Kubernetes Autoscaling
Kubernetes Event Driven Autoscaling KEDA
KEDA Scaling With Redis List
In this guide, you’ll learn how to automatically scale a Kubernetes worker service by monitoring a Redis list backlog with KEDA. This approach is perfect for scenarios like an online store during a flash sale, where incoming orders outpace your processing capacity.
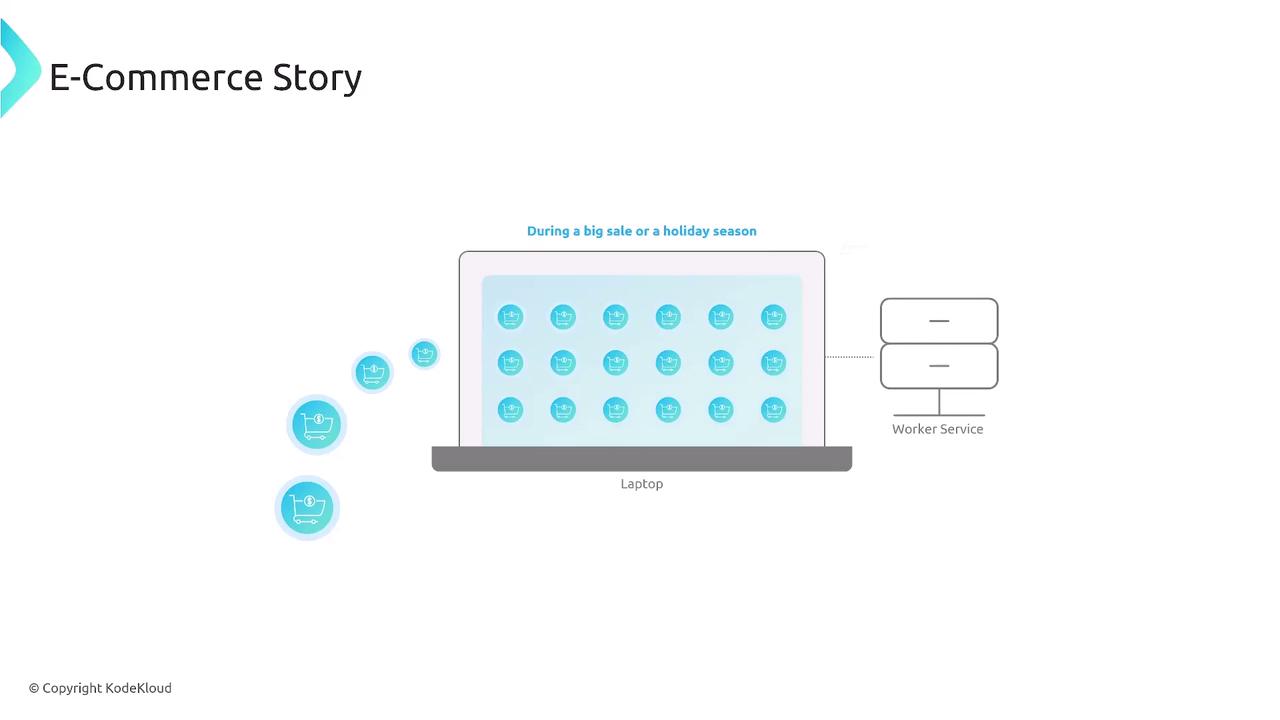
Why Redis List Scaling?
Traditional CPU- or memory-based scaling won’t address a growing Redis queue. By using KEDA’s Redis List scaler, you can dynamically adjust pod replicas based on the number of pending items:
- Scale out when the backlog grows.
- Scale in when work completes.
- Avoid overprovisioning during low traffic.
Architecture and Flow
Below is a high-level diagram showing how Redis, KEDA, and your worker deployment interact:
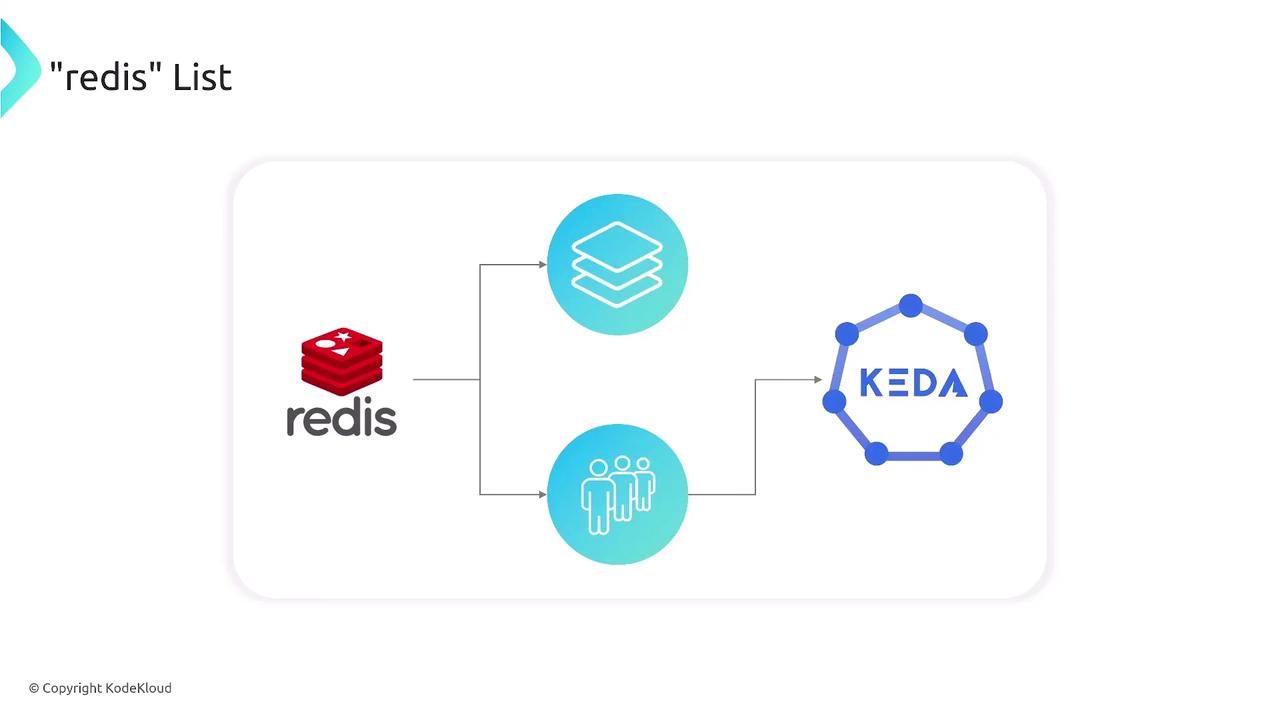
KEDA monitors the length of the Redis list and drives the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) for your target deployment.

KEDA Resources Overview
| Resource | Purpose | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| Secret | Stores the Redis password (Base64-encoded) | Kubernetes Secrets |
| TriggerAuthentication | References the secret to authenticate KEDA to Redis | KEDA Auth Concepts |
| ScaledObject | Defines how to scale your worker based on the list | KEDA ScaledObject |
1. Create the Redis Password Secret
Encode your Redis password in Base64 and store it in a Kubernetes Secret:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: auth-redis-secret
type: Opaque
data:
redis_password: amhibm9pdWhramo=
Note
Ensure you encode the plaintext password with base64.
For example: echo -n 'yourRedisPassword' | base64
2. Define TriggerAuthentication
Create a TriggerAuthentication so that KEDA can retrieve the password from the secret:
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: TriggerAuthentication
metadata:
name: keda-trigger-auth-redis-secret
spec:
secretTargetRef:
- parameter: password
name: auth-redis-secret
key: redis_password
3. Configure the ScaledObject
Finally, define the ScaledObject to tie everything together:
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: ScaledObject
metadata:
name: redis-scaledobject
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
name: nginx
minReplicaCount: 1
triggers:
- type: redis
metadata:
address: redis.default.svc.cluster.local:6379
listName: myList
listLength: "10"
authenticationRef:
name: keda-trigger-auth-redis-secret
advanced:
horizontalPodAutoscalerConfig:
behavior:
scaleDown:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 20
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 50
periodSeconds: 20
scaleUp:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 0
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 100
periodSeconds: 15
Warning
Review your HPA policies carefully. Aggressive scaling (100% every 15 s) can lead to resource spikes. Adjust thresholds to match your cluster capacity.
With this setup, KEDA will watch the myList backlog in Redis and automatically scale the nginx worker pods—scaling out under heavy load and scaling in as the queue drains.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab