GitOps with ArgoCD
ArgoCD Intermediate
Git Webhook Configuration
In this article, we describe how to configure a Git webhook on your repository so that any push event triggers a notification to the ArgoCD server. Previously, we created two applications; here, we'll create another application and examine the reconciliation process in detail.
Creating the Git Webhook Application
Begin by creating a new application called "Git Webhook" that will handle the webhook configuration. Use the default project with a manual synchronization policy and enable the auto-creation of the namespace. For the repository, reference the GitOps ArgoCD repository that contains an Nginx application. This Nginx application includes a directory with a deployment manifest that deploys the Nginx app with one replica.
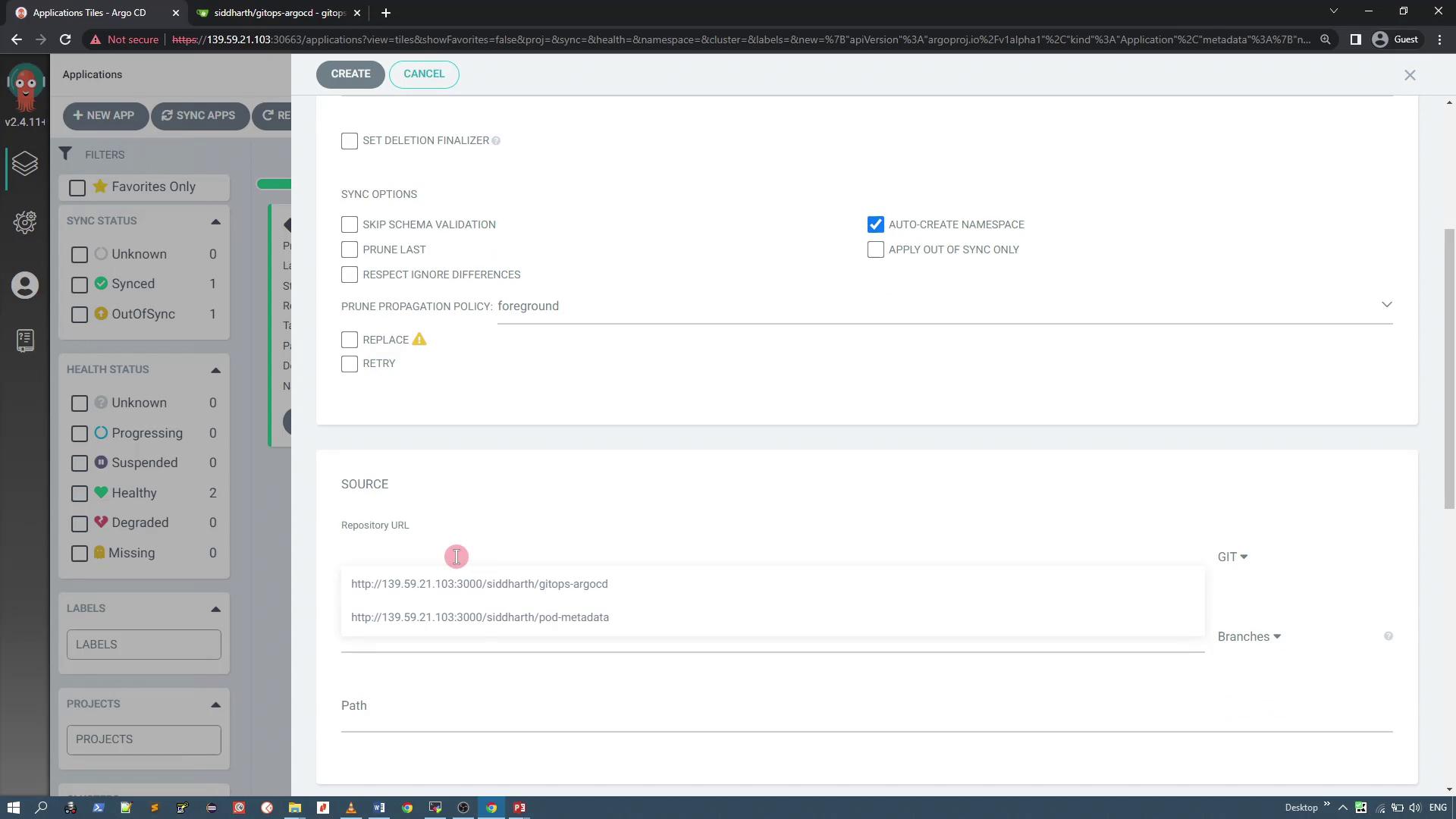
Below is the deployment manifest for the Nginx application:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
name: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 80
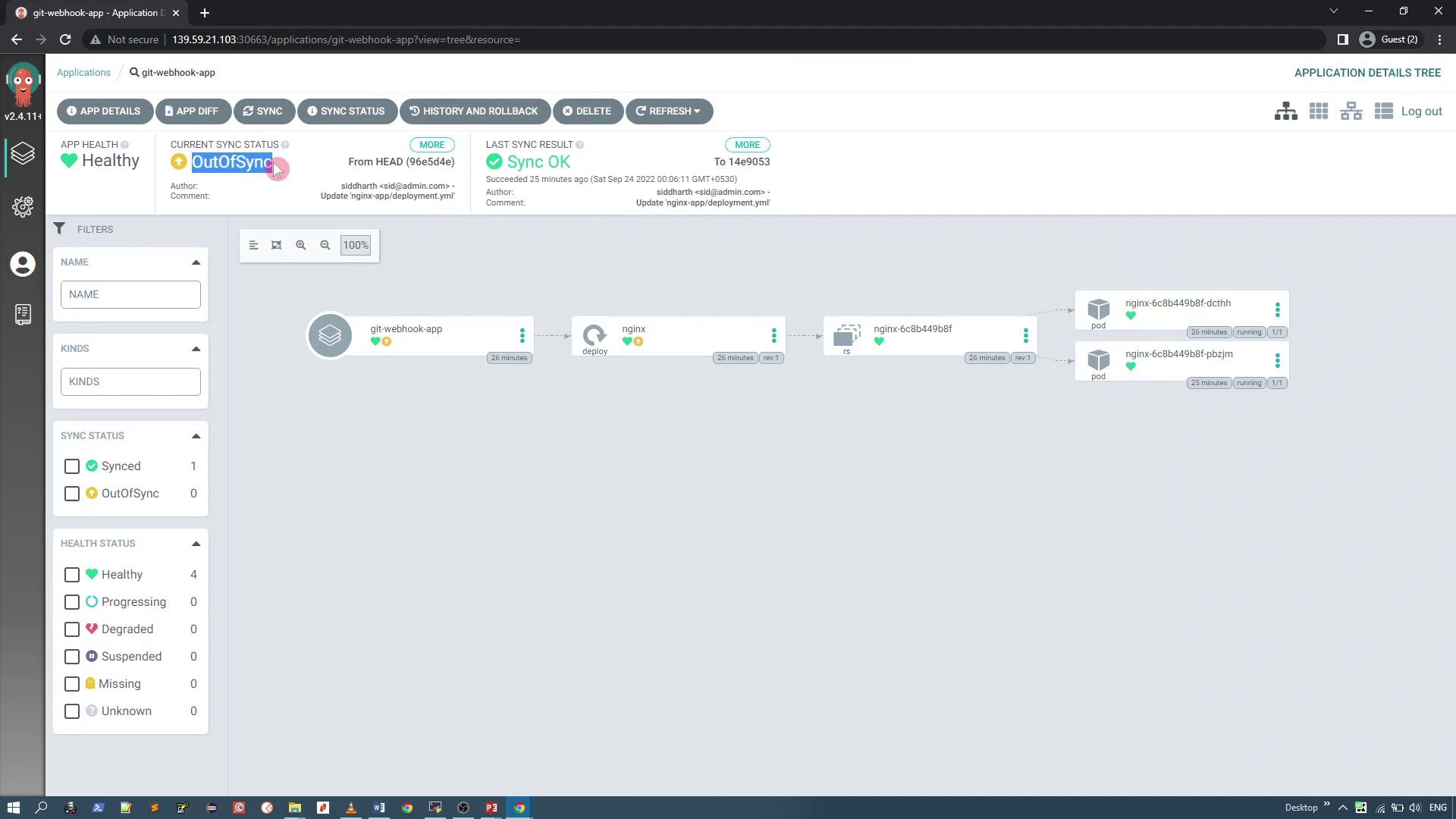
Deploy this application in a namespace named "webhook." Once the application is created and synchronized, it deploys the Nginx application and creates an Nginx pod.
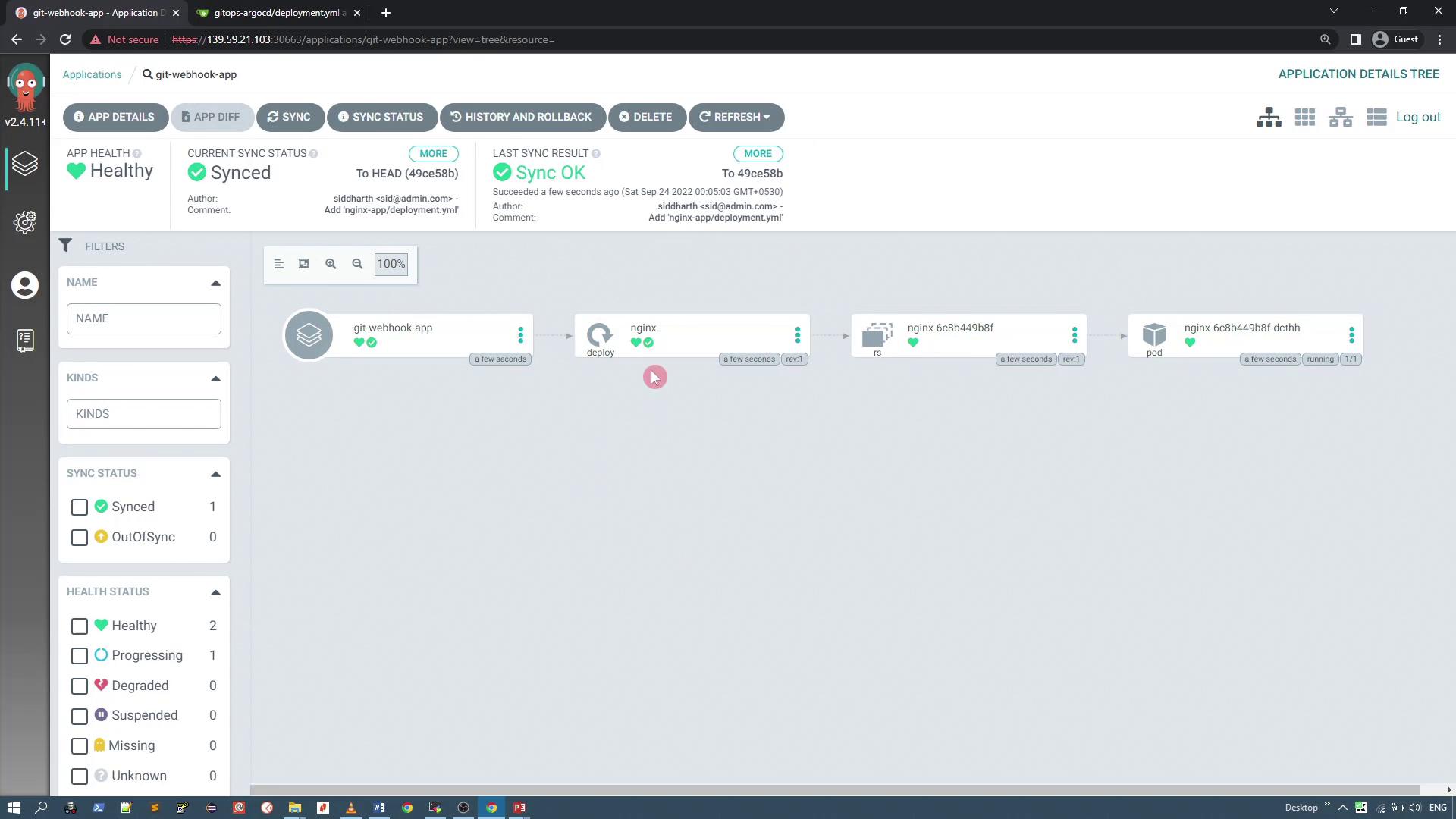
At this point, since there is no service defined (as we are focusing solely on reconciliation), the application status remains synced.
Modifying the Deployment and Checking Reconciliation
To test ArgoCD's response to changes, update the deployment manifest by changing the number of replicas from one to two. Below is the manifest before any modification:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
name: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Commit these changes. Even after the update, if you inspect the ArgoCD application, the sync status remains "Synced" because ArgoCD polls the repository every three minutes by default. To expedite the process, click the "Refresh" button manually. This forces ArgoCD to recheck the repository and update the synchronization status accordingly. At this point, the Nginx application scales to two pods.
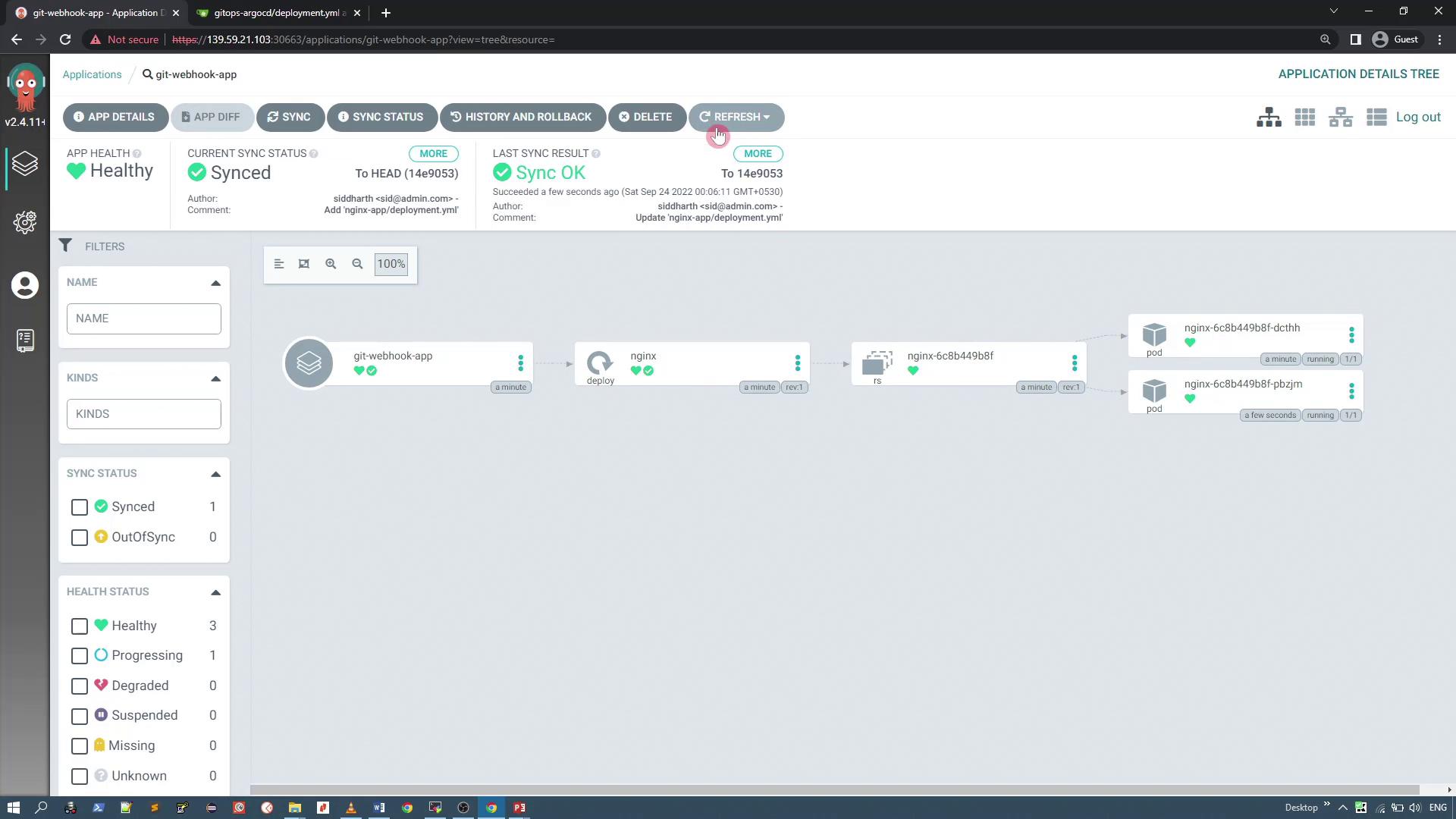
Adjusting Polling Time via Repository Server Configuration
If you need a different polling interval (for example, one, five, or ten minutes instead of three), modify the polling time in the ArgoCD repository server configuration. First, check the ArgoCD repo server pod in the ArgoCD namespace by running:
k -n argocd describe po argocd-repo-server-5576f8d84b-whtsg | grep -i recon
This command shows several volume configurations and environment parameters. The ArgoCD repo server fetches data from the Git repository and performs reconciliation based on the ARGOCD_RECONCILIATION_TIMEOUT environment parameter. This parameter derives its value from the ArgoCD config map.
To update the reconciliation timeout (for example, to 300 seconds), edit the ArgoCD config map (argocd-cm). Start by retrieving the config map:
k -n argocd get cm argocd-cm -o yaml
The retrieved configuration might look like:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"ConfigMap","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"app.kubernetes.io/name":"argocd-cm","app.kubernetes.io/part-of":"argocd"},"name":"argocd-cm","namespace":"argocd"},"data":{}}
creationTimestamp: "2022-09-23T14:01:01Z"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: argocd-cm
name: argocd-cm
namespace: argocd
resourceVersion: "81266"
uid: 898f14a2-4f23-456f-9561-0767f2388485
Add an entry for "timeout.reconciliation": "300" (or any desired timeout value) inside the data field. The repository server will detect the change and adjust its polling frequency thereafter.
An alternative approach is to use webhooks to update the synchronization status immediately when a push event occurs.
To verify the updated reconciliation timeout, run:
k -n argocd describe po argocd-repo-server-5576f8d84b-whtsg | grep -i recon
And check the config map again with:
k -n argocd get cm argocd-cm -o yaml
The output should now display the timeout.reconciliation field with your configured value.
Configuring the Git Webhook
Navigate to the webhooks section in your Git repository settings. With no webhooks configured initially, add a new webhook with the following details:
- Target URL: Your ArgoCD server URL appended with
/api/webhook - HTTP Method: POST
- Content Type: application/json
- Secret: (Leave empty if not used)
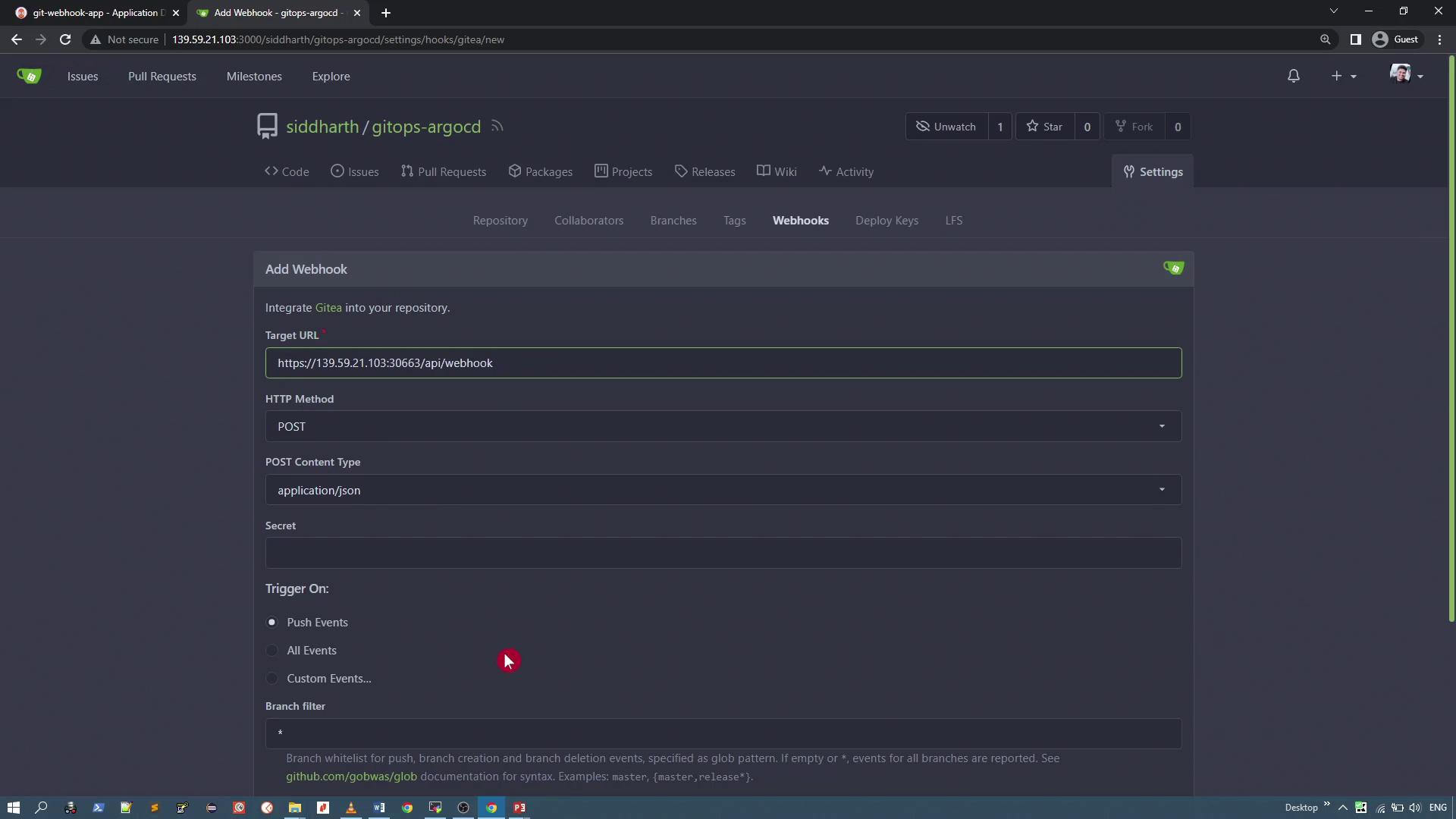
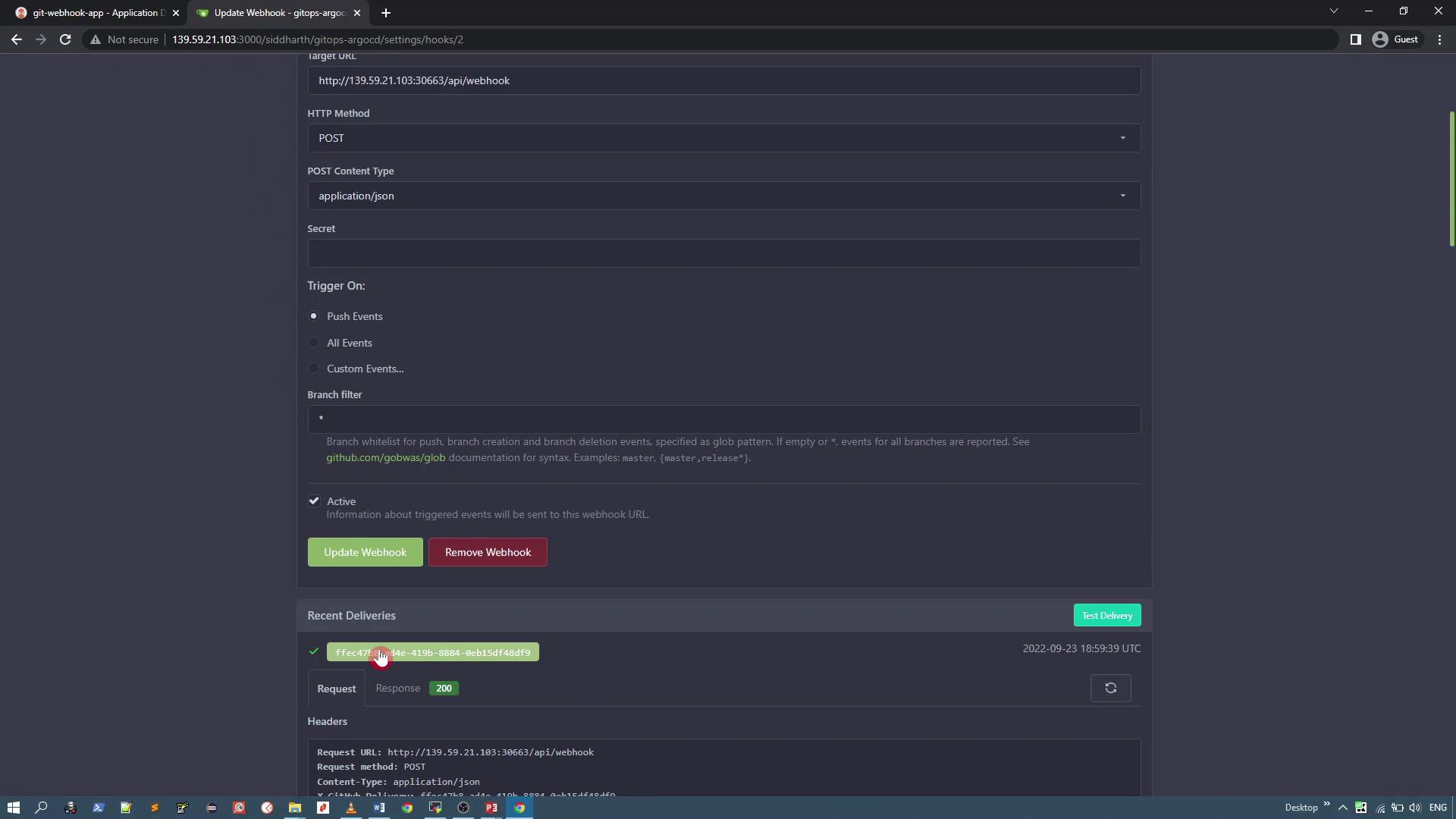
Select push events as the trigger and save the webhook configuration. Once configured, test the delivery. If the webhook delivery fails with a certificate error (for example, "cannot validate the certificate" due to a self-signed certificate), adjust your ArgoCD server settings to allow insecure connections.
Configuring ArgoCD Server for Insecure (HTTP) Connections
To bypass certificate validation issues (often encountered with self-signed certificates), configure the ArgoCD server deployment to run in insecure mode using plain HTTP. Edit the ArgoCD server deployment with the following command:
k -n argocd edit deployments.apps argocd-server
Within the deployment specification, locate the container command that starts argocd-server and modify the environment variables by adding a tag named ARGCOD_SERVER_INSECURE. Below is an excerpt of the configuration:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: argocd-server
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: argocd-server
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
weight: 100
containers:
- command:
- argocd-server
env:
- name: ARGCOD_SERVER_INSECURE
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
key: server.insecure
name: argocd-cmd-params-cm
optional: true
- name: ARGCOD_SERVER_BASEHREF
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
key: server.basehref
name: argocd-cmd-params-cm
optional: true
- name: ARGCOD_SERVER_ROOTPATH
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
key: server.rootpath
name: argocd-cmd-params-cm
Save your changes so that the ArgoCD server redeploys. Monitor the new pods coming up by running:
k -n argocd get po
After the new ArgoCD server pod is running, it will listen on HTTP instead of HTTPS. Update the webhook URL accordingly (i.e., replace https:// with http://).
Finally, update the webhook configuration to use HTTP and test the delivery again.
Warning
Running the ArgoCD server in insecure mode (HTTP) can expose your environment to potential security risks. Use this configuration only for testing or in controlled environments.
Testing Reconciliation with Webhooks
To demonstrate how synchronization occurs when the Git repository is updated, open the deployment manifest for the Nginx application which currently deploys two pods:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
name: nginx
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 80
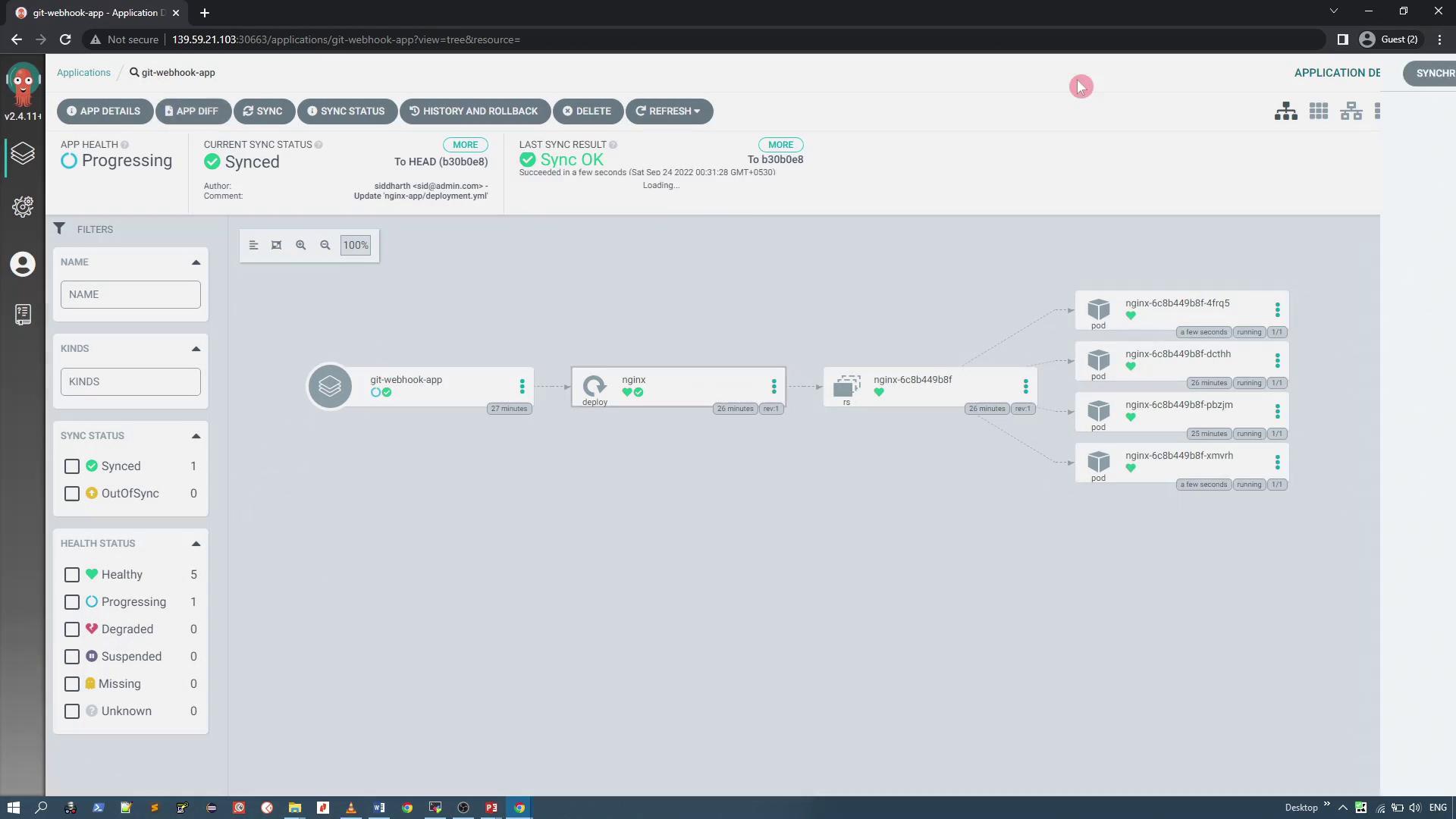
Edit the file to change the replica count (for example, increase it to four replicas), and commit the change. The push event triggers the webhook, which immediately notifies the ArgoCD server. Consequently, the application status in the ArgoCD dashboard will change from "Synced" to "OutOfSync."
Synchronize the application to update the deployment. ArgoCD will then scale the application accordingly. You can further experiment by scaling down to one replica; after committing this change, the status turns out of sync, and synchronizing will adjust the deployment to match the desired state.
Summary
In summary, this article demonstrated two effective approaches for triggering reconciliation in ArgoCD:
- Adjusting the reconciliation timeout in the ArgoCD config map to control how often the repository server polls the Git repository.
- Configuring webhooks in your Git repository so that ArgoCD is notified immediately upon a push event.
Important Note
Ensure that when using webhooks, the target URL utilizes a valid TLS certificate. If you are using self-signed certificates, you must configure your ArgoCD server to run in insecure mode (HTTP) or use a certificate that can be validated.
Always verify that configuration changes (whether for timeouts or insecure mode) are correctly applied by checking the associated pod details.
Thank you.
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab