nginx:latest Docker image, scale it to two replicas, and expose it externally via a LoadBalancer service.
Prerequisites
- An active LKE cluster with at least one node
kubectlconfigured to target your LKE cluster- Basic familiarity with Kubernetes concepts
1. Define Your Deployment and Service
Create a manifest file namednginx.yaml:
The
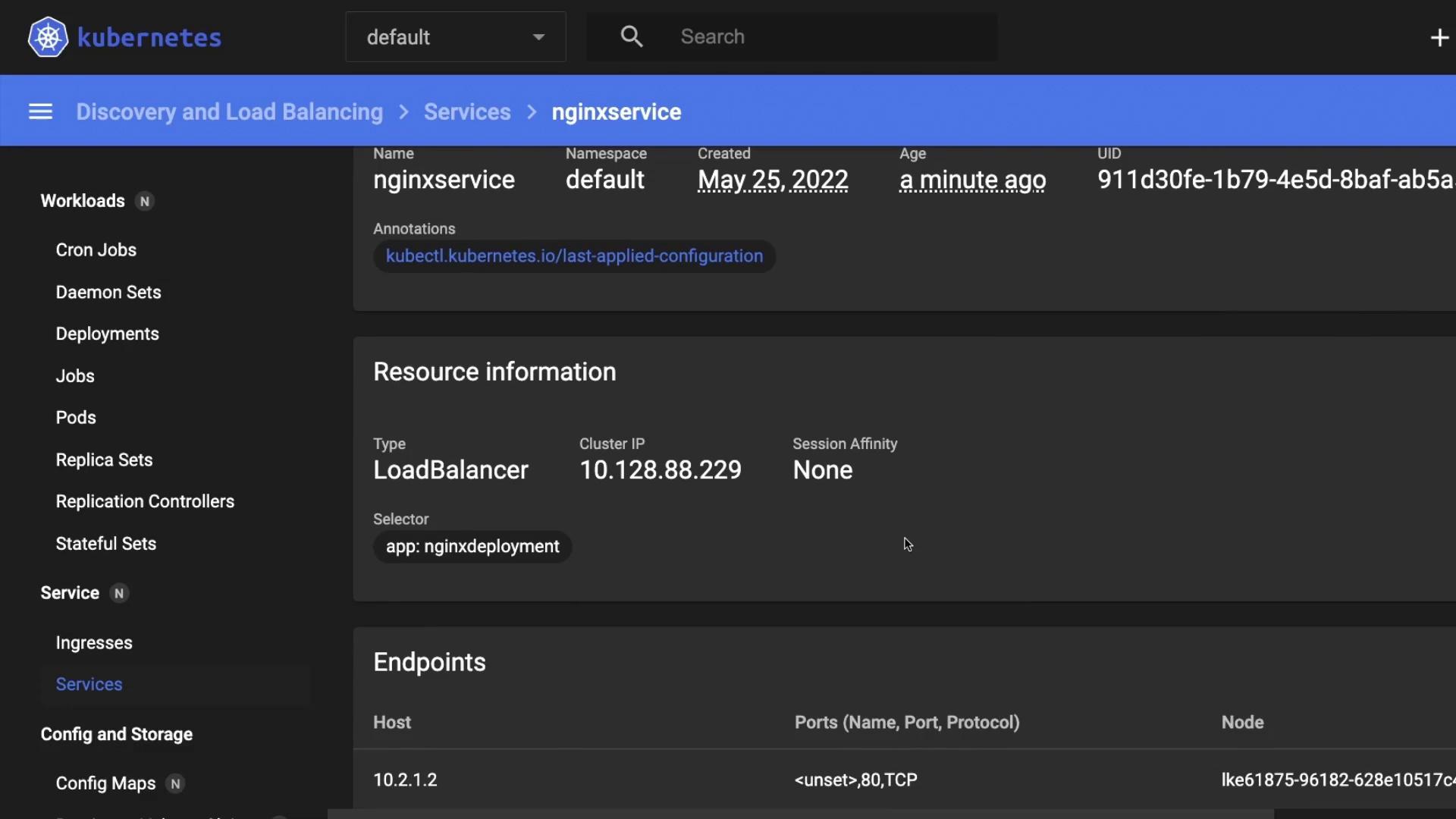
LoadBalancer service type on LKE provisions a cloud load balancer and assigns it an external IP automatically.2. Verify Your Context and Apply the Manifest
-
Confirm you’re connected to the correct cluster:
-
List your nodes to ensure they’re Ready:
-
Deploy the Nginx resources:
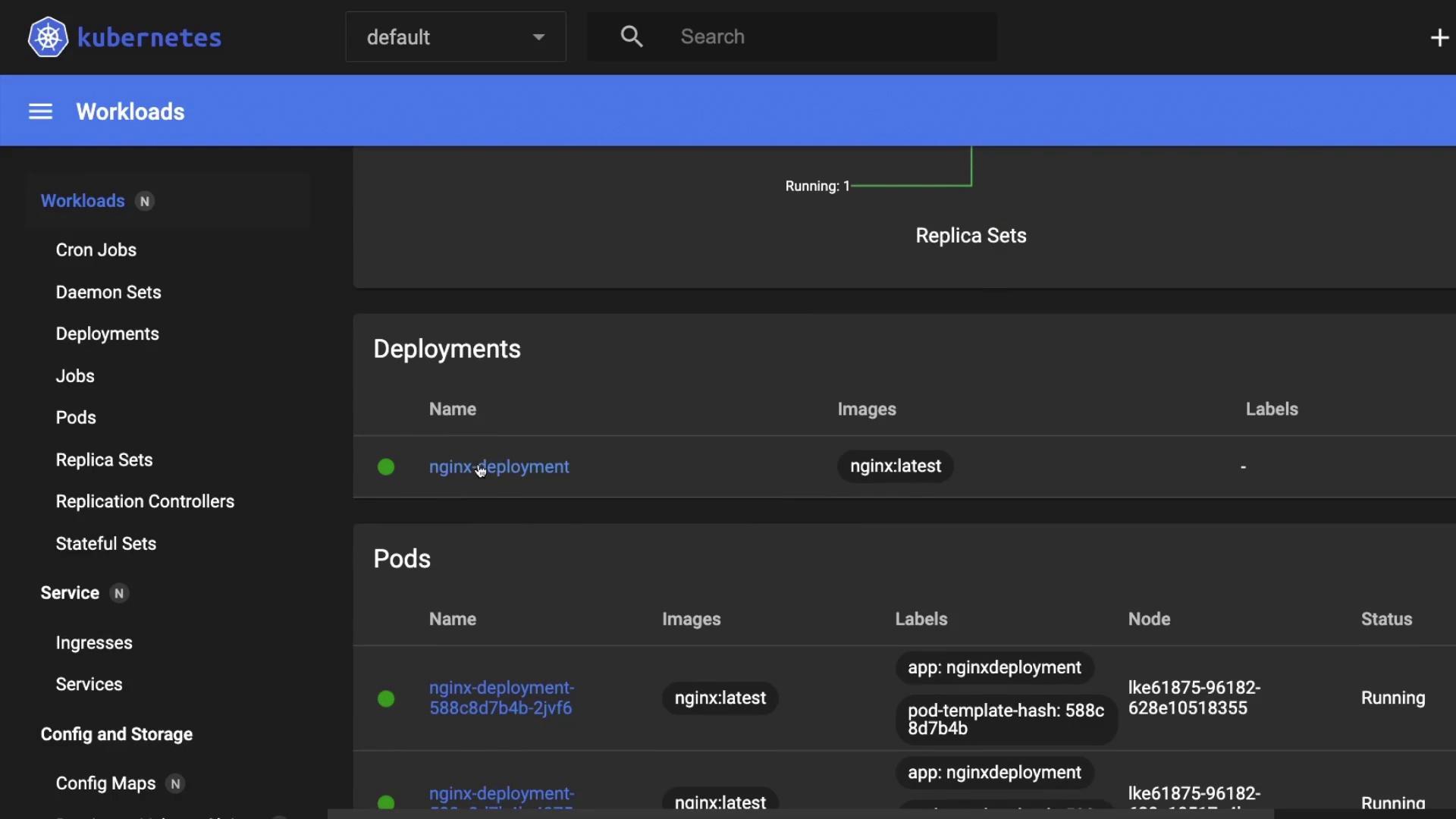
3. Monitor Your Deployment
Use these commands to check the status of your pods, deployments, and service:| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl get pods | List all pods and their status |
kubectl get deployments | Show deployment rollout status |
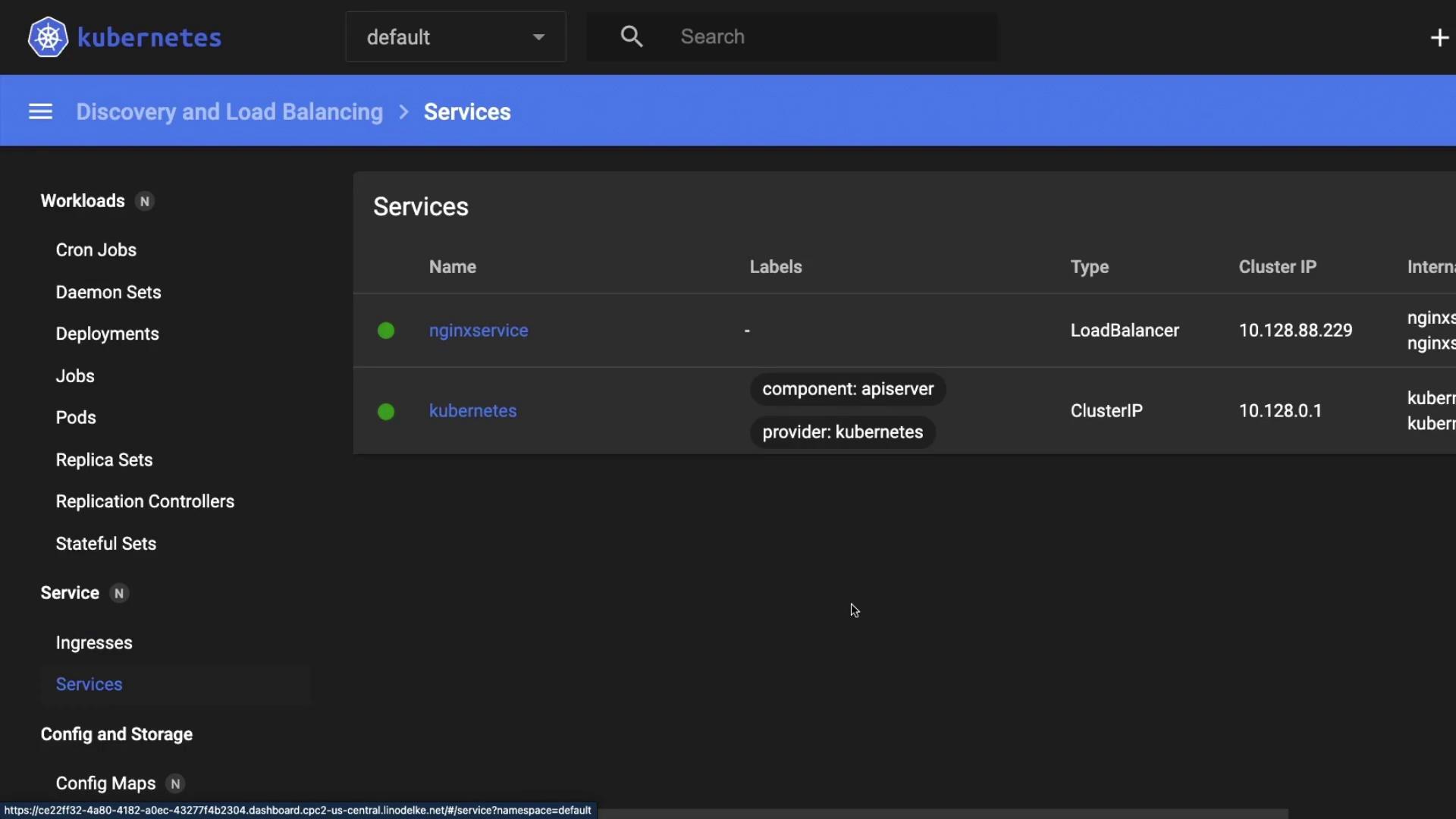
kubectl get svc | Display service endpoints |
4. Retrieve the External IP
It can take a minute or two for the
EXTERNAL-IP to provision. If <pending> appears, wait a bit and run the command again.5. Access Nginx in Your Browser
Open your web browser and navigate to:6. Inspect via the Kubernetes Dashboard
You can also verify the deployment and service in the Kubernetes Dashboard.