Storage classes allow you to optimize costs by balancing storage expenses with data access frequency and durability. They help ensure that you only pay the necessary cost for data that is seldom accessed.
Storage Class Details
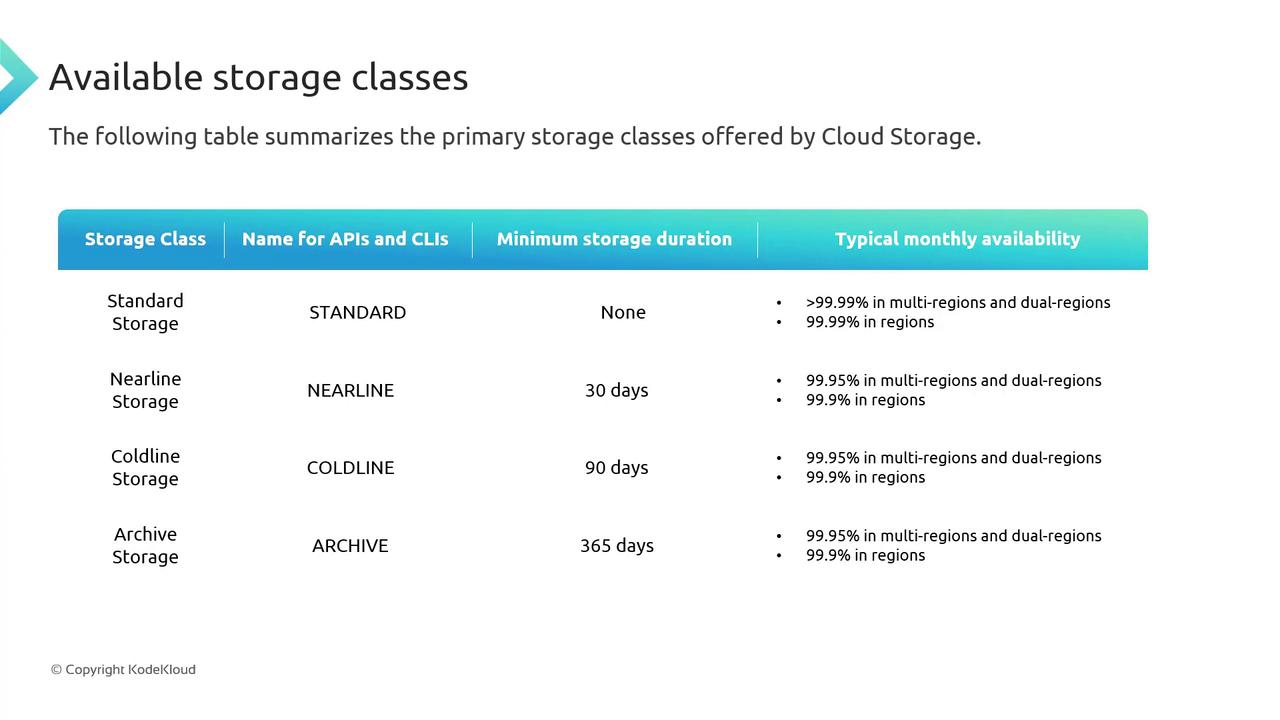
Standard Storage
Standard Storage is the default option. With Standard Storage, there is no minimum storage duration requirement. You can delete files immediately after uploading, and you only pay for the duration that the file is stored.Nearline, Coldline, and Archive Storage
The other storage classes, such as Nearline, Coldline, and Archive Storage, are designed for cost-effective storage of infrequently accessed data. For example, when you upload data to Nearline Storage, it must be retained for at least 30 days. Despite the lower storage costs compared to Standard Storage, retrieval fees can be higher. As you progress from Standard to Nearline, then to Coldline and Archive Storage, costs decrease. Archive Storage is particularly ideal for long-term retention of data that might not be accessed regularly—such as files from over a year ago that are retained solely for archival or auditing purposes.Remember that while Nearline, Coldline, and Archive Storage offer cost-effective solutions, the cost of retrieving data from these classes is higher. Ensure that you only move data that is not required for rapid, daily access into these storage classes.