Istio Service Mesh
Traffic Management
Demo Circuit Breaking
In this lesson, we explore implementing a circuit breaker pattern to help prevent service disruptions during high-load scenarios. By configuring strict rules, we can ensure that our services maintain stability even when overwhelmed by excessive requests.
Removing Unnecessary Subsets
First, remove the subsets from the product page's DestinationRule and VirtualService. This is achieved by applying the following configuration:
kind: DestinationRule
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
metadata:
name: productpage
namespace: default
uid: 918ecad4-3744-4235-ae53-c86193695a56
resourceVersion: '4771'
generation: 12
creationTimestamp: '2021-08-16T22:40:09Z'
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: >
{"apiVersion":"networking.istio.io/v1alpha3","kind":"DestinationRule","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"productpage","namespace":"default"},"spec":{"host":"productpage","subsets":[{"labels":{"version":"v1"},"name":"v1"}]}}
managedFields: |
spec:
host: productpage
Configuring Traffic Policies with Strict Rules
Next, we implement a strict circuit breaker by configuring the traffic policy. In this configuration:
- The HTTP section limits:
- The maximum number of pending requests to 1.
- The maximum requests handled per connection to 1.
- The TCP section restricts the maximum number of connections to 1.
Apply the configuration below to enforce these limits:
kind: DestinationRule
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
metadata:
name: productpage
namespace: default
uid: 918ecad4-3743-425a-ae53-ec8163965a56
resourceVersion: '4878'
generation: 14
creationTimestamp: '2021-08-16T22:40:09Z'
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: >
{"apiVersion":"networking.istio.io/v1alpha3","kind":"DestinationRule","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"productpage","namespace":"default"},"spec":{"host":"productpage","subsets":[{"labels":{"version":"v1"}},{"name":"v1"}]}}
managedFields: []
spec:
productpage:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http:
maxPendingRequests: 1
maxRequestsPerConnection: 1
tcp:
maxConnections: 1
Note
In this configuration, limiting connections and request queues ensures that when the load exceeds these parameters, the circuit breaker triggers, protecting the service from overload.
Testing the Circuit Breaker with HTLOAD
To evaluate the circuit breaker, we use HTLOAD (via its h2load command) to generate concurrent HTTP calls.
Single Concurrent Client Test
Start by sending 1,000 HTTP requests with a single concurrent client. The -n flag specifies the total number of requests, while -c sets the concurrency level:
h2load -n1000 -c1 'http://"${INGRESS_HOST}":"${INGRESS_PORT}"/productpage'
During this test, HTLOAD displays the progress and confirms that all requests are handled successfully.
Increasing Concurrency
While a single concurrent client may succeed, increasing the concurrency will test the resilience of the circuit breaker. Below are examples of tests with higher concurrency:
Test with 1 Concurrent Client (Repeat):
$ h2load -n1000 -c1 'http://"$INGRESS_HOST":"$INGRESS_PORT"/productpage' finished in 50.12s, 19.95 req/s, 95.26KB/s requests: 1000 total, 1000 started, 1000 done, 1000 succeeded, 0 failed, 0 errored, 0 timeout status codes: 1000 2xx, 0 3xx, 0 4xx, 0 5xx traffic: 4.66MB (4888438) total, 12.42KB (12719) headers (space savings 91.23%), 4.62MB (4848664) data time for request: 16.31ms 125.48ms 50.10ms 20.78ms 57.90% time for connect: 515us 515us 515us 0us 100.00% time to 1st byte: 32.32ms 32.32ms 32.32ms 0us 100.00% req/s: 19.95 19.95 0.00 100.00%Test with 2 Concurrent Clients:
If the service begins to hang while processing a request, the remaining requests will be denied:
istio-training@local istio-1.10.3 $ h2load -n1000 -c2 'http://"$INGRESS_HOST":"$INGRESS_PORT"/productpage'Test with 3 Concurrent Clients:
More requests are denied as the concurrency increases:
bash istiotraining@local istio-1.10.3 $ h2load -n1000 -c3 'http://"$INGRESS_HOST":"$INGRESS_PORT"/productpage'Test with 4 Concurrent Clients:
With 4 concurrent clients, the service handles only 46 connections before the circuit breaker denies further requests:
istio-training@local istio-1.10.3 $ h2load -n1000 -c4 'http://"$INGRESS_HOST":"$INGRESS_PORT"/productpage'
Warning
Under the strict circuit breaker configuration, you'll observe that the product page starts to fail and deny requests under higher concurrency. This behavior is critical to prevent service overload and maintain overall system stability.
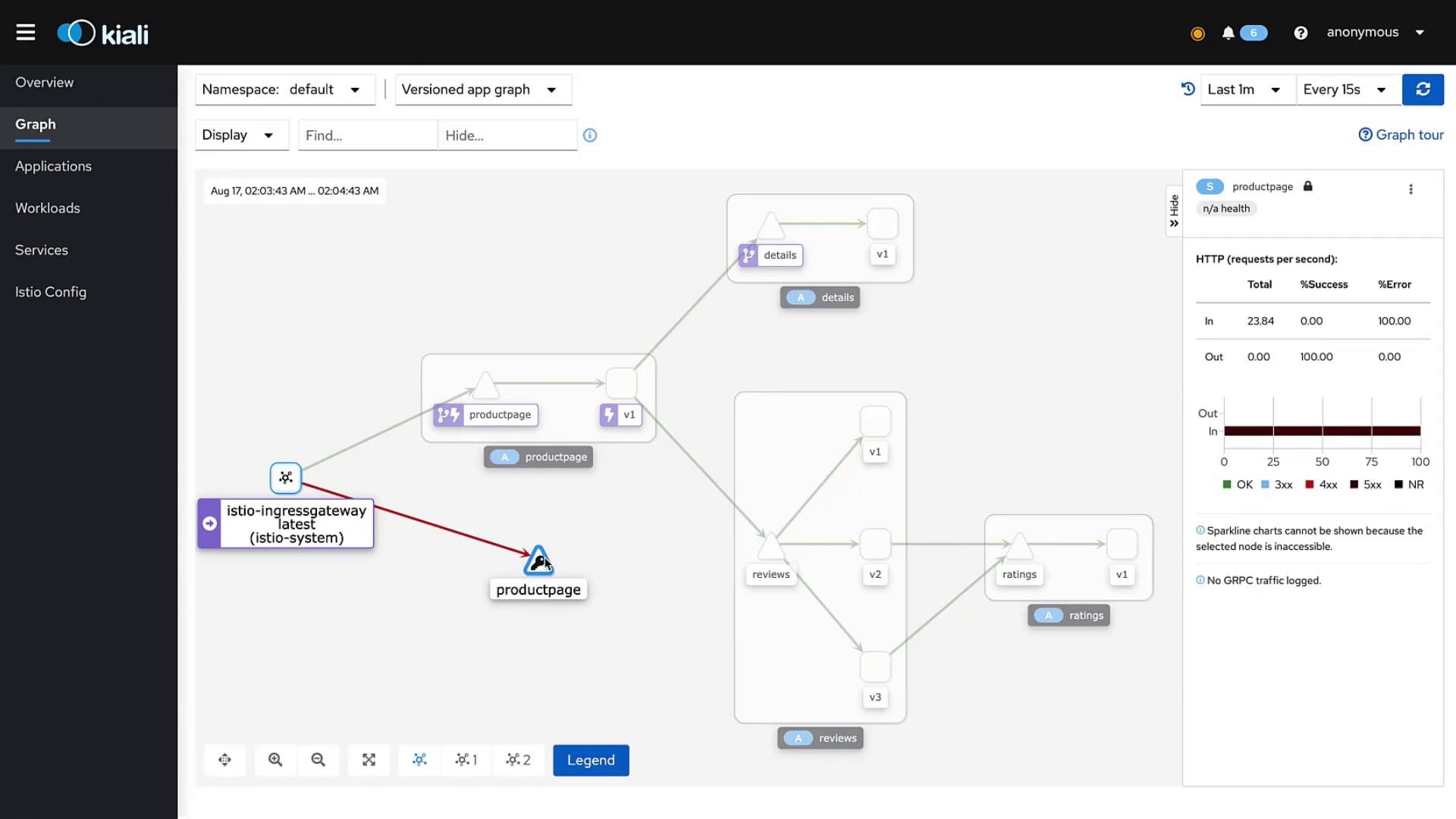
Observing Telemetry
Telemetry data captured from the service mesh confirms that the product page fails gracefully when the load exceeds the set limits. This indicates that the circuit breaker is effectively rejecting excessive requests, thereby ensuring the continuous stability of your service under high load conditions.
Watch Video
Watch video content