GitOps with ArgoCD
Multi cluster application deployment 2
In this lesson, we will explore how ArgoCD can deploy applications to an external Kubernetes cluster where ArgoCD is not installed. This approach, often called the multi-cluster deployment model, allows you to manage applications across multiple clusters effectively.
To implement this solution, you will need two Kubernetes clusters:
- Demo Cluster: The cluster where ArgoCD is running and your demos are executed.
- External Dev Space Cluster: The cluster where the application will be deployed.
Below is a step-by-step guide to setting up and deploying an application to an external cluster.
────────────────────────
Verifying the Clusters
────────────────────────
Before proceeding, ensure that both clusters are operational by checking the nodes on each cluster.
Tip
Use the kubectl command (k for short) to quickly verify your node status.
On the dev space cluster, run the following command:
k get node
Expected output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
dev-space Ready control-plane 7d4h v1.24.3
Next, on the demo cluster (running ArgoCD), verify the nodes:
k get node
Expected output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
demo-cluster Ready control-plane 25h v1.24.3
────────────────────────
Adding an External Cluster to ArgoCD
────────────────────────
By default, ArgoCD targets the cluster on which it is installed. To manage the external dev space cluster, you need to add its context to ArgoCD. Ensure the external cluster's context is defined in your kubeconfig by listing available contexts:
k config get-contexts
Verify that the dev space context (for example, admin@devspace) is available. Then, add the external cluster to ArgoCD:
argocd cluster add admin@devspace
During this process, you will receive a warning about the creation of a service account and associated roles on the external cluster. Confirm by typing “y” when prompted. Below is a sample interaction:
argocd cluster add admin@devspace
WARNING: This will create a service account `argocd-manager` on the cluster referenced by context `admin@devspace` with full cluster level privileges. Do you want to continue [y/N]? y
INFO[0015] ServiceAccount "argocd-manager" created in namespace "kube-system"
INFO[0015] ClusterRole "argocd-manager-role" created
INFO[0015] ClusterRoleBinding "argocd-manager-role-binding" created
INFO[0020] Created bearer token secret for ServiceAccount "argocd-manager"
Cluster https://165.22.209.118:6443 added
After adding the cluster, verify that ArgoCD is now managing both clusters:
argocd cluster list
Expected output:
SERVER NAME VERSION STATUS MESSAGE
https://165.22.209.118:6443 admin@devspace Unknown Successful Cluster has no applications and is not being monitored.
https://kubernetes.default.svc in-cluster 1.24 Successful Cluster has no applications and is not being monitored.
ArgoCD stores external cluster credentials as secrets. To inspect the secret for the external cluster, execute:
k -n argocd get secrets cluster-165.22.209.118-2127792194 -o json | jq .data.server -r | base64 -d
────────────────────────
Deploying an Application to the External Cluster
────────────────────────
Now, you will deploy an application from the ArgoCD UI to the external dev space cluster.
In the ArgoCD UI, click to create a new application with the following settings:
- Application Name: multi-app demo (or multi-cluster demo)
- Project: default
- Sync Policy: Automatic (enable auto-create namespaces)
- Repository: GitOps EchoCD repository
- Path: Manifest path for the geocentric application
In the destination section, select the external cluster (
admin@devspace) and designate the namespace as "multi-cluster-demo".
The following image displays the ArgoCD application settings UI: 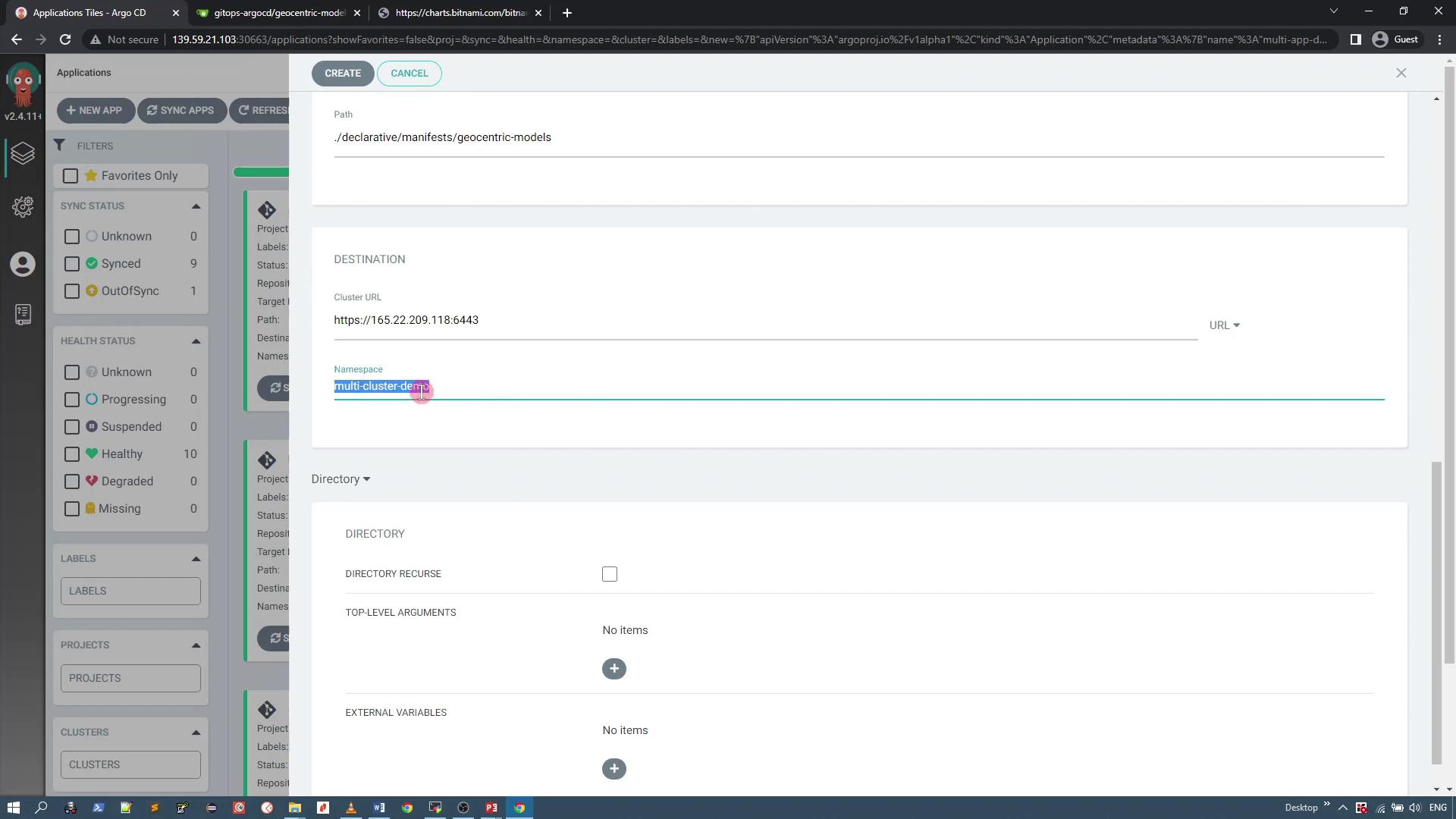
Before creating the application, ensure that the namespace "multi-cluster-demo" does not already exist on the external cluster:
k get ns multi-cluster-demo
Expected output:
Error from server (NotFound): namespaces "multi-cluster-demo" not found
Once you create the application, ArgoCD will automatically generate the required namespace and deploy the geocentric manifest. Monitor the application’s progress using the ArgoCD dashboard: 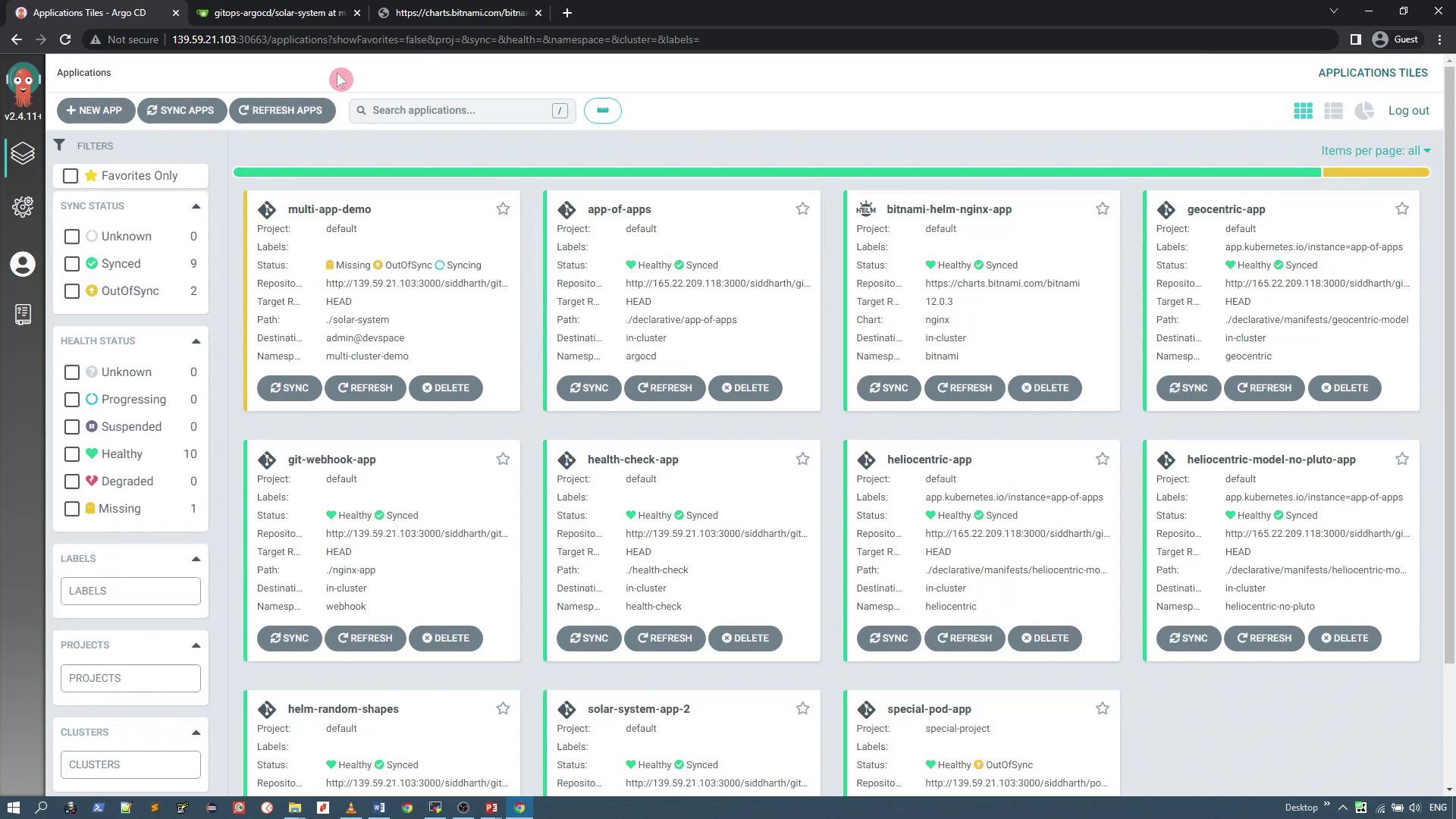
After deployment, the dashboard should reflect the application as "multi-app-demo" (ensure you use the intended name "multi-cluster demo" if required): 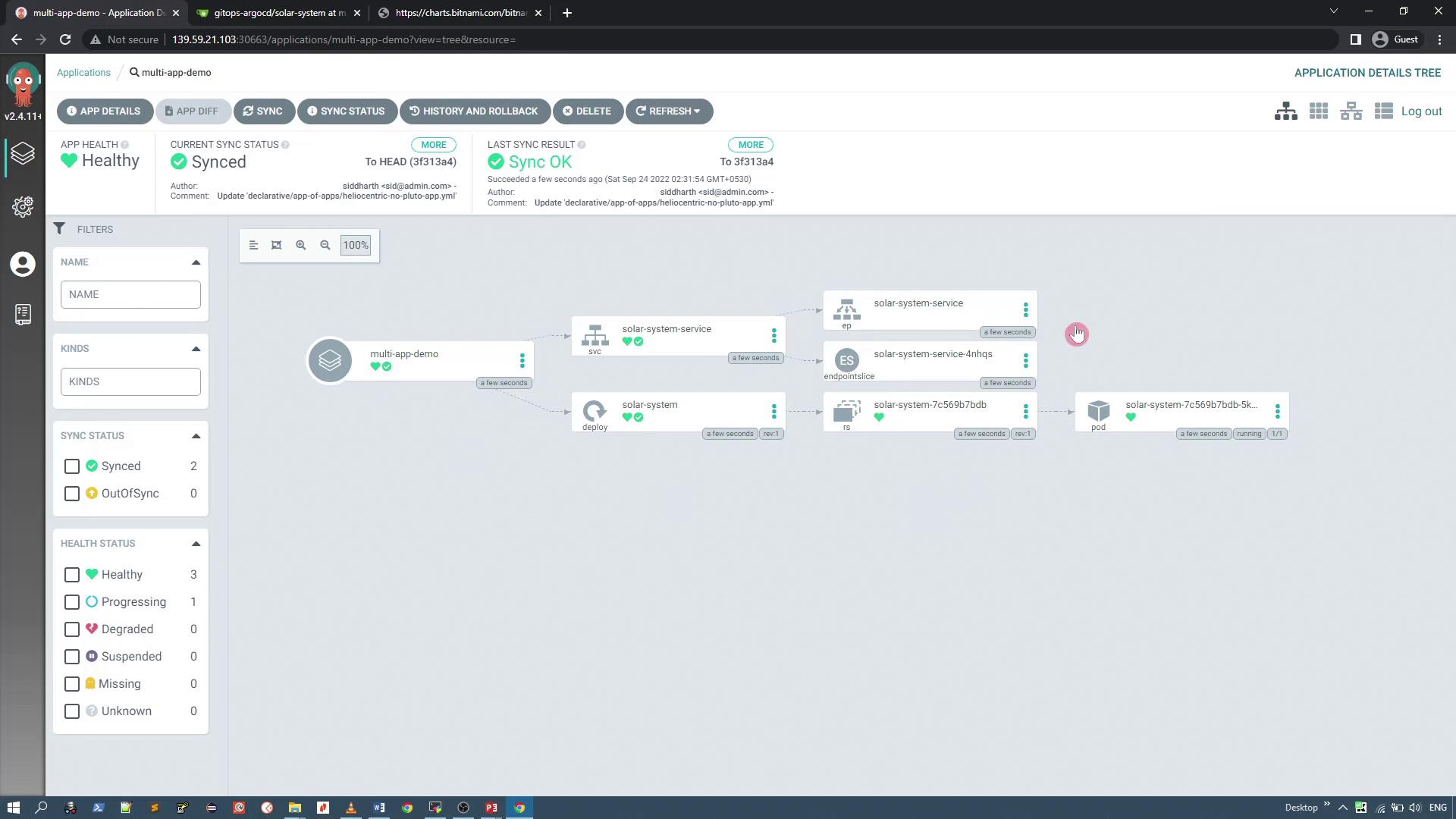
────────────────────────
Verifying the Deployment
────────────────────────
To confirm that the application has been deployed successfully, verify the resources on the external dev space cluster:
k -n multi-cluster-demo get all
Expected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/solar-system-7c569b7bdb-5km65 1/1 Running 0 25s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/solar-system-service NodePort 10.98.162.127 <none> 80:32646/TCP 25s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
deployment.apps/solar-system 1/1 Up-to-date 0 25s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/solar-system-7c569b7db 1 1 1 25s
To verify that these resources are exclusive to the external cluster, check the demo cluster:
k get node
Expected output on the demo cluster:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
demo-cluster Ready control-plane 25h v1.24.3
Then, ensure that the namespace "multi-cluster-demo" is not present on the demo cluster:
k get ns multi-cluster-demo
Expected output:
Error from server (NotFound): namespaces "multi-cluster-demo" not found
────────────────────────
Summary
────────────────────────
This lesson demonstrated how to deploy applications to an external Kubernetes cluster using ArgoCD. By adding the external cluster’s context to ArgoCD, automating the creation of service accounts, and managing application deployment, you can extend GitOps practices across multiple clusters. The external dev space cluster hosts your application while the demo cluster remains dedicated to running ArgoCD.
Thank you for following this multi-cluster deployment lesson.
For more comprehensive details on Kubernetes and GitOps, visit the following resources:
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab