What Is a Prompt?
A prompt is the input you provide to an LLM to guide its response. It combines both syntax and semantics, telling the model exactly what you want it to do—whether that’s answering a question, completing a sentence, or carrying on a conversation. Key aspects of an effective prompt:- Clear intent: State your goal or question explicitly.
- Relevant context: Include background information when needed.
- Specific instructions: Guide the model’s form, tone, or length.
Prompt engineering is the practice of designing inputs that direct the LLM toward high-quality, accurate outputs. Small tweaks in wording can produce vastly different results.
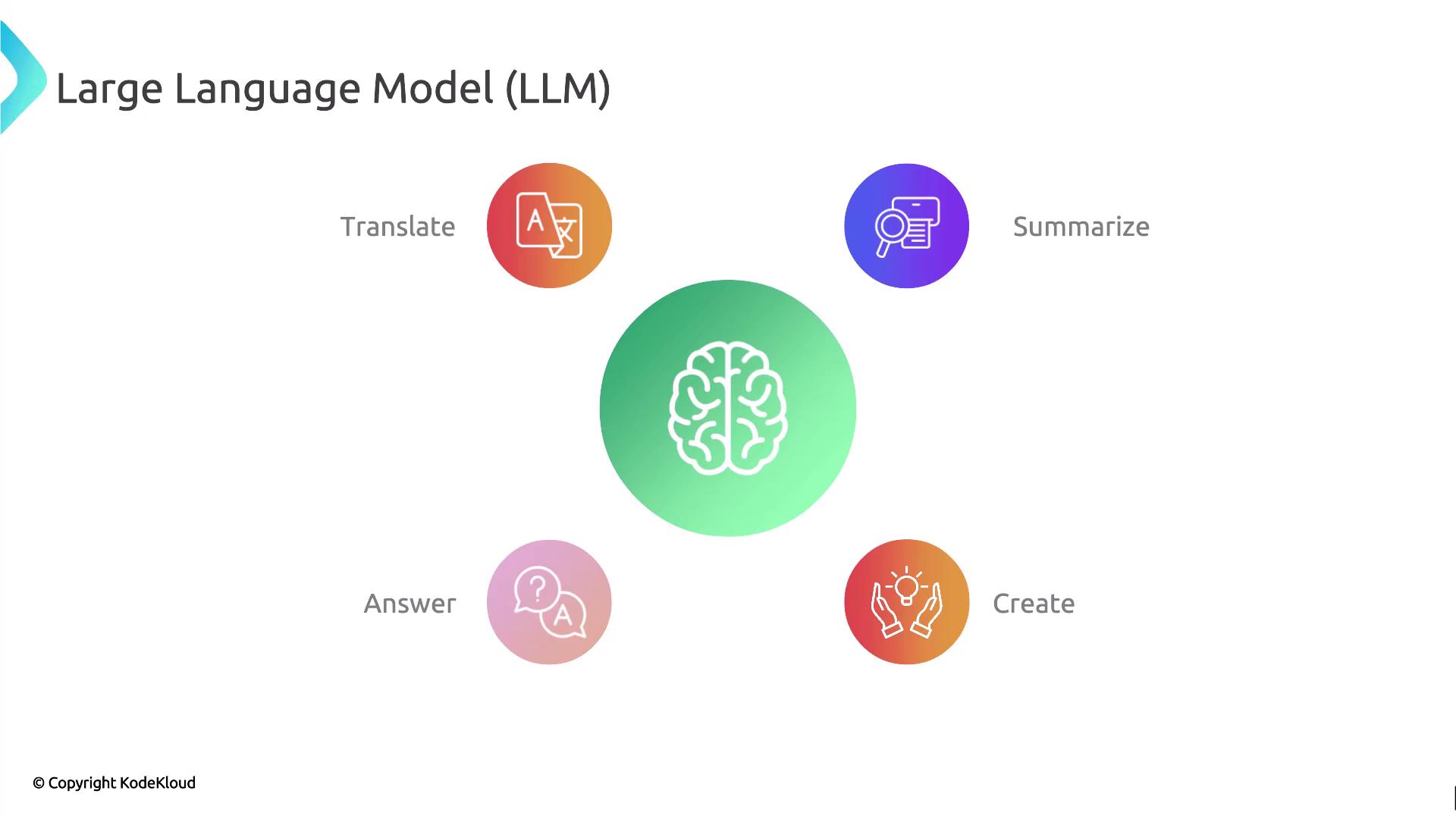
What Is an LLM?
A large language model is a deep-learning system trained on massive text corpora. It serves as the “brain” behind AI-driven language tasks, with capabilities such as:| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Translate Text | Automatically convert text between languages. |
| Summarize Documents | Condense long passages into concise summaries. |
| Answer Questions | Provide fact-based or conversational responses. |
| Generate New Content | Create articles, stories, code snippets, and more. |
LLM vs. Expert Writers
LLM-generated text can rival or even exceed human writing in clarity and readability. The comparison below shows identical passages about the benefits of sports for physical and mental health—one by an LLM, the other by a professional writer.
Because LLMs can mimic expert writing so closely, be cautious of potential misinformation or unverified claims. Always validate critical output against reliable sources.
Best Practices for Prompt Engineering
- Begin with a clear objective.
- Provide examples or formats to follow.
- Use system messages or few-shot examples for complex tasks.
- Iterate and refine: compare outputs, adjust phrasing.
- Enforce constraints (length, tone, style) with explicit instructions.