HashiCorp Certified: Consul Associate Certification
Explain Consul Architecture
Introduction to HashiCorp Consul
HashiCorp has become synonymous with its flagship tools—Terraform, Vault, Consul, and Nomad—each available in a free open source edition and an enterprise version tailored for large organizations. The broader suite also includes Packer and Vagrant (open source only), plus the newer Waypoint and Boundary.
In this guide, we dive into Consul, HashiCorp’s solution for automating cloud networking in dynamic infrastructure. As applications shift from monolithic deployments to microservices, Consul provides the service discovery, segmentation, and configuration features needed to keep networks healthy, secure, and responsive.

Consul’s core capabilities:
- Service Discovery: Locate healthy service instances via DNS or HTTP API.
- Service Segmentation: Define and enforce which services may communicate.
- Configuration Management: Store and retrieve configuration in a distributed K/V store.
Beyond these, Consul offers a full service mesh, health checking, ACLs, and more—covered in depth below.
HashiCorp Products at a Glance
| Product | Editions | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Terraform | Open Source & Enterprise | Infrastructure-as-Code for provisioning any cloud or on-prem resource. |
| Vault | Open Source & Enterprise | Secrets management, encryption as a service, and credential brokering. |
| Consul | Open Source & Enterprise | Service networking, discovery, segmentation, and mesh. |
| Nomad | Open Source & Enterprise | Scheduler for containers, VMs, and batch jobs. |
| Packer | Open Source only | Image-building tool for multiple platforms. |
| Vagrant | Open Source only | Development environments as portable VMs. |
| Waypoint | Open Source only | Build, deploy, and release applications to any platform. |
| Boundary | Open Source only | Secure remote access to infrastructure without VPNs. |
Open Source vs. Enterprise Editions
Consul’s open source edition works great for small teams and proofs of concept. Enterprise adds scale, governance, and automation features:
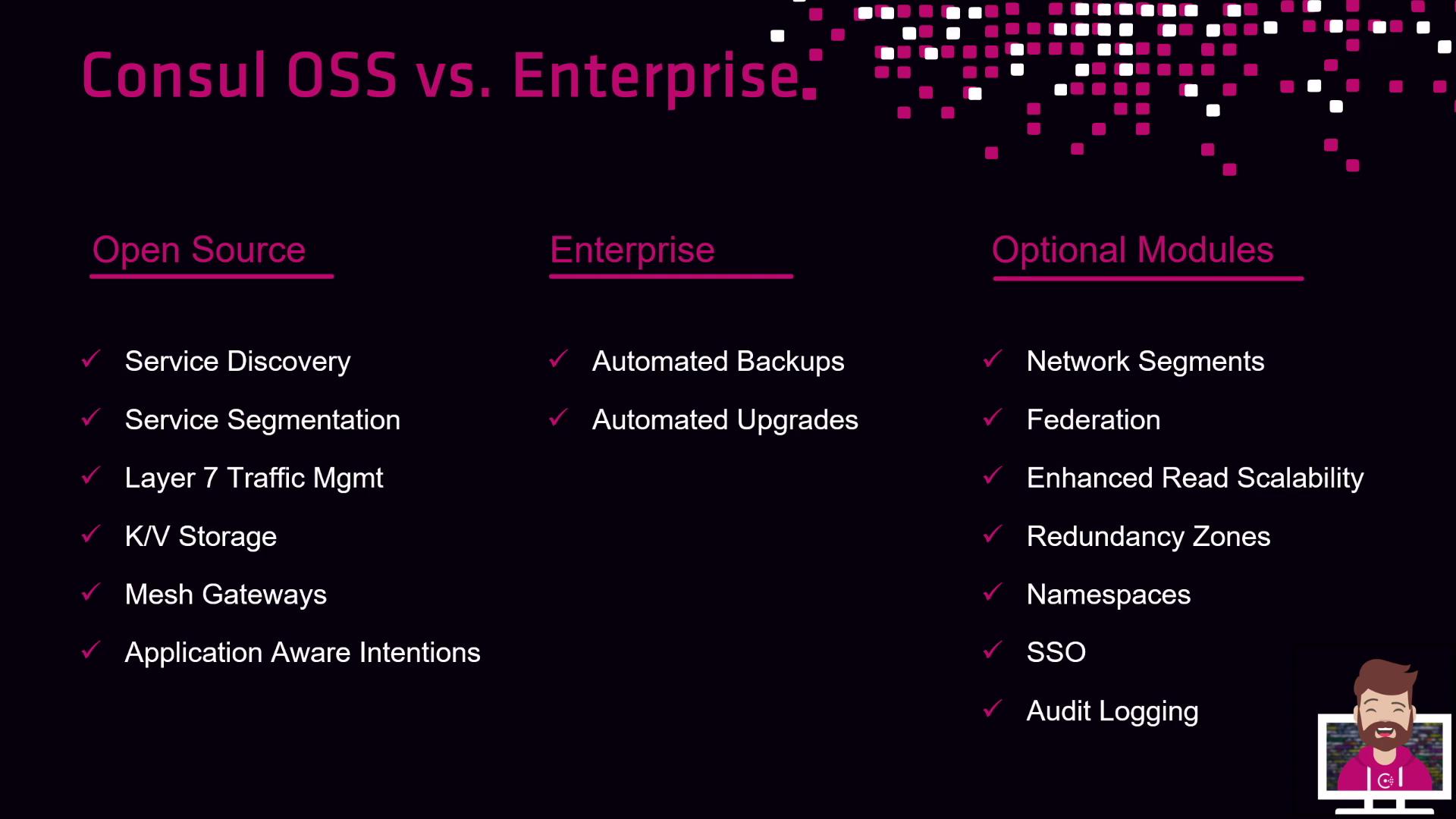
| Edition / Module | Core Features | Enterprise Add-Ons |
|---|---|---|
| Open Source | Service discovery, segmentation, L7 traffic, K/V store, mesh gateways, intentions | — |
| Enterprise | — | Snapshot Agent (backups), Autopilot (quorum & upgrades) |
| Enterprise Modules | — | Network Segments, Multi-cluster federation, Read scalability, Redundancy zones, Namespaces, SSO integration, Audit logs |
Enterprise Licensing
Enterprise-only features require a valid Consul Enterprise license.
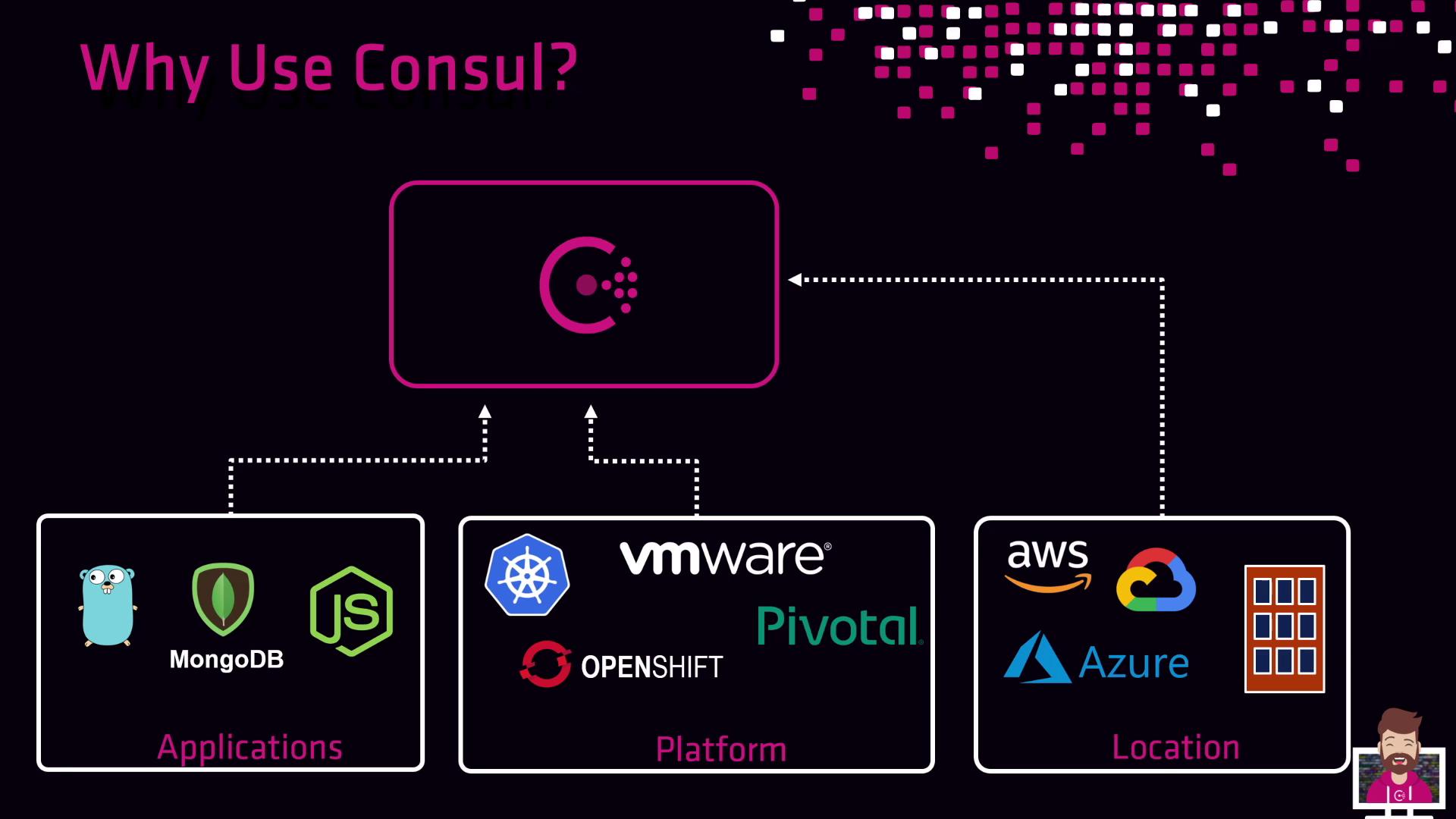
Why Choose Consul?
Consul is adopted by organizations looking for unified networking across services, platforms, and environments:
| Attribute | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Application agnostic | Works with any service; segmentation and mesh work transparently. |
| Platform agnostic | Deploy on Kubernetes, VMs, bare‐metal, OpenShift, and more. |
| Cloud agnostic | Run on AWS, Azure, GCP, on-premises, or federate clusters across clouds. |
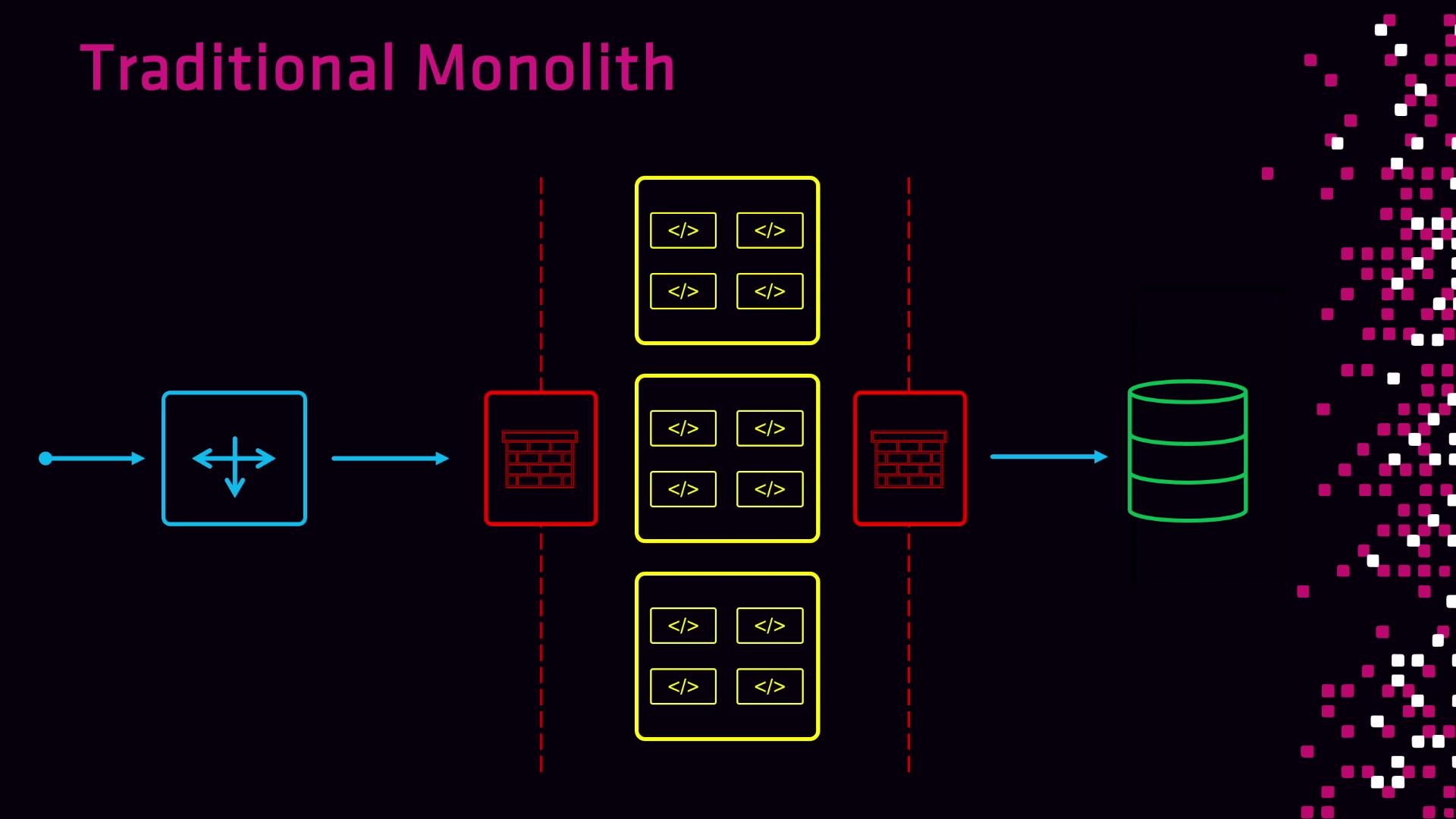
Evolution: Monoliths vs. Microservices
Traditional Monolith
Applications live behind fixed load balancers and firewalls, scale by replicating the entire stack, and rely on static IPs. A failure in any component can bring down the service.
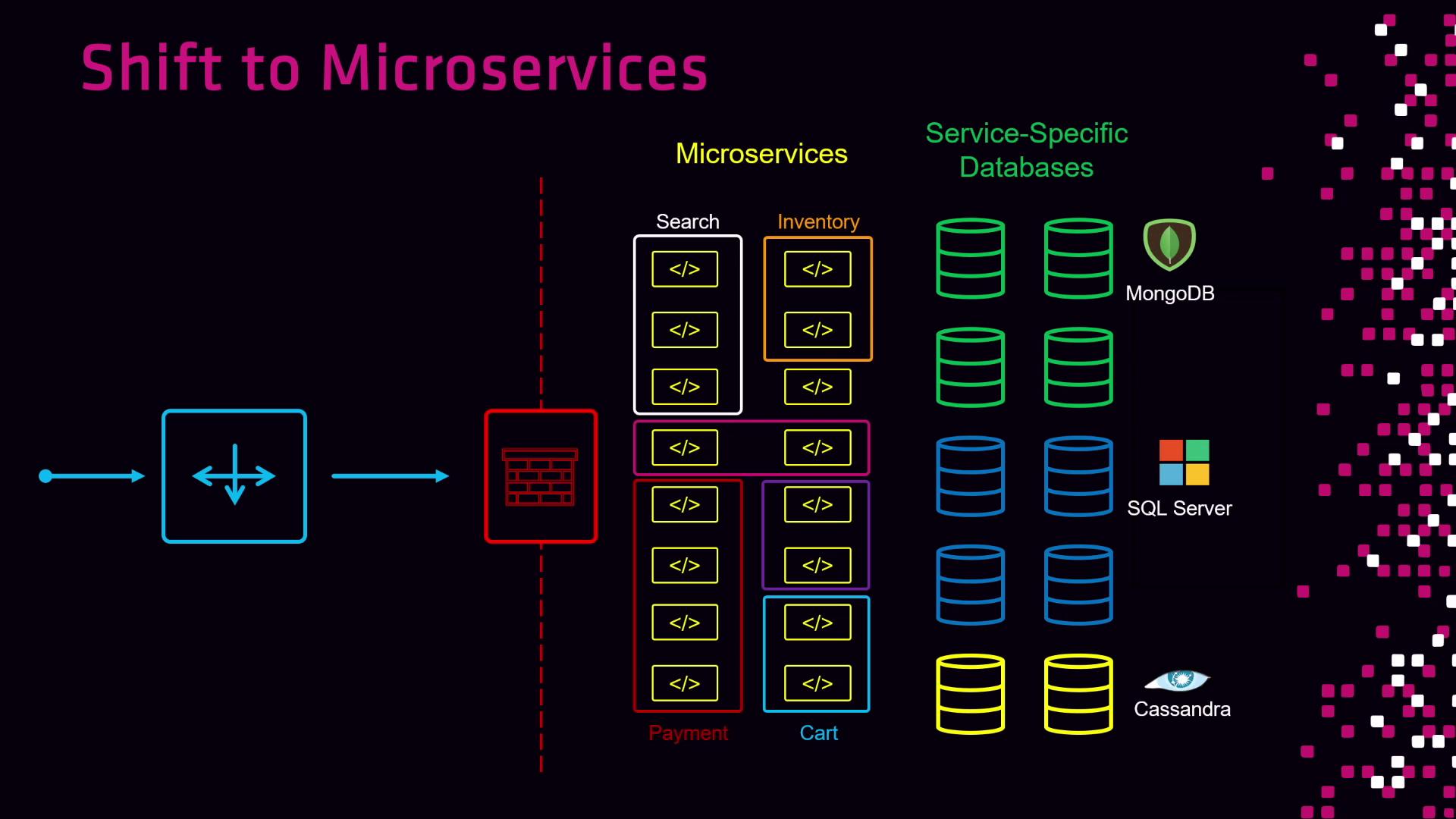
Microservices Architecture
Breaking applications into discrete services improves agility but introduces network complexity:
- Ephemeral services with dynamic IPs
- Traffic routing only to healthy instances
- Fine-grained communication policies for security
Consul automates service connectivity, health monitoring, and secure communication in real time.
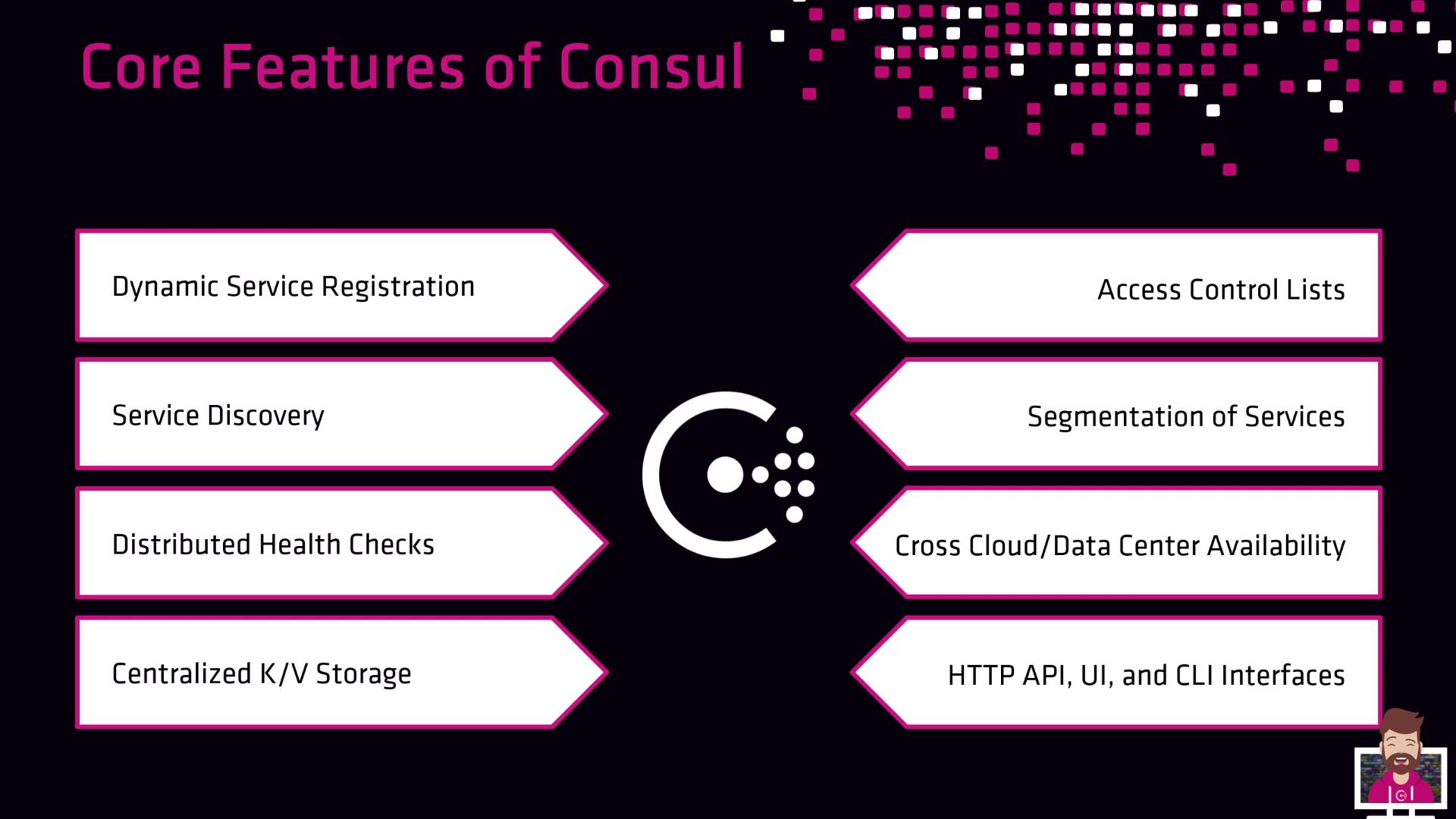
Consul Core Features
To meet dynamic infrastructure needs, Consul delivers:
- Dynamic Service Registration: Agents register services at startup.
- Service Discovery: DNS queries or HTTP API locate healthy endpoints.
- Distributed Health Checks: Continuous monitoring of service and node health.
- Centralized K/V Store: Hierarchical storage for configuration, certificates, and more.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Fine-grained permissions for keys and services.
- Service Mesh (Connect): Mutual TLS segmentation and secure sidecar proxies.
- Multi-Datacenter & Cross-Cloud: Federate clusters with global view.
- API, UI, & CLI: Full-featured interfaces for automation and inspection.
Now that we’ve outlined Consul’s problem space and solution overview, let’s explore hands-on examples and configuration patterns in the following sections.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content