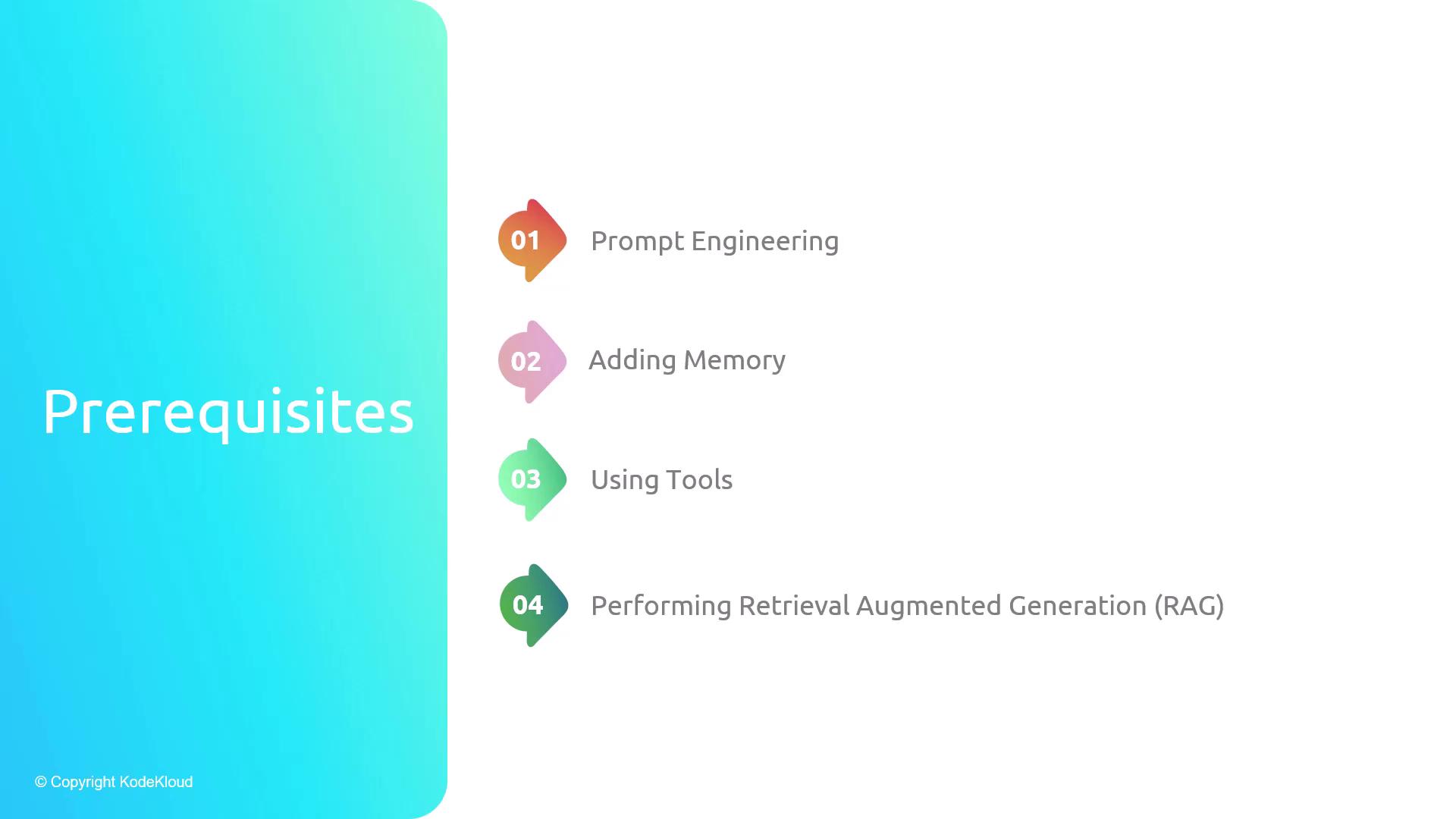
Prerequisites
- Prompt engineering best practices
- Short-term and long-term memory strategies
- Integrating external tools (APIs, Python REPL, search)
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation for grounding responses
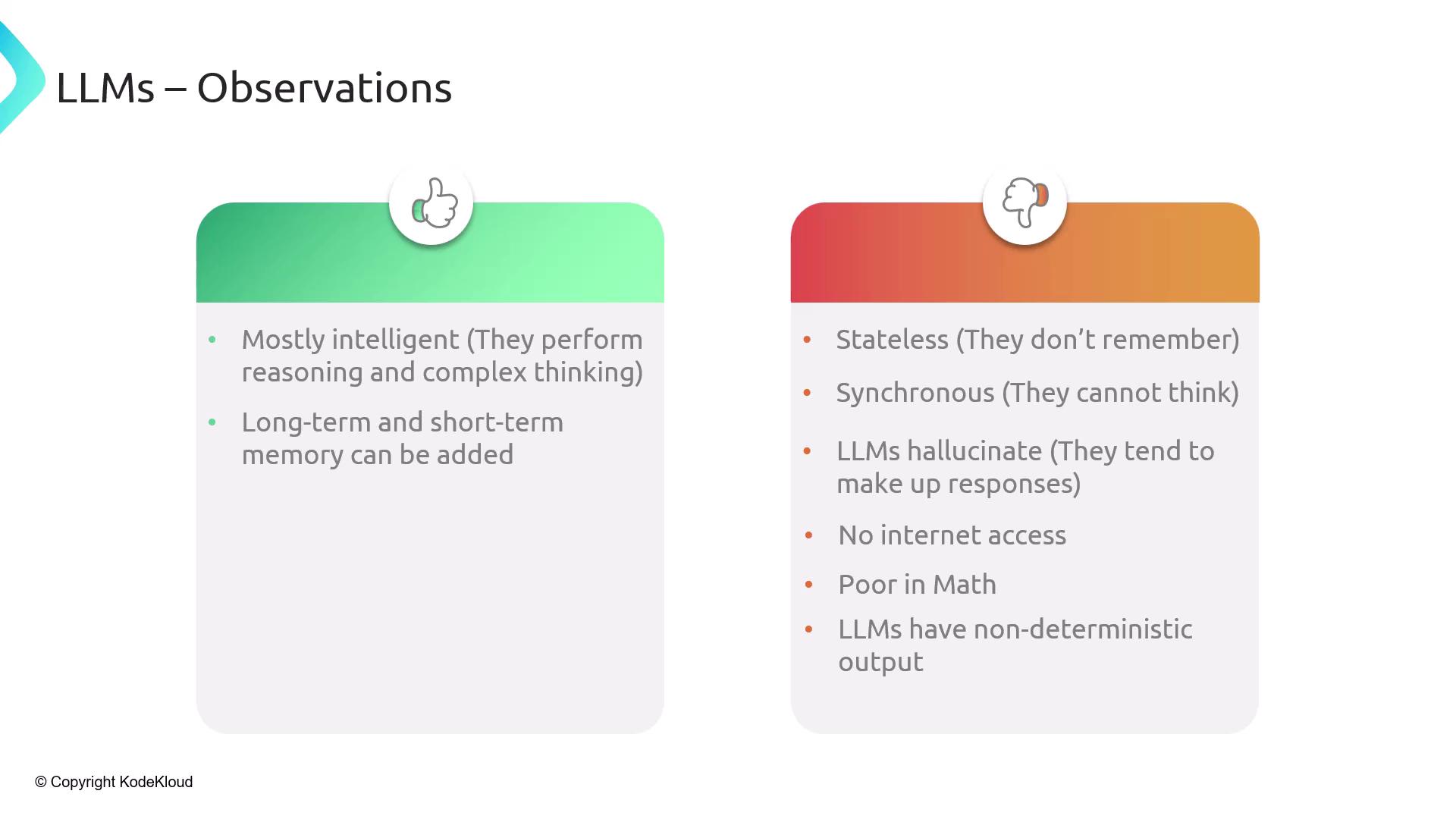
Observations on Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs power modern AI but come with both strengths and limitations:- Statelessness: No built-in memory across calls
- Synchronous execution: Single-turn prompt processing
- Varying intelligence: GPT-4 vs. smaller models
- Hallucination risk: Inventing unsupported details
- No internet access: Stuck with training data cutoff
- Weak math: Simple arithmetic often fails
- Non-deterministic: Outputs and formats can change
Addressing LLM Limitations
LangChain modules help overcome these challenges:- Memory: Short-term scratchpads & long-term stores
- Grounding: RAG with vector stores and document retrieval
- Real-time data: API/tool integrations (e.g., search, weather)
- Accurate math: Python REPL tool for calculations
- Consistent output: Prompt templates + output parsers
Introducing LangChain Agents
Agents are orchestration layers that combine LLMs with tools, memory, and custom code to handle multi-step tasks.An agent acts as a controller: it queries the LLM for required data, invokes external tools, updates memory, and composes the final structured response.
- Expose functions in any language as REST endpoints
- Seamlessly integrate Python, Java, or custom libraries
- Scale from simple chatbots to multi-step pipelines
Advantages of Agents
By unifying LangChain modules, agents offer:- Modularity: Plug-and-play tools, memory, and parsers
- Flexibility: Adapt to domains like healthcare, service, or education
- Efficiency: Automated prompt engineering & formatting
- Scalability: From quick scripts to enterprise systems

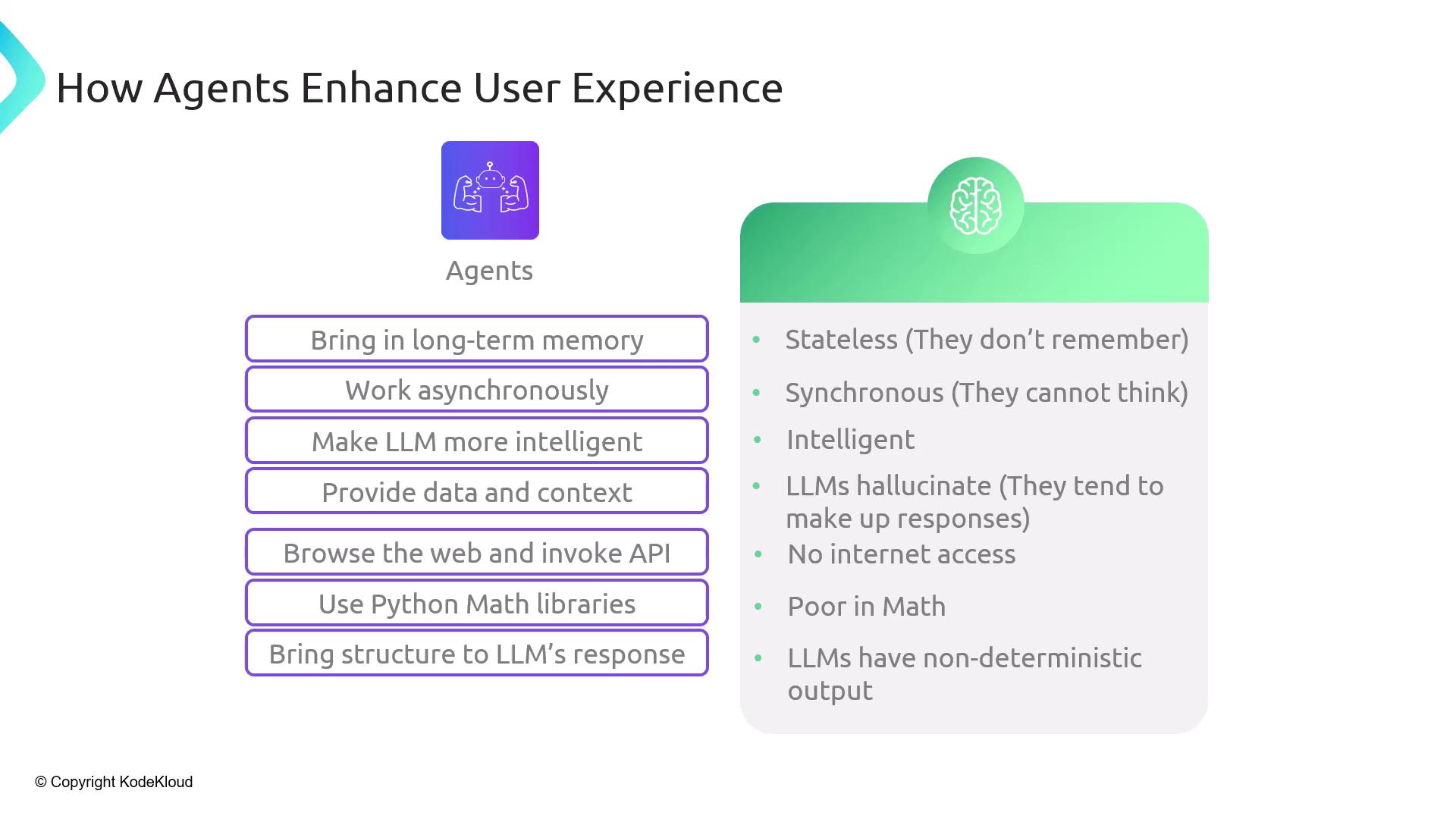
Agents vs. LLMs: A Comparison
| Limitation of LLMs | Agent Enhancement |
|---|---|
| Stateless | Long-term & short-term memory |
| Synchronous | Asynchronous workflows |
| Variable intelligence | Chain-of-thought reasoning |
| Hallucination | Grounded with contextual data |
| No internet access | Web browsing & API invocation |
| Poor at math | Python REPL calculations |
| Unpredictable output | Structured output via parsers |
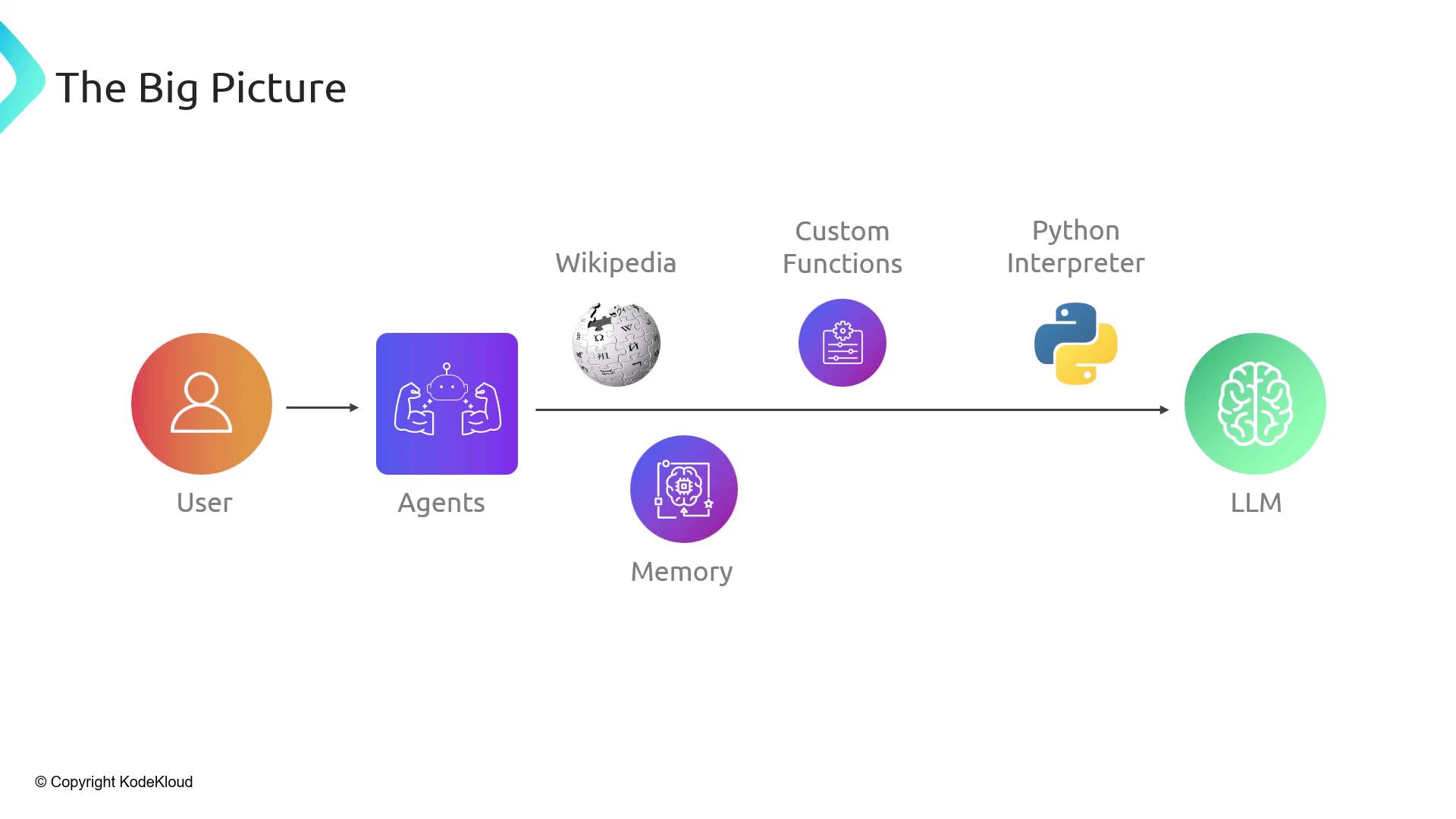
The Big Picture Architecture
An agent orchestrates end-to-end AI workflows:- User sends a query
- Agent analyzes intent and decides on tools/memory
- Tools (Wikipedia, search APIs, custom functions, Python) fetch data
- LLM processes prompts with context and returns structured output
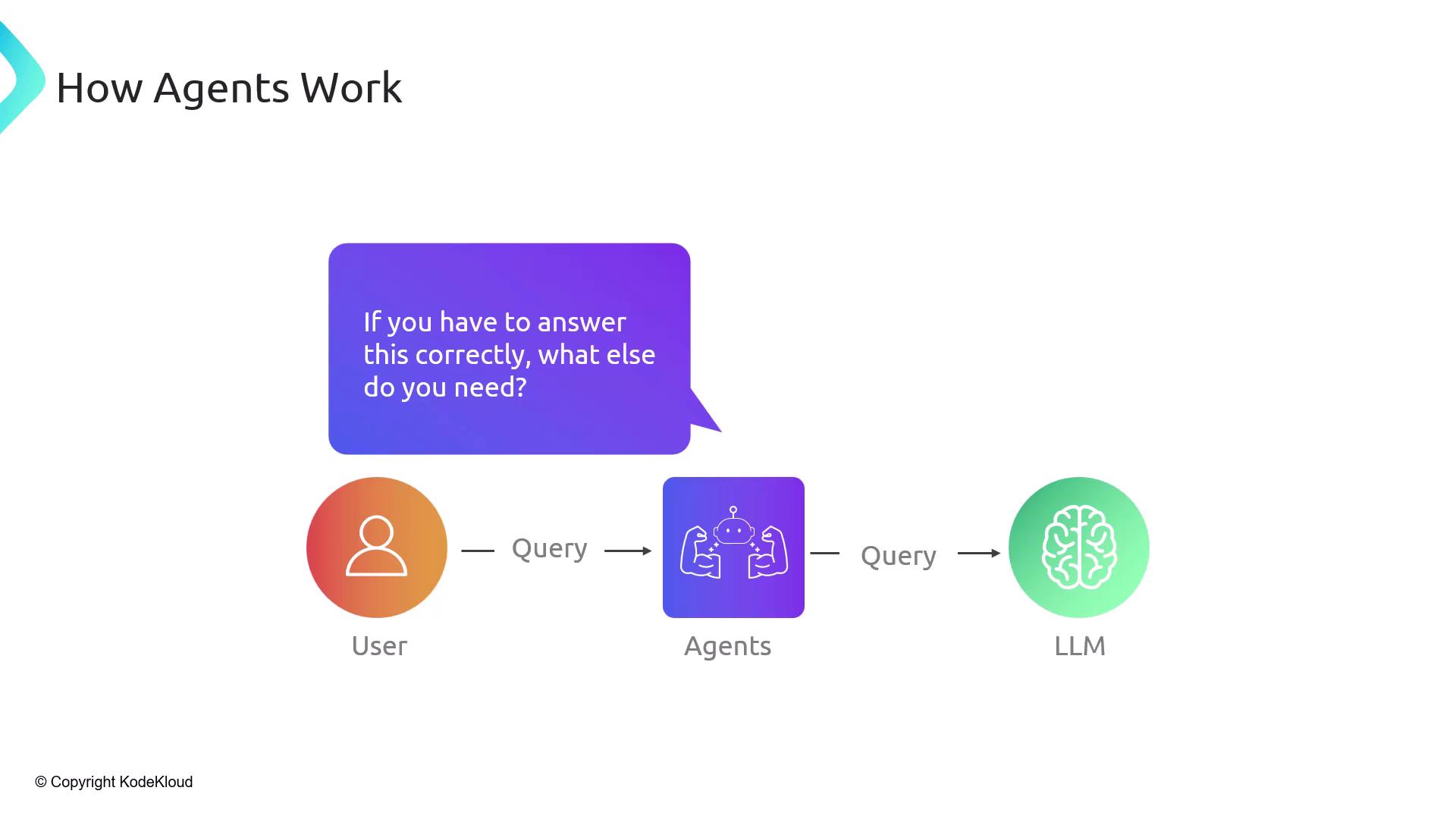
How Agents Work
At runtime, the agent uses the LLM as a reasoning engine with external support:- Agent asks the LLM: “What else do you need to answer this?”
- LLM lists data points (A, B, C)
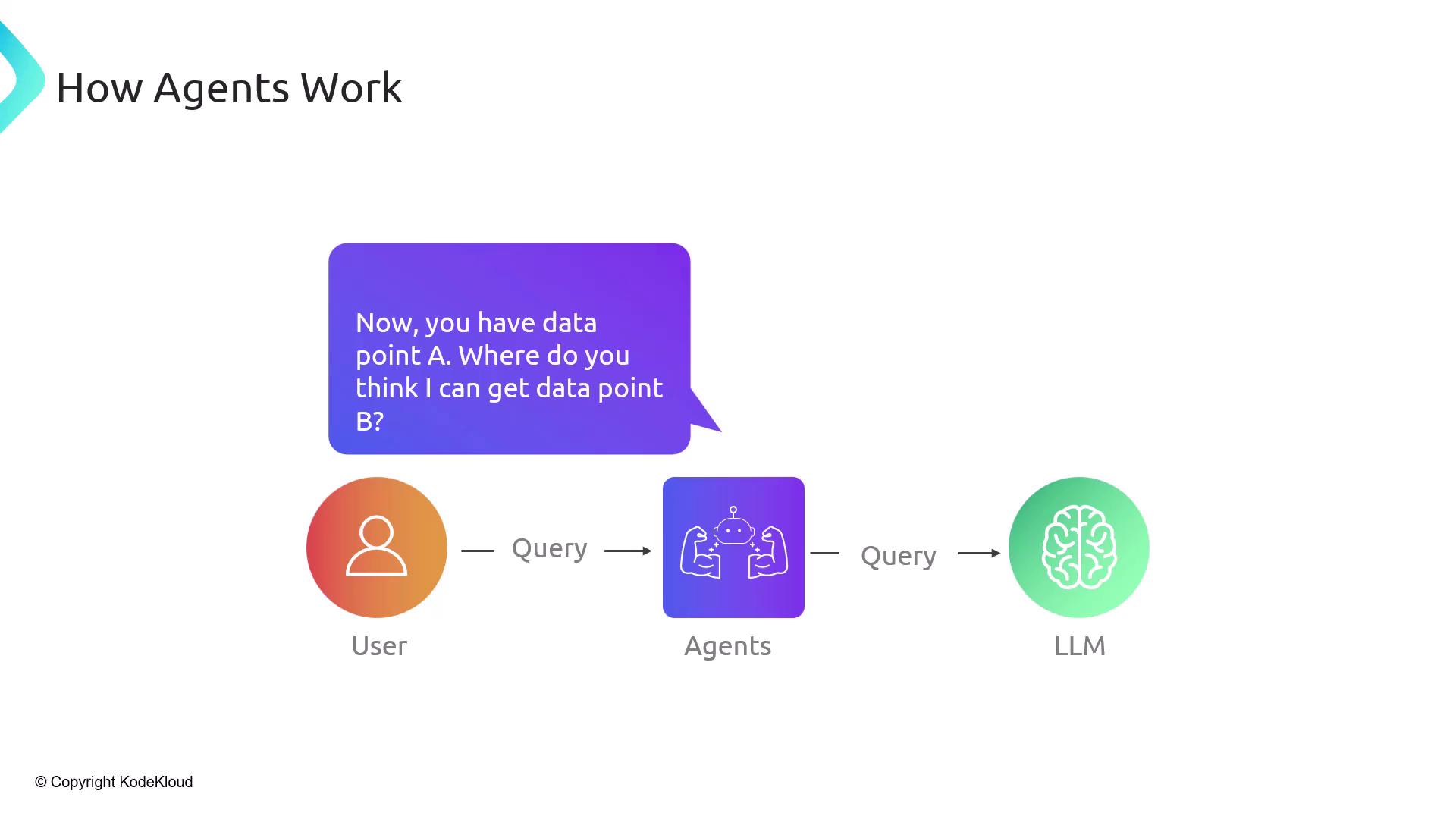
- Agent invokes tools (search, Wikipedia, Python REPL) to gather data
- New data is fed back to the LLM iteratively
- Loop continues until the LLM returns the final result
Always secure API keys and protect sensitive data when configuring memory stores and external tools.
Agent Use Cases
- Customer Support Agent: FAQs, troubleshooting, escalation
- Student Guide Agent: Step-by-step problem solving
- Travel Coordinator Agent: Itinerary planning, booking
- Meeting Scheduler Agent: Calendar integration, invites