How Vault Handles Authentication
Vault maps external identities (users or machines) into its own identity system via Auth Methods. Each Auth Method validates credentials against an external provider and issues a Vault token upon success.
Auth Methods enable you to integrate Vault with various identity providers—human (username/password, Okta, GitHub) or machine-to-machine (AWS, Kubernetes). Regardless of the method, the goal is to obtain a Vault token.
Vault Tokens: The Core of Authentication
Regardless of whether you sign in via LDAP, OIDC, AWS IAM, or another provider, Vault’s built-in token mechanism is always the final step. Tokens encapsulate:- Your authenticated identity
- Attached policies defining your permissions
- A configurable TTL

Missing a Token Means Access Denied
Every non-authentication request to Vault—whether reading secrets, writing data, listing keys, or enabling engines—requires a valid token. If you omit the token or provide an invalid one, Vault immediately returns a403 Forbidden error.
Always include
X-Vault-Token in your HTTP headers or use the VAULT_TOKEN environment variable. Otherwise, Vault will not prompt for credentials and will deny access.
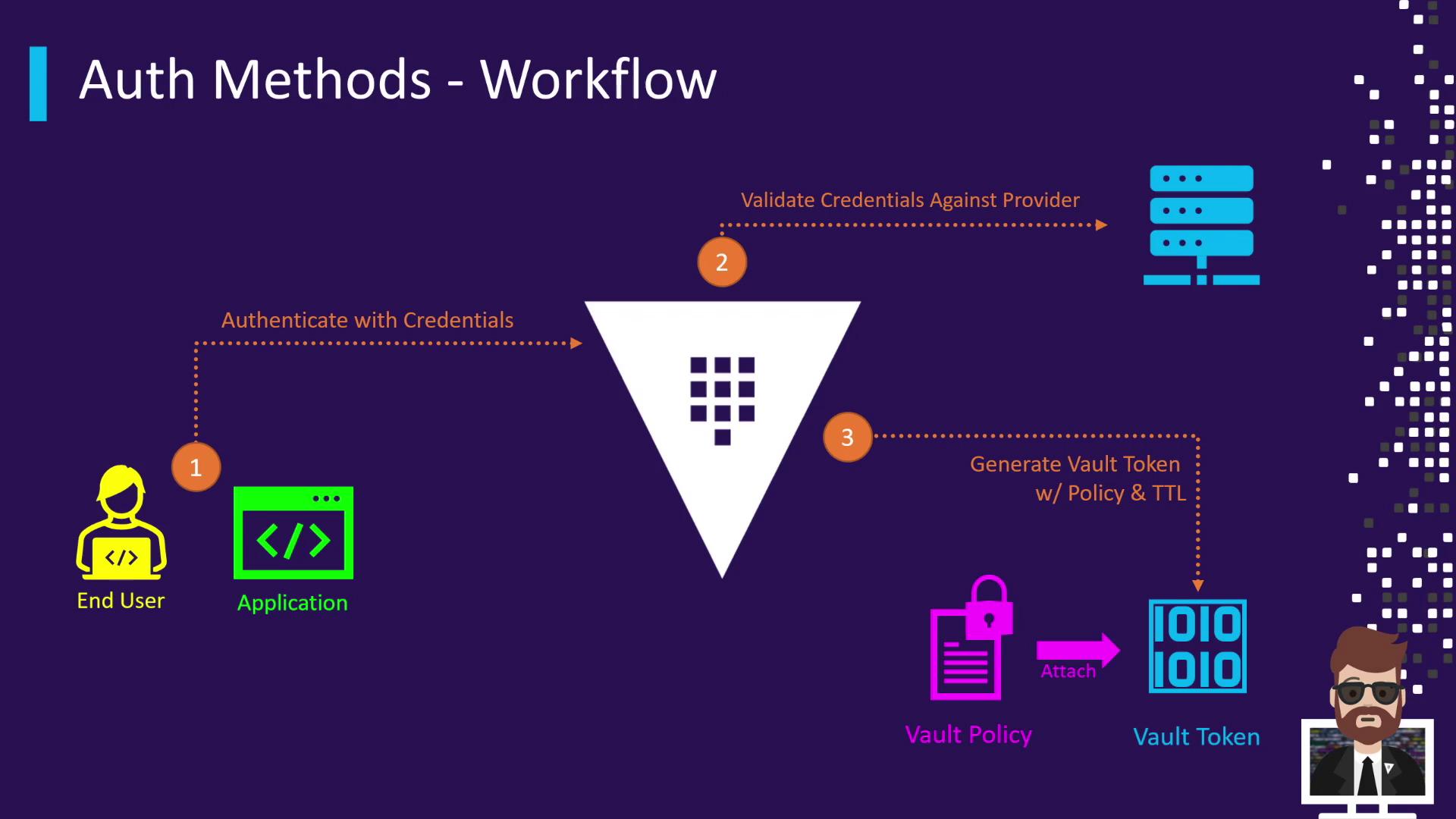
Auth Method Workflow
The typical authentication flow in Vault looks like this:- The Vault client (user or application) submits credentials to an Auth Method.
- Vault validates those credentials against the configured identity provider (LDAP, AWS IAM, OIDC, etc.).
- Upon successful validation, Vault generates a token, attaches the appropriate policies, and sets a TTL.
- Vault returns the token to the client.
- The client uses that token for all subsequent operations until it expires or is revoked.
Available Authentication Methods
Vault supports a broad range of Auth Methods for both humans and machines. Below is a summary of common types:| Auth Method | Use Case | Enable Command |
|---|---|---|
| Token | Built-in Vault token auth | vault auth enable token |
| LDAP | Corporate directory for users | vault auth enable ldap |
| AWS IAM | EC2 and IAM-based machine auth | vault auth enable aws |
| Kubernetes | In-cluster pod authentication | vault auth enable kubernetes |
| OIDC | Single sign-on (SSO) integration | vault auth enable oidc |
| GitHub | GitHub organization users | vault auth enable github |
